We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +36 18508731 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Do you need help meeting project deadlines or dealing with an erratic workflow in Kanban? Then, Kanban Estimation is the solution. Kanban Estimation is crucial for enhancing productivity and Project Management. By making precise task estimations in Kanban, you can streamline processes, establish practical expectations, and enhance team productivity. This blog will walk you through the fundamental concepts of Kanban Estimation, providing hands-on methods to improve your task organisation.
Gain knowledge on how to split up tasks, prioritise efficiently, and utilise Kanban Estimation to remain competitive in your industry. Read further to discover how these insights can assist you in meeting deadlines with assurance, enhancing your productivity to higher levels!
Table of Contents
1) What is Kanban?
2) What is an Estimate in Kanban?
3) How to use estimation in Kanban
4) How to Embrace Forecasting with Kanban?
5) How not to estimate in Kanban
6) Estimating vs. Forecasting
7) Conclusion
What is Kanban?
Kanban aids teams in handling their work by visualising tasks on a board, serving as a visual management tool. It emphasises on constantly delivering work without overwhelming team members. The board is divided into columns that represent the different stages of work in the system.
Tasks moves through various phases, starting from "To Do" and ending at "Done," allowing teams to track their advances visually. Kanban concentrates on ensuring smooth flow, limiting the amount of Work in Progress (WIP) to improve efficiency and maximise throughput. This visual method helps teams in pinpointing bottlenecks, improving processes, and preserving a steady work pace.
What is an Estimate in Kanban?
In Kanban, an estimation is a forecast of the time a task could need to be finished, typically relying on past information. In contrast to Scrum, which heavily relies on estimations for planning, Kanban is more flexible. In Kanban, the emphasis is on grasping the flow and forecasting future performance when making estimations. They don't focus on establishing deadlines, but on improving the predictability of the process.
The objective is to utilise estimation for enhanced flow control and process enhancement instead of rigid time limits.
How to use Estimation in Kanban?
Utilising estimation in Kanban requires a change in attitude from conventional time or point-based estimations. Below are a few actionable measures:
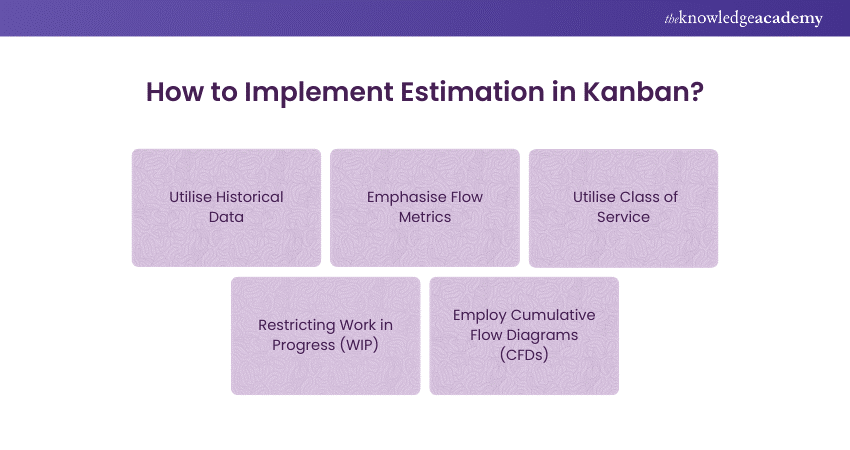
a) Utilise Historical Data: Analyse previous performance data to determine the time it took to complete similar tasks. This aids in establishing attainable goals without relying on speculation.
b) Emphasise Flow Metrics: Metrics such as cycle time (duration to finish a task) and lead time (time from task beginning to end) are crucial. These metrics offer understanding of how tasks move through the system.
c) Utilise Class of Service: Categorise tasks according to their level of urgency and significance. This assists in organising tasks without thorough estimation, keeping productivity steady and minimising setbacks.
d) Restricting Work in Progress (WIP): Setting limits on WIP ensures a steady flow and minimises the necessity for intricate estimations. The emphasis is on completing existing tasks before moving on to new ones.
e) Employ Cumulative Flow Diagrams (CFDs): CFDs display the progression of tasks, illustrating both ongoing and finished tasks throughout time. They assist in recognising patterns and predicting future accomplishments.
How to Embrace Forecasting with Kanban?
Predicting future results in Kanban involves using current and past data to anticipate what will happen. Here is the proper way to adopt forecasting efficiently:
a) Use Little’s Law: Little's Law explains that the average quantity of objects in a system equals the arrival rate times the average duration of each object's stay within the system. In Kanban, this can help predict the duration of tasks using average cycle times.
