We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Business is an ever-evolving domain and effective Management is the key to success. Understanding and applying Management Concepts is vital for any organisation to thrive and grow. Whether you are a seasoned manager or aspiring to become one, understanding key concepts of Management will provide valuable insights into the world of business and leadership.
According to Glassdoor, a person in a Management position in the UK earns around £63,993 per year on average. With such competitive pay grades, you will do well to understand basic concepts and theories in Management. In this blog, we will delve into the fundamental Management Concepts, exploring various theories essential for effective leadership and decision-making.
Table of Contents
1) Introduction to Management Concepts
2) Understanding key Management Principles
3) Fundamental Management theories
4) Strategic Management Concepts
5) Human resource Management Concepts
6) Financial Management Concepts
7) Marketing Management Concepts
8) Innovation and change Management Concepts
9) Ethical and social responsibility in Management
10) Conclusion
Introduction to Management Concepts
Management is the art of coordinating resources, people, and processes to achieve organisational goals efficiently and effectively. It involves a wide range of concepts that have evolved over time to address various challenges and opportunities faced by managers. Understanding these concepts empowers leaders to make informed decisions, foster innovation, and create a positive work environment.
Management Concepts are fundamental ideas and practices that guide managers in their roles. These concepts provide a framework for understanding and addressing organisational challenges, setting goals, and making decisions that align with the overall vision of the company. They encompass various disciplines such as planning, organising, leading, and controlling.
Effective Management Concepts are crucial for the success and growth of any organisation. They provide a roadmap for achieving objectives, optimising resources, and maximising productivity. By implementing these concepts, businesses can adapt to changing market conditions, foster employee engagement, and maintain a competitive edge.
Management theories have evolved over time, reflecting changes in the business landscape and advancements in social sciences. From the classical approaches of scientific Management and administrative Management to the contemporary theories of systems and contingency, each era has contributed valuable insights to the field of Management.
Understanding key Management principles
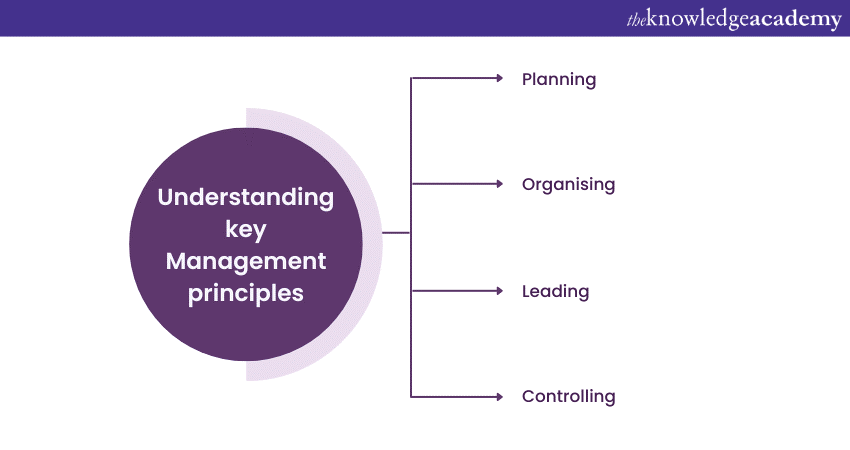
A few key Management principles are planning, organising, leading and controlling:
Planning
Planning is the foundation of effective Management. It involves setting goals, defining strategies, and outlining the steps required to achieve objectives. By careful planning, managers can anticipate potential challenges and develop proactive solutions.
Organising
Organising involves structuring resources and tasks in a way that supports the achievement of organisational goals. It includes designing the organisational structure, allocating responsibilities, and establishing communication channels.
Leading
Leading refers to the process of inspiring and motivating employees to perform at their best. Effective leadership encourages innovation, fosters a positive work culture, and builds strong teams.
Controlling
Controlling entails monitoring performance and comparing it with set standards. This allows managers to identify deviations and take corrective actions to ensure the organisation stays on track.
Fundamental Management theories
Management Theories can be broadly classified into three categories: classical, behavioural and contemporary. Each of these theories has a few basic Management Concepts which can be applied to make the work of managers much simpler.
Classical Management Theories
Classical Management theories emerged in the early 20th century and laid the groundwork for modern Management practices.
Scientific Management
Scientific Management, pioneered by Frederick Taylor, focuses on optimising individual work processes through time and motion studies. It emphasises efficiency and productivity in the workplace.
Administrative Management
Administrative Management, developed by Henri Fayol, centres on the five functions of Management: planning, organising, commanding, coordinating, and controlling.
Behavioural Management Theories
Behavioural Management theories shifted the focus from the tasks to the people performing them, recognising the significance of human behaviour in the workplace.
Hawthorne studies
The Hawthorne studies conducted by Elton Mayo highlighted the influence of social factors on employee productivity and emphasised the importance of employee morale and motivation.
