We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +36 18508731 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Six Sigma Case Study is a data-driven methodology widely used in organisations to improve process efficiency and quality. It helps reduce process defects and variations, enhancing customer satisfaction and increasing profitability. It provides a real-world example of how its methodology was applied to identify and solve a problem, showcasing the effectiveness of its principles and tools.
By analysing such case studies, one can gain insights into the successful application of Six Sigma in various industries and understand its impact on process improvement. Read this blog on Six Sigma Case Study to learn how real-world businesses have achieved remarkable process improvement and cost savings.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding Six Sigma Methodology
2) Six Sigma Case Study
a) Improving customer service
b) Improving delivery efficiency
3) Conclusion
Understanding Six Sigma Methodology
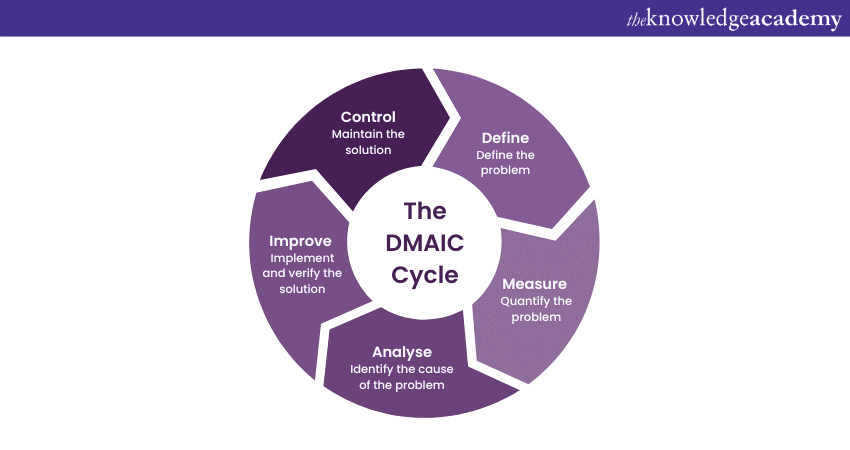
Six Sigma is a set of tools and techniques that helps improve business processes and reduce defects. It focuses on identifying and eliminating variations and errors that can lead to inefficiencies and customer dissatisfaction. Six Sigma methodology is a powerful approach organisations use to improve processes and enhance quality. It revolves around reducing defects and variations to achieve near-perfect results.
By applying statistical analysis and data-driven decision-making, Six Sigma helps organisations identify the root cause of problems and implement effective solutions. It emphasises the importance of process standardisation, continuous improvement, and customer satisfaction. With its focus on rigorous measurement and analysis, Six Sigma enables organisations to drive efficiency, reduce waste, and deliver exceptional products and services. The methodology follows a step-by-step process called Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve, and Control (DMAIC). These five phases are briefly explained below:
a) Define: The project goals and customer requirements are clearly defined in this phase.
b) Measure: In this phase, data is collected to understand the process's current state and identify improvement areas.
c) Analyse: This phase focuses on analysing data to determine the root cause of defects or variations.
d) Improve: This phase involves implementing solutions and making necessary changes to eliminate the identified issues.
e) Control: In this phase, measures are implemented to sustain the improvements and remain stable over time.

Six Sigma Case Study
In this section we discuss two Six Sigma Case Study that will help you understand and use it better.
Case Study 1: Improving customer service
This Six Sigma Case Study will focus on a telecommunications company facing significant customer service challenges. The issues included long wait times, frequent call transfers, unresolved issues, and many more. The company decided to apply Six Sigma methodologies to enhance customer satisfaction.
a) Define phase: Using the DMAIC approach, the team began by defining the problem: long wait times and inefficient call handling. They set a goal to reduce average wait time and increase first-call resolution rates.
b) Measure phase: In this phase, data was collected to analyse call volume, wait times, and reasons for call transfers. This helped identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement.
c) Analyse phase: During this phase, the team discovered that inadequate training and complex call routing were key contributors to the problems. They also found that certain product issues required better resolution protocols.
d) Improve phase: In this phase, targeted solutions were introduced and implemented to address these issues. The team revamped the training program, ensuring agents were well-trained and equipped to handle customer inquiries. They simplified call routing and introduced automated prompts for quicker issue resolution.
e) Control phase: Finally, monitoring systems were established in the control phase to track key metrics and ensure sustained improvements. Regular feedback loops were implemented to identify emerging challenges and make necessary adjustments.
