We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +36 18508731 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Motivation is the force that drives employees to pursue their goals and aspirations. But how can one improve their motivation levels? That's where Motivation Theories come into action. Motivation pushes employees to work harder and more efficiently. Introducing Motivation Theories in your organisation can be fruitful. However, if you aren’t aware of these Theories, then look no further. Read this blog to learn about the five Motivation Theories. Also, explore their key components and why learning about these Theories is crucial.
Table of contents
1) What is a Motivation Theory?
2) Importance of Motivation Theories
3) What are the five Motivation Theories?
a) Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
b) Herzberg's Two-factor Theory
c) McClelland's Theory of Needs
d) Vroom's Expectancy Theory
e) Deci and Ryan's Self-determination Theory
4) Conclusion
What is a Motivation Theory?
A Theory of Motivation can be a study involving the understanding of what drives a person to work towards a goal or outcome. It is essential for personal and professional success because it influences our performance, productivity, creativity, and well-being.
Motivation Theory can help people identify what motivates them and how to improve one’s motivation levels. It can also help managers and organisations support their employees efficiently and effectively.
Different types of Motivation Theories, such as content, process, and cognitive, explain what motivates us and how motivation is instilled. Some popular Motivation Theories are Maslow's hierarchy of needs, Herzberg's two-factor theory, McClelland's theory of needs, Vroom's expectancy theory, and Deci and Ryan's self-determination theory.
Importance of Motivation Theories
Motivation Theories are crucial because of the following reasons:
a) Motivation Theories help understand what drives our behaviours and how to improve our motivation levels.
b) These Theories help identify our goals, needs, values and interests and how they can influence our choices and actions.
c) They help design effective strategies and interventions to enhance our performance, productivity, creativity and well-being.
d) They aid in coping with stress, overcoming challenges, and learning from feedback.
e) Motivation Theories also help managers and organisations support their employees efficiently and effectively.
What are the five Motivation Theories?
Motivation Psychology is a vast field of study. Many famous Psychologists have proposed different Theories of Motivation. So, let’s explore the top five Motivation Theories in detail:
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
In Psychology, Maslow's hierarchy of needs proposes that humans have five needs that must be satisfied in a particular order. These needs involve the following:
a) Physiological needs: These are the basic biological needs for survival. They include food, water, air, shelter, and sleep. These needs are necessary to be fulfilled for people to function properly.
b) Safety needs: These are the needs for security, stability, and protection from harm. People need to feel safe from physical and psychological threats like violence, disease, accidents, or natural disasters.
c) Love and belonging needs: These are the needs for social connection, affection, and intimacy. People must feel loved and accepted by others, such as family, friends, and romantic partners. They must also belong to a group or community that shares their values and interests.
d) Esteem needs: These are the needs for self-respect, recognition, and achievement. People need to feel confident and competent in their abilities and skills. They also need to receive respect and appreciation from others for their contributions and accomplishments.
e) Self-actualisation needs: These are the needs for personal growth, fulfilment, and creativity. People must realise their full potential and express their unique talents and passions. They also need to seek new challenges and experiences that enrich their lives.

According to Maslow, people can only move up the hierarchy of needs when the lower-level needs are sufficiently satisfied. However, he also acknowledged that the satisfaction of each need is not an all-or-none phenomenon but rather a matter of degree. Moreover, he suggested that some people may have different priorities or preferences for certain needs over others.
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs is one of the most influential Motivation Theories in Psychology and has many applications in various fields, such as education, management, health care, and counselling. It can help people understand what motivates human behaviour and how it can improve our well-being and happiness.
Herzberg's Two-factor Theory
Herzberg's Two-Factor Theory proposes two factors influencing job satisfaction and dissatisfaction: motivators and hygiene factors. Here's a complete explanation of these factors:
a) Motivators: These are the factors that relate to the nature of the work, such as achievement, recognition, responsibility, and growth. These factors increase job satisfaction and performance as they fulfil the higher-level psychological needs of employees.
b) Hygiene factors: They relate to the work conditions, such as salary, security, supervision, and policies. These factors do not increase job satisfaction, but they prevent job dissatisfaction, fulfilling employees' lower-level physiological and safety needs.
