We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +36 18508731 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Project Management involves various complex processes, from planning and execution to monitoring and evaluation of projects. As projects grow in complexity and importance, the need for a systematic and thorough assessment becomes undeniable. One essential aspect of effective Project Management is Project Audit. But What is Project Audit?
A Project Audit is a systematic and independent examination of a project's processes, outcomes, and performance. It aims to assess the project's effectiveness, identify areas for improvement, and ensure that project objectives align with the organisation's goals and standards. In this blog, you are going to learn in detail about What is Project Audit, its types, the steps involved and the benefits of conducting these audits.
Table of Contents
1) What is Project Audit?
2) Importance of Project Audit
3) Key components of Project Audit
4) Types of Project Audit
5) Steps involved in conducting Project Audit
6) Benefits of conducting Project Audits
7) Conclusion
What is Project Audit?
Project Audit is the rigorous scrutiny and evaluation of a Project’s Processes, objectives, methodologies, and outcomes. It serves as a strategic tool in the realm of Project Management, providing a meticulous examination of every facet of a project’s lifecycle. This comprehensive analysis aims to ensure that the project aligns with organisational goals, industry standards, and best practices.
It acts as a diagnostic check, illuminating both the accomplishments and the pitfalls, allowing project managers and stakeholders to make data-driven decisions. Through Project Audit, organisations gain valuable insights into resource allocation, Risk Management, team performance, and overall project health. Ultimately, Project Audit empowers organisations to refine strategies, optimise processes, and enhance project outcomes, ensuring that every project undertaken becomes a stepping stone toward organisational excellence.
Importance of Project Audit
Project Audit holds a pivotal role in the landscape of Project Management, ensuring accountability, transparency, and continuous improvement. Its significance can be outlined through several key points:
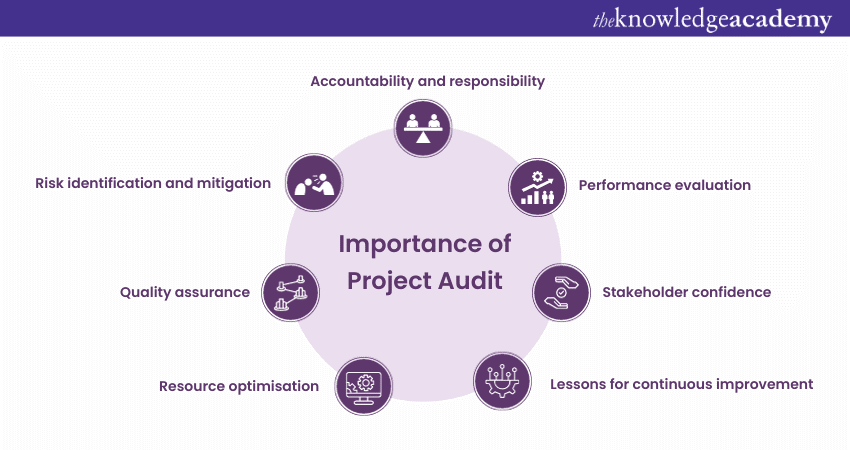
a) Accountability and responsibility: Project Audits establish clear accountability, ensuring that team members are responsible for their designated tasks and outcomes, fostering a sense of ownership and dedication.
b) Risk identification and mitigation: By systematically analysing project processes, audits identify potential risks, enabling proactive risk management strategies to mitigate these challenges effectively.
c) Quality assurance: Audits assess the quality of work, ensuring that project deliverables meet established standards and client expectations, thus maintaining the reputation and credibility of the organisation.
d) Resource optimisation: Through evaluation, audits analyse resource allocation and utilisation, enabling organisations to optimise resources, reduce wastage, and enhance cost-effectiveness.
e) Performance evaluation: Audits provide a comprehensive overview of project performance, allowing organisations to assess the effectiveness of strategies, identify bottlenecks, and make data-driven decisions for future projects.
f) Stakeholder confidence: Well-conducted audits instil confidence in stakeholders, assuring them that projects are being managed efficiently, leading to stronger partnerships and support.
g) Lessons for continuous improvement: Audit findings serve as a valuable source of lessons learned, guiding organisations in refining their Project Management Processes and fostering a culture of constant improvement and innovation.