The results were exceptional. Average wait times were reduced by 40%, and first-call resolution rates increased by 25%. Customer satisfaction scores improved significantly, leading to increased loyalty and positive word-of-mouth.
This Six Sigma Case Study highlights how Six Sigma methodologies can drive transformative improvements in customer service. By focusing on data analysis, process optimisation, and continuous monitoring, organisations can achieve outstanding outcomes and deliver exceptional customer experiences.
Understand the in-depth process of Six Sigma with our Six Sigma Yellow Belt Course. Join now!
Case Study 2: Improving delivery efficiency
In this case study, we explore how a plumbing product distributor applied Six Sigma methodologies to address delivery inefficiencies and enhance customer satisfaction.
a) Define phase: The business used the Voice of the Customer (VoC) tool to understand customer needs and expectations. They identified prompt delivery, correct product selection, and a knowledgeable distribution team as crucial customer requirements.
b) Measure phase: The team collected data to evaluate the problem of slow delivery. They discovered that their Order Fulfillment Cycle Time (OFCT) was 46% longer than competitors, leading to customer dissatisfaction.
c) Analyse phase: The team brainstormed potential causes of slow delivery, including accuracy of sales plans, buffer stock issues, vendor delivery performance, and manufacturing schedule delays. They conducted a regression analysis, revealing that inadequate buffer stock for high-demand products was the main issue affecting delivery efficiency.
d) Improve phase: The distributor implemented a monthly demand review to ensure that in-demand products are readily available. They emphasised ordering and providing customers with the specific products they desired.
e) Control phase: The team developed plans to monitor sales of the top 20% of bestselling products, avoiding over or under-supply situations. They conducted annual reviews to identify any changes in demand and proactively adjust product offerings.
By applying Six Sigma Principles, the plumbing product distributor significantly improved its delivery efficiency, addressing the root cause of customer dissatisfaction. Prompt action, data-driven decision-making, and ongoing monitoring allowed them to meet customer expectations, enhance its reputation, and maintain a competitive edge in the industry. This case demonstrates the power of Lean Six Sigma in driving operational excellence and customer-centric improvements.
Take the next step in your professional development and boost your career by joining our Six Sigma Green Belt course.
Conclusion
We hope this blog gives you enough insights into the Six Sigma Case Study. This blog showcased the effectiveness of its methodology in driving transformative improvements. By applying DMAIC and using customer insights and data analysis, organisations have successfully resolved delivery inefficiencies, improving customer satisfaction and operational performance. The blog highlights how Six Sigma can be a powerful framework for organisations seeking excellence and exceptional value.
Learn the six-sigma methodology to achieve business objectives with our Six Sigma Certification Training today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Business Improvement Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Six Sigma Green Belt
Six Sigma Green Belt
Mon 6th Jan 2025
Mon 13th Jan 2025
Mon 20th Jan 2025
Mon 27th Jan 2025
Mon 3rd Feb 2025
Mon 10th Feb 2025
Mon 17th Feb 2025
Mon 24th Feb 2025
Mon 3rd Mar 2025
Mon 10th Mar 2025
Mon 17th Mar 2025
Mon 24th Mar 2025
Mon 31st Mar 2025
Mon 7th Apr 2025
Mon 14th Apr 2025
Tue 22nd Apr 2025
Mon 28th Apr 2025
Tue 6th May 2025
Mon 12th May 2025
Mon 19th May 2025
Tue 27th May 2025
Mon 2nd Jun 2025
Mon 9th Jun 2025
Mon 16th Jun 2025
Mon 23rd Jun 2025
Mon 30th Jun 2025
Mon 7th Jul 2025
Mon 14th Jul 2025
Mon 21st Jul 2025
Mon 28th Jul 2025
Mon 4th Aug 2025
Mon 11th Aug 2025
Mon 18th Aug 2025
Tue 26th Aug 2025
Mon 1st Sep 2025
Mon 8th Sep 2025
Mon 15th Sep 2025
Mon 22nd Sep 2025
Mon 29th Sep 2025
Mon 6th Oct 2025
Mon 13th Oct 2025
Mon 20th Oct 2025
Mon 27th Oct 2025
Mon 3rd Nov 2025
Mon 10th Nov 2025
Mon 17th Nov 2025
Mon 24th Nov 2025
Mon 1st Dec 2025
Mon 8th Dec 2025
Mon 15th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