Herzberg's theory has been influential in the field of management and organisational behaviour, as it provides a practical framework for designing jobs, motivating employees, and improving work environments. However, it has also been criticised for its methodological limitations, cultural bias, oversimplification, and lack of generalisability.
Unlock your full potential and achieve your dreams with our Motivation and Goal Setting Training – start your journey to success today!
McClelland's Theory of Needs
McClelland's Theory of Needs proposes that three types of needs drive human behaviour. These are as follows:
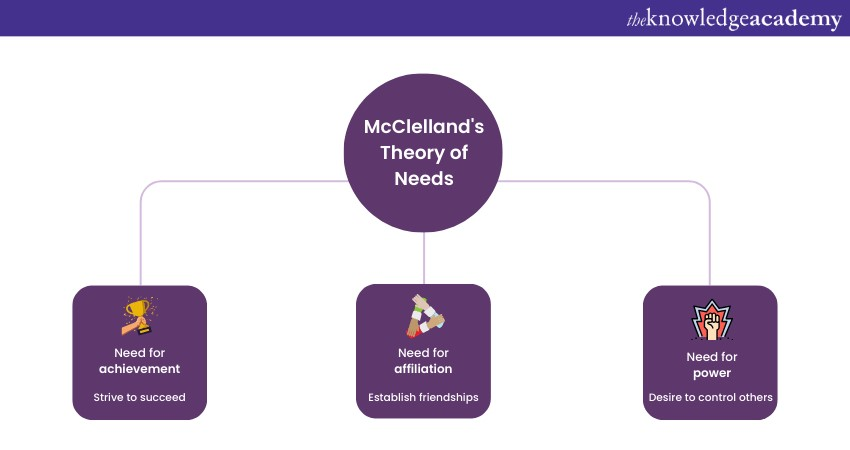
a) The need for achievement: It is the desire to accomplish challenging goals to excel in one's field and seek feedback on one's progress. People with a high need for achievement are motivated by moderately difficult tasks, require personal responsibility, and offer clear and timely feedback. They prefer to work independently or with other high achievers and value recognition and rewards for their achievements.
b) The need for affiliation: It means the desire to form and maintain positive relationships with others to belong to a group or community and avoid conflict and rejection. People with a high need for affiliation are motivated by cooperation, collaboration, and social interaction tasks. They prefer to work in teams or groups and value acceptance and friendship from their peers and superiors.
c) The need for power: The need for power entails the desire to influence, control, or lead others, impact one's environment, and gain prestige and status. People with a high need for power are motivated by tasks that involve authority, responsibility, and competition. They prefer to work in leadership positions or influence, and they value respect and admiration from others.
These needs are acquired and shaped by one's life experiences and vary in intensity among individuals and situations. According to McClelland, each need has different characteristics and implications for motivation and performance.
McClelland's Theory of Needs can help managers and organisations understand what motivates their employees and how to design jobs, rewards, and feedback systems that match their needs.
For example, employees with a high need for achievement may benefit from challenging assignments, performance-based incentives, and constructive criticism. Employees with an increased need for affiliation may benefit from team-based projects, social events, and positive reinforcement. Employees with a high need for power may benefit from leadership opportunities, decision-making authority, and public recognition.
Unlock your team's full potential with our Staff Motivation Training – inspire, empower and excel!