Theory X and Theory Y
Douglas McGregor's Theory X and Theory Y present differing views on employee motivation. Theory X runs on the assumption that employees dislike work and must be closely supervised. On the other hand, Theory Y posits that employees are self-motivated and capable of taking responsibility.
Contemporary Management theories
Contemporary Management theories address the complexities of the modern business environment, emphasising flexibility and adaptability.
Systems theory
Systems theory views organisations as interconnected entities with interdependent parts. Changes in one part can affect the entire system, making it crucial for managers to consider the holistic impact of their decisions.
Contingency theory
In line with contingency theory, a universal management approach that suits all situations does not exist. Instead, managers must adapt their strategies based on the specific circumstances and context they face.
Bring the best out of people with our Introduction to Managing People Course!
Strategic Management Concepts
Strategic Management involves formulating and implementing long-term plans to achieve organisational objectives.
SWOT analysis
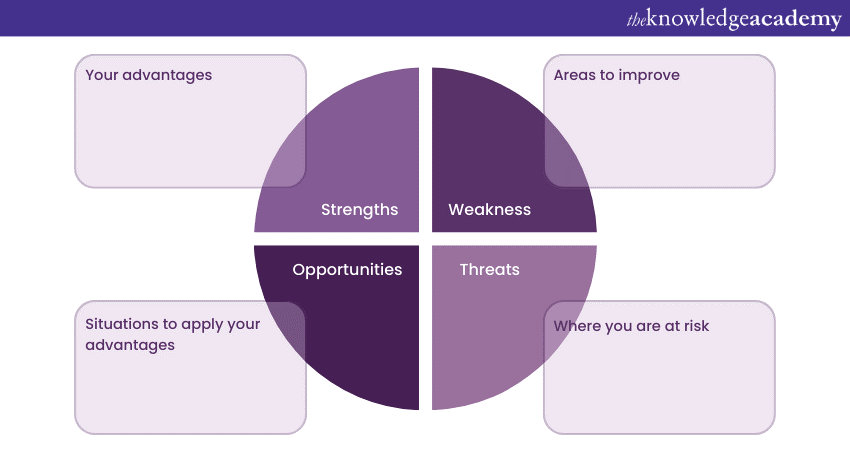
SWOT analysis represents a strategic planning tool used to evaluate an organisation's internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats. The acronym stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. By conducting a SWOT analysis, businesses gain valuable insights into their current position in the market and can develop effective strategies.
It helps identify areas where the organisation excels and where improvements are needed. Furthermore, the analysis highlights potential growth opportunities and potential challenges that may impact the company's success. Utilising SWOT analysis enables businesses to make well-informed decisions, capitalise on their strengths, and proactively address potential risks, fostering sustainable growth and success.
PESTEL analysis
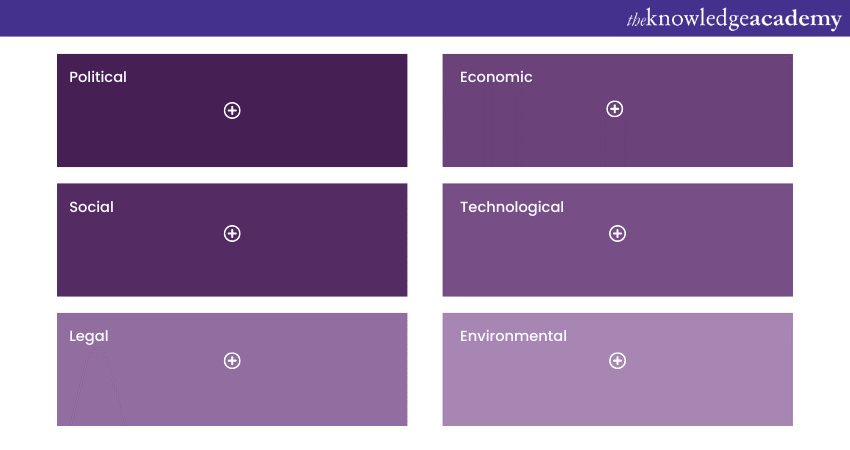
PESTEL analysis is a strategic tool that businesses use to evaluate the external factors that may impact their operations and decision-making. It stands for Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal factors. This analysis helps organisations gain a comprehensive understanding of the broader macro-environment in which they operate.
By assessing the political stability, economic trends, social attitudes, technological advancements, environmental regulations, and legal frameworks, companies can identify opportunities and threats, formulate effective strategies, and make informed business decisions. PESTEL analysis empowers businesses to adapt to changing circumstances and stay ahead in a dynamic and competitive landscape.
Human Resource Management Concepts
Human Resource Management focuses on recruiting, developing, and retaining a skilled workforce.