b) Cumulative Flow Diagram Projections: Projections can be made using Cumulative Flow Diagrams to predict future tasks. By studying patterns in the chart, teams can anticipate the potential completion dates of forthcoming tasks.
c) Probabilistic Forecasting: This method involves using data to anticipate probable results instead of specific dates. It recognises that task completion times can vary, offering a range of potential results.
d) Service Level Expectations (SLEs): Service Level Expectations (SLEs) show the anticipated duration for finishing tasks in a specific category. These procedures are not strict deadlines but tools to align stakeholder expectations.
Fast-track your Kanban Mastery with our Certified Kanban Foundation And Practitioner Training – Register now!
How not to Estimate in Kanban?
Although estimation is valuable in Kanban, it is important to steer clear of typical mistakes. Here are the things you should avoid doing:
Avoid Overly Detailed Estimates: Kanban values flow over detailed initial planning. Exaggerating the importance of each task can impede progress and cause a shift in attention from execution to organisation.
Do Not Use Story Points: Story points are better fitting for Scrum, where velocity is compared to estimations. Kanban works without time limits, making story points unimportant.
Avoid Commitment-Based Estimates: Refrain from making commitment-based estimates in Kanban as they should not be considered as promises. These are forecasts, not assurances, and should be regarded as such.
Level up your Lean skills with our Certified Kanban Practitioner Training – Sign up now!
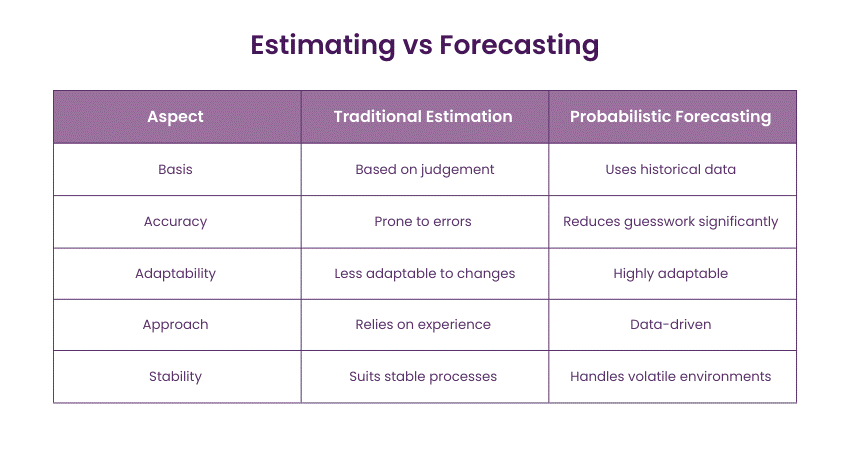
Estimating vs Forecasting
In Kanban, estimation and prediction serve distinct functions. Estimation consists of forecasting the duration of specific tasks, usually by considering past data. Forecasting, on the flip side, considers the broader scope by forecasting general results derived from current flow metrics. Although estimates offer immediate insights, forecasting allows teams to prepare for the future. Both are important, but they should be used in line with Kanban's focus on flow and constant delivery.
Conclusion
With your newfound understanding of Kanban Estimation, you're now well-equipped to enhance your workflow and optimise decision-making in Project Management. By integrating these estimation techniques, you can better visualise tasks, prioritise effectively, and ensure your team remains aligned with overall objectives. Stay committed to applying these strategies, and watch as your passion for efficiency turns into tangible success.
Transform your Project Management skills with our Certified Kanban Foundation Training today!
Frequently Asked Questions

Teams handle changes by regularly updating their flow metrics and modifying forecasts. Kanban's adaptability enables changing priorities seamlessly without affecting the overall process.

Indeed, teams can use Kanban Estimation to make data-driven predictions about future outcomes using cumulative flow diagrams and probabilistic forecasting for long-term forecasting.

Common difficulties involve guaranteeing precise flow measurements, preventing excessive estimates, and adjusting to shifting priorities without interrupting the flow. Teams must balance estimation and Kanban's focus on ongoing delivery and adaptability.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Kanban Training, including the Certified Kanban Foundation Training, Certified Kanban Practitioner Training, and Certified Kanban Foundation And Practitioner Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Kanban in OneNote.
Our Business Improvement Blogs cover a range of topics related to Kanban, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Business Improvement skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Business Improvement Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Certified Kanban Foundation and Practitioner Training
Certified Kanban Foundation and Practitioner Training
Wed 18th Dec 2024
Mon 6th Jan 2025
Mon 7th Apr 2025
Mon 4th Aug 2025
Mon 3rd Nov 2025
 Halloween sale! Upto 40% off - Grab now
Halloween sale! Upto 40% off - Grab now







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