Interested to learn more about Project Management? Sign up now for our Introduction to Project Management Certification Course
Key components of Project Audit
Here are some key components of Project Audit:
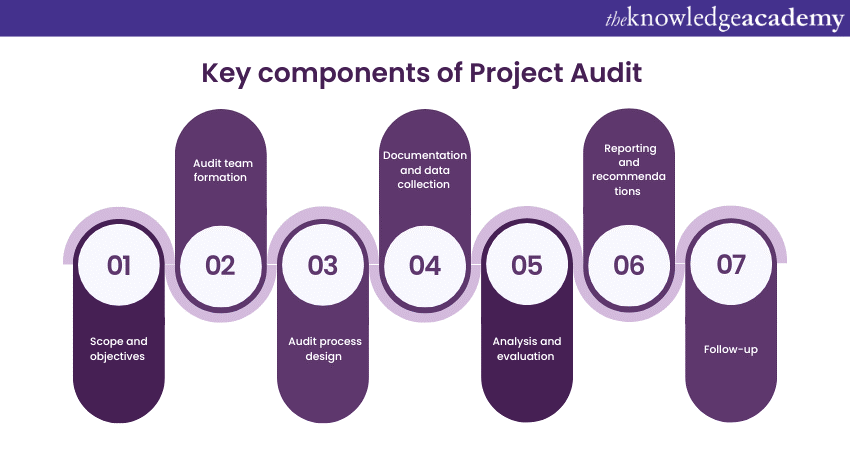
Scope and objectives
a) Clearly define the scope of the audit, outlining the specific areas, processes, and objectives that will be evaluated.
b) Establish the goals of the audit, whether it's performance improvement, risk identification, or compliance assessment.
Audit team formation
a) Assemble a skilled and diverse audit team comprising individuals with expertise in project management, analysis, and evaluation techniques.
b) Assign roles and responsibilities within the team to ensure a comprehensive approach to the audit process.
Audit process design
a) Develop a structured and systematic audit process outlining the Project Management Methodologies, data collection techniques, and evaluation criteria to be employed.
b) Plan the timeline, detailing when each phase of the audit will take place and allocating resources accordingly.
Documentation and data collection
a) Gather relevant project documents, including plans, reports, financial records, and communication logs, ensuring a comprehensive review.
b) Collect data through interviews, surveys, and direct observations, ensuring the information gathered is accurate, reliable, and representative of the project's activities.
Analysis and evaluation
a) Analyse the collected data to identify patterns, Project Management Trends, and discrepancies in project performance and outcomes.
b) Evaluate the project against predetermined benchmarks, industry standards, and organisational objectives, identifying areas of success and areas needing improvement.
Reporting and recommendations
a) Document audit findings in a clear, concise, and structured report, highlighting strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
b) Provide actionable recommendations based on the audit results, offering specific strategies for improvement and outlining the potential benefits of implementing these changes.
Follow-up and implementation monitoring
a) Establish a follow-up mechanism to track the implementation of audit recommendations, ensuring that identified issues are addressed promptly.
b) Monitor the progress of recommended changes, assess their impact on the project, and make necessary adjustments to the project management strategies based on the outcomes of the audit.
Advance your career with expertise in our course in Programme Management Fundamentals. Join now!