Recruitment and selection
Recruitment and selection are critical processes in Human Resource Management that aim to attract and hire the best-suited candidates for an organisation. The recruitment stage involves identifying and reaching out to potential applicants through job advertisements, networking, and career fairs. It tries to gather and generate a pool of qualified candidates.
On the other hand, the selection process involves evaluating and assessing candidates to determine their suitability for the job. This includes conducting interviews, reviewing resumes, and administering tests. Effective recruitment and selection practices ensure that organisations acquire talented individuals who align with the company's values, culture, and job requirements, ultimately contributing to its success.
Performance appraisal
Performance appraisal, a critical aspect of Human Resource Management, is the systematic evaluation of an employee's job performance. It involves assessing an individual's strengths, weaknesses, achievements, and areas for improvement. Through performance appraisal, organisations can provide constructive feedback to employees, recognise their contributions, and identify development needs.
This process not only helps in measuring an employee's effectiveness but also plays a vital role in aligning individual goals with organisational objectives. Effective performance appraisals foster a culture of continuous improvement, enhance employee engagement, and contribute to the overall success of the company. Regular and well-structured appraisals are essential for nurturing a motivated and high-performing workforce.
Master verbal and non-verbal communication with our Senior Management Training!
Financial Management Concepts
Financial Management involves planning, organising, and controlling an organisation's financial resources.
Budgeting and forecasting
Budgeting and forecasting are vital practices in financial Management that help organisations plan and allocate resources effectively. Budgeting involves setting financial targets and allocating funds to various activities, ensuring that expenses align with revenue projections. It provides a roadmap for financial decision-making and resource allocation. On the other hand, forecasting involves taking historical data and market trends and predicting future financial performances. It empowers businesses to foresee potential challenges and opportunities, enabling informed decision-making and proactive actions. Together, budgeting and forecasting empower businesses to navigate uncertainties, maintain financial stability, and achieve their long-term objectives.
Financial ratio analysis
Financial Ratio Analysis is a powerful tool used by businesses to assess their financial health and performance. By analysing key financial ratios, such as liquidity, profitability, and solvency, companies gain valuable insights into their operational efficiency and overall stability.
Liquidity ratios, like the current ratio, gauge a company's ability to meet short-term obligations. Profitability ratios, such as return on equity, indicate the company's ability to generate profits. Solvency ratios, like debt-to-equity ratios, measure the company's long-term debt-paying capacity. Financial Ratio Analysis aids in informed decision-making, helps investors assess potential investments, and allows Management to identify areas for improvement, ensuring sustained growth and success.
Marketing Management Concepts
Marketing Management focuses on identifying and satisfying customer needs profitably.
Marketing Mix (4Ps)
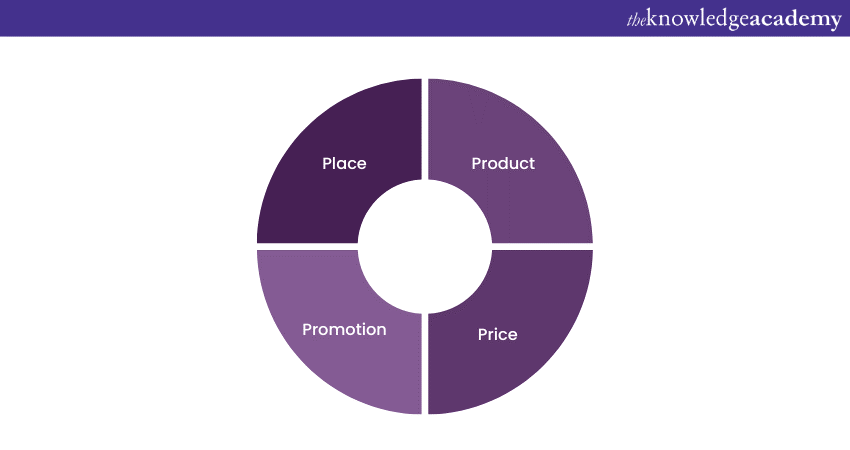
The concept of the "Marketing Mix" centres on the fundamental 4Ps - Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. Each component plays a pivotal role in shaping a prosperous marketing strategy. Firstly, the Product refers to what a company offers to meet the needs and desires of its target customers. Secondly, Price determines the value consumers perceive and the profitability of the business.
Thirdly, Place involves the distribution channels through which the product reaches the customers. Lastly, Promotion encompasses all the communication efforts aimed at creating awareness and persuading customers to choose the product. Mastering the 4Ps is fundamental for businesses to thrive in today's competitive marketplace.