Vroom's Expectancy Theory
Vroom's Expectancy Theory proposes that an individual's motivation to perform a specific task is based on their belief that their effort will lead to top performance and that top performance will lead to a desirable outcome. The theory is based on three factors that are as follows:
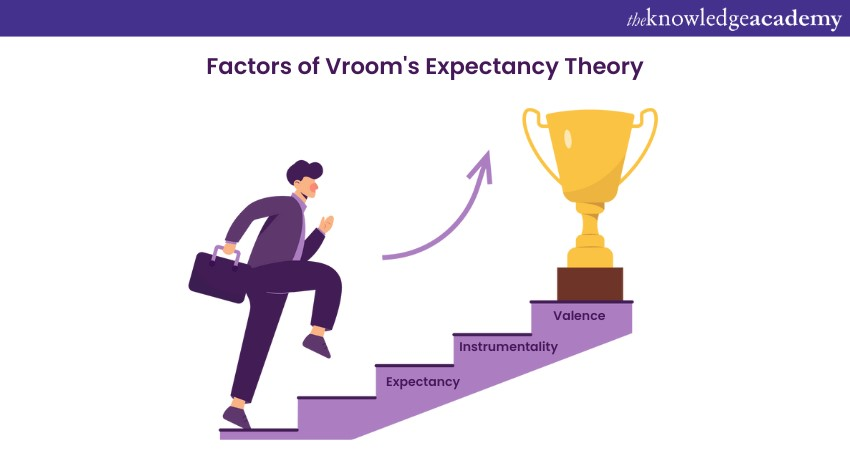
a) Expectancy: It means that one's effort will result in a certain level of achievement. For example, if an employee believes that working hard will increase their sales, they have a high expectancy. If they believe that working hard will not make a difference, they have a low expectancy.
b) Instrumentality: It is the belief that one's performance will lead to a certain outcome. For example, if an employee believes that increasing their sales will earn them a bonus, they have a high instrumentality. If they believe that increasing their sales will not affect their bonus, they have a low instrumentality.
c) Valence: It is the value that one assigns to the outcome. For example, if an employee values the bonus highly, they have a high valence. If they do not care about the bonus, they have a low valence.
According to Vroom's theory, motivation is the product of expectancy, instrumentality, and valence. This means that an individual will be motivated to perform a task if they highly value it and expect that their effort will lead to good performance and a favourable outcome. Conversely, an individual will not be motivated to perform a task if any of these factors are low or zero.
Vroom's theory can help managers and organisations understand what motivates their employees and how to design jobs, rewards, and feedback systems that match their expectations and values. However, the theory also has some limitations, such as its complexity, subjectivity, and variability.
Deci and Ryan's Self-determination Theory
Deci and Ryan's Self-determination theory proposes that people have three basic psychological needs that influence their behaviour and well-being. These needs include the following:
a) Autonomy: It is the need to act in accordance with one's own values and interests without feeling pressured or controlled by external forces. People who experience autonomy feel that they have a choice and a voice in their actions and goals.
b) Competence: Competence is the need to master skills and challenges and achieve a desired performance level. People who experience competence feel that they are capable and effective in their activities and tasks.
c) Relatedness: It is the need to connect with others and feel accepted and cared for. People who experience relatedness feel that they belong to a group or community that shares their values and interests.
According to Deci and Ryan, these three needs are essential for psychological growth and well-being. When these needs are satisfied, people are motivated from within rather than from external rewards or punishments. Intrinsic motivation leads to more engagement, creativity, persistence, and satisfaction in one's activities.
Deci and Ryan's Self-determination Theory has many applications in various fields, such as education, health care, work, sport, religion, and psychotherapy. It can help us understand what motivates human behaviour and how we can enhance our own and others' motivation and well-being.
Conclusion
Motivation is a complex phenomenon that influences human behaviour and performance. There are many Motivation Theories that explain how and why people are motivated. By understanding these Theories, one can better appreciate the diversity and complexity of human motivation and apply them to enhance their own and others’ motivation levels.
Unlock your full potential with our Personal Development Training and embrace a brighter future today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Motivation and Goal Setting Training
Motivation and Goal Setting Training
Fri 28th Feb 2025
Fri 4th Apr 2025
Fri 27th Jun 2025
Fri 29th Aug 2025
Fri 24th Oct 2025
Fri 5th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