Types of Project Audit
Project Audits come in various forms, each designed to focus on specific aspects of a project’s performance, compliance, or management. Understanding these types is crucial for tailoring the audit process to meet the unique needs of the project. Here are the primary types of Project Audits:
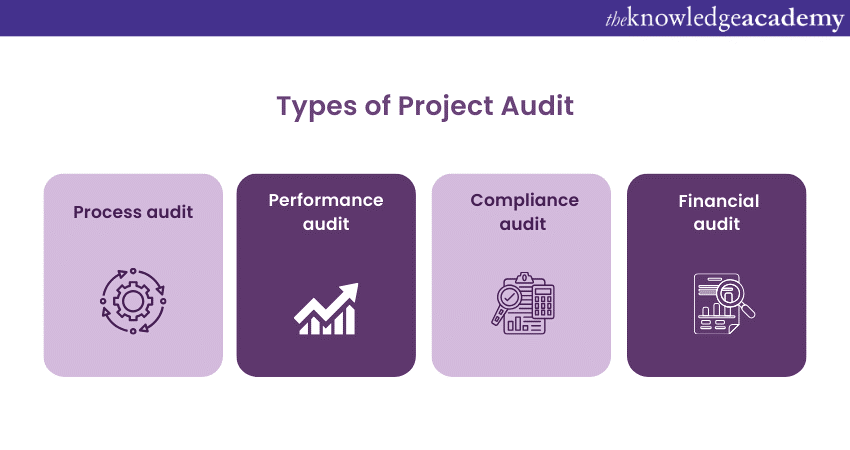
Process audit
Process audits concentrate on evaluating the Project Management processes and methodologies employed during Project Execution. It assesses whether the operations are efficient, effective, and aligned with industry best practices. This type of audit helps in identifying bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas where process improvements are necessary.
Performance audit
Performance audits provide a comprehensive assessment of the project’s overall performance. This includes evaluating project deliverables, timelines, budget adherence, and stakeholder satisfaction. By analysing these aspects, performance audits offer insights into the project's effectiveness in meeting objectives and satisfying stakeholders.
Compliance audit
Compliance audits focus on ensuring that the project adheres to legal, regulatory, and organisational guidelines. This is particularly important in industries with strict regulations, such as healthcare or finance. Compliance audits help minimise legal risks and ensure that the project activities align with established standards and regulations.
Financial audit
Financial audits concentrate on the project’s financial aspects. This includes a detailed review of project budgets, expenditures, financial controls, and adherence to economic policies. Financial audits ensure transparency in financial transactions, prevent financial mismanagement and verify that project funds are utilised judiciously.
Learn Project Management quickly without having a project background -Register now for our course on Project Management for Non-Project Managers
Steps involved in conducting Project Audit
A Project Audit is a systematic and structured process aimed at evaluating various aspects of a project to ensure its effectiveness, Compliance, and alignment with organisational goals. The audit process involves several key steps, each crucial in providing a comprehensive analysis of the project's performance. These are the steps which are involved in Project Audit:
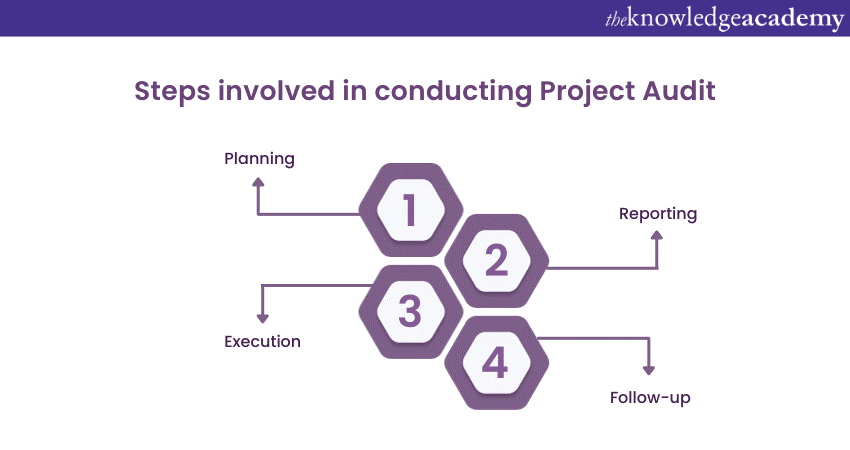
Planning
a) Define objectives: The first step in any Project Audit is to define the audit objectives clearly. This involves determining what aspects of the project will be audited, such as processes, deliverables, budget management, or compliance with regulations.
b) Assemble the audit team: Formulate a team of skilled auditors with expertise in project management, financial analysis, compliance, and other relevant areas. The team's composition should be diverse to ensure a well-rounded assessment.
c) Develop audit plan: Create a detailed audit plan outlining the methodologies, tools, and techniques to be used during the audit. Determine the scope, Project Management Timeline, and resource requirements for the audit process.