Market segmentation
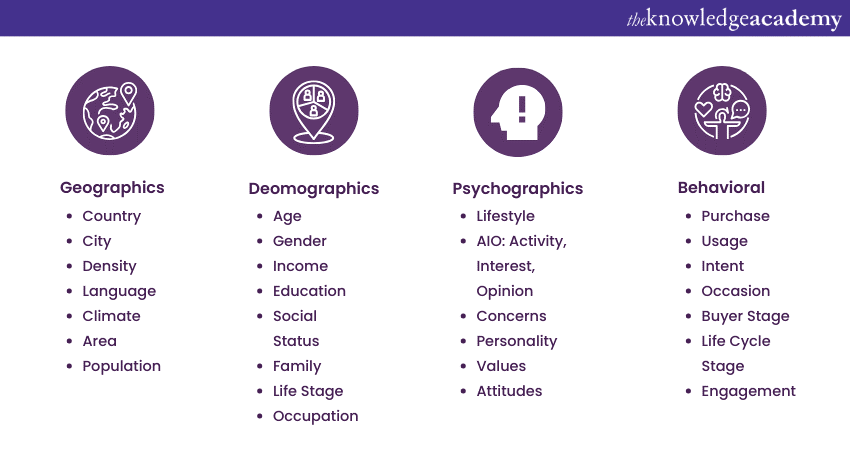
Market segmentation is a strategic marketing concept that involves dividing a broader market into distinct groups based on common characteristics, needs, or preferences. Market segmentation is usually done based on 4 broad categories: geographics, demographics, psychographics and behavioural. Through comprehending the distinct characteristics and behaviours of each segment, businesses can customise their marketing endeavours to precisely target and fulfil the particular requirements of these demographics.
This strategy enables companies to allocate their resources more effectively, delivering personalised products and messages that deeply resonate with their intended audience. Market segmentation empowers businesses to enhance customer satisfaction, build strong brand loyalty, and ultimately drive sales and revenue growth in a highly competitive marketplace.
Innovation and Change Management Concepts
Innovation and change Management are crucial for organisations to stay competitive and adapt to evolving markets.
Innovation Strategies
Innovation strategies are vital for businesses seeking to thrive in today's competitive landscape. These strategies encompass a range of approaches aimed at fostering creativity, embracing new ideas, and driving breakthrough solutions. By encouraging a culture of innovation, organisations can empower their teams to think outside the box, explore uncharted territories, and challenge traditional norms.
Embracing innovative technologies and processes allows companies to stay ahead of the curve, meet evolving customer demands, and seize untapped market opportunities. Whether through continuous improvement or disruptive innovations, effective innovation strategies fuel growth, enhance competitiveness, and position companies at the forefront of their industries.
Change Management Models
Change Management models are structured approaches that facilitate the smooth implementation of organisational transformations. These models provide a systematic framework to navigate through periods of change and minimise disruptions to the business. One popular model is the ADKAR model, which focuses on individual change by addressing Awareness, Desire, Knowledge, Ability, and Reinforcement.
Another widely used model is Kotter's 8-Step Change Model, which emphasises creating a sense of urgency, forming a powerful guiding coalition, and fostering short-term wins to drive successful change. These models help leaders effectively lead their teams through change, ensuring positive outcomes and increased adaptability in today's dynamic business landscape.
Ethical and Social Responsibility in Management
Ethical and socially responsible practices contribute to an organisation's reputation and long-term sustainability.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is a business practice that goes beyond profit-making and encompasses the ethical and responsible conduct of companies towards society and the environment. It involves voluntarily taking action to address social and environmental issues, demonstrating a commitment to sustainable practices, and giving back to the community.
Embracing CSR helps businesses build a positive brand image, foster stakeholder trust, and enhance long-term sustainability. By engaging in initiatives such as philanthropy, environmental conservation, and fair labour practices, companies can make a meaningful impact on society while contributing to a more equitable and sustainable world.
Ethical decision-making
Ethical decision-making is a vital aspect of responsible leadership. It involves the process of evaluating choices from a moral standpoint to ensure actions align with ethical principles and values. When faced with complex dilemmas, individuals or managers must consider the consequences of their decisions on stakeholders, society, and the environment.
By adhering to ethical decision-making frameworks, such as utilitarianism or deontology, leaders can make choices that prioritise the greater good while upholding integrity and fairness. Embracing ethical decision-making not only fosters trust and credibility but also contributes to a positive organisational culture that values transparency and social responsibility.
Bring structure and order to events with our Event Management Masterclass!
Conclusion
Management Concepts form the backbone of successful organisations. By understanding and applying these principles, managers can steer their teams toward achieving shared goals, fostering innovation, and adapting to dynamic business environments. Effective Management is a continuous journey of learning and improvement, and it plays a crucial role in shaping the destiny of businesses.
Unlock new sets of managerial skills with our training in Management Courses!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Introduction to Management
Introduction to Management
Fri 17th Jan 2025
Fri 7th Mar 2025
Fri 23rd May 2025
Fri 18th Jul 2025
Fri 12th Sep 2025
Fri 14th Nov 2025
Fri 12th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