Execution
a) Data collection: Gather relevant data and documentation related to the project. This includes project plans, contracts, financial records, progress reports, communication logs, and stakeholder feedback. Data can be collected through interviews, surveys, direct observations, and document reviews.
b) Interviews and stakeholder engagement: Conduct interviews with project team members, stakeholders, and other relevant parties. Engaging with key stakeholders provides valuable insights into their expectations, concerns, and perceptions regarding the project.
c) On-site observations: In some instances, auditors may conduct on-site visits to observe project activities firsthand. This direct observation helps in understanding the actual implementation of project processes.
Reporting
a) Analysis of findings: Analyse the collected data and evaluate it against predetermined benchmarks, industry standards, and organisational objectives. Identify patterns, trends, strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement.
b) Preparation of audit report: Document the audit findings, conclusions, and recommendations in a comprehensive report. The information should be structured, clear, and concise, making it easy for stakeholders to understand the audit outcomes.
c) Incorporate visuals: Utilise charts, graphs, and other visual aids to present data effectively. Visual representations enhance the clarity of the report and provide a quick overview of key findings.
Follow-up
a) Implementation of recommendations: Provide stakeholders with actionable advice for addressing identified issues and improving project performance. Proposals should be Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART).
b) Monitoring and evaluation: Establish a follow-up mechanism to track the implementation of recommendations. Regular monitoring ensures that corrective actions are taken and improvements are made as per the audit findings.
c) Feedback and continuous improvement: Gather input from project stakeholders regarding the implemented changes. Use this feedback to assess the impact of the audit recommendations and identify further areas for improvement. This continuous improvement loop is essential for enhancing future project management practices.
Get a better understanding of Project Management with our Project Management Masterclass
Benefits of conducting Project Audits
Project Audits, far from being mere assessments, offer several benefits that contribute significantly to the success of projects and the overall growth of organisations. Here’s an in-depth exploration of these advantages:
Enhanced decision-making
Project Audits provide actionable insights and data-driven recommendations, enabling Project Managers and stakeholders to make informed decisions. By understanding the project’s strengths and weaknesses, organisations can devise strategies that lead to more effective decision-making at various project stages.
Stakeholder confidence
A successfully conducted Project Audit instils confidence in stakeholders, including clients, investors, and team members. When stakeholders are assured that projects are managed efficiently and transparently, it fosters trust, resulting in stronger relationships and sustained support.
Process optimisation
Through rigorous evaluation, Project Audits identify inefficiencies and bottlenecks in project processes. Armed with this knowledge, organisations can optimise workflows, streamline operations, and enhance project efficiency. This optimisation often leads to significant cost savings and resource utilisation improvements.
Proactive risk management
Project Audits are invaluable for identifying potential risks and challenges early in the project lifecycle. By proactively addressing these risks, organisations can develop risk mitigation strategies, reducing the likelihood of project delays or failures.
Quality assurance
Audits ensure that project deliverables meet established quality standards and client expectations. By validating the quality of work, organisations can uphold their reputation, gain customer satisfaction, and establish themselves as providers of high-quality services or products.
Knowledge transfer and learning
Audit findings serve as repositories of knowledge and experience. Lessons learned from audits offer invaluable insights into both successes and failures. This knowledge transfer facilitates organisational learning, allowing teams to avoid past mistakes and adopt best practices for future projects.
Continuous improvement
Project Audits create a culture of continuous improvement within organisations. By analysing audit results and implementing recommendations, organisations foster an environment where learning from past experiences becomes integral to the Project Management process. Continuous improvement ensures that each project iteration is more refined and successful than the last, enhancing the organisation’s overall effectiveness.
Conclusion
Understanding What is Project Audit is invaluable, as it can be used as one of the efficient tools for organisations. The audits offer insights that lead to better decision-making, enhanced project outcomes, and increased stakeholder satisfaction. By diligently following these steps, Project Auditors ensure a thorough and effective evaluation, contributing significantly to the success of projects and the organisations that undertake them.
Want to take the next step in your Project Management journey? Then sign up now for our course on Project Management Green Belt!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Project Management Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Waterfall Project Management Certification Course
Waterfall Project Management Certification Course
Fri 14th Feb 2025
Fri 9th May 2025
Fri 12th Sep 2025
Fri 19th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


