We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Picture this: You are lounging on your couch, sipping your favourite cup of tea, and within minutes, you have ordered everything you need from Amazon, your go-to ecommerce website, ranging from groceries to gadgets. However, the question here: What is Ecommerce?
It’s like having a 24/7 personal shopping assistant at your fingertips. Continue reading this blog to dive deep into What is Ecommerce understanding, exploring its origins, how it works, and the various existing types. Ready to explore the Ecommerce world? Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
1) What is Ecommerce?
2) How Does Ecommerce Work?
3) Different Types of Ecommerce
4) How to Launch an Ecommerce Business on an Online Marketplace?
5) Benefits and Drawbacks of Ecommerce
6) Applications of Ecommerce
7) Challenges of Ecommerce
8) Difference Between Ecommerce Business and Traditional Business Models
9) What's the Best Ecommerce Platform?
10) Conclusion
What is Ecommerce?
E-commerce comprises goods ‘buying and selling and services over the internet. This broad term includes virtual auctions, shopping, banking, and digital payments, encompassing various digital platform activities.
Ecommerce enables businesses to reach worldwide scale audiences, offering consumers the convenience of purchasing the products or services from their home’s comfort, making it an ideal option for learning How to Make Money Online through digital sales. Whether it's a small business or a large corporation, ecommerce goes beyond boundaries at the geographical levels.
History of Ecommerce
ecommerce, or electronic commerce’s history, is a fascinating journey that has transformed how goods and services are sold and bought. Here are some key milestones:
Early Beginnings (1960s - 1980s)
a) Electronic Data Interchange (EDI): In 1960, there was a development of EDI, which allowed businesses in documents exchange in electronic forms, ranging from orders and purchases to invoices. This system laid the groundwork for ecommerce for transaction of businesses, their automation and streamlining, paving the way for the digital marketplace what we know today.
b) Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT): In the 1970s, EFT systems enabled the inter-bank transfer of electronic money in 1970s, paving the way for online payments.
The Birth of the Internet and Online Shopping (1990s)
a) World Wide Web: In 1989, Berners-Lee invented the World Wide Web, which became public accessible in the year 1991. Since then, it has revolutionised continuously how information is shared and accessed in today’s time. This innovation resulted in the transformation of communication and commerce, laying the foundation for modern ecommerce ecosystems.
b) First Online Transactions: The first secure online transaction was made on NetMarket in 1994, marking the online retail beginning.
Growth and Expansion (2000s - 2010s)
a) Amazon and eBay: Amazon and eBay were founded in the mid-1990s, these platforms became the ecommerce world giant, offering a wide range of products and services.
b) Mobile Commerce: With smartphones and tablets advent, there was a mobile commerce emergence (m-commerce, which enabled consumers to shop whenever they wanted. This development expanded the ecommerce reach and convenience, making it easier for people to make purchases anytime, anywhere.
Modern Era (2020s)
a) Global Reach: Ecommerce has become a phenomenon at the global level, with Alibaba and Shopify, among other platforms, which have streamlined businesses of all sizes to reach global markets. These platforms provide the tools and infrastructure needed for companies for their overall reach expansion and global customer connection, making global commerce more accessible than ever before.
b) Technological Advancements:
Artificial Intelligence (AI), Augmented Reality (AR), and Blockchain, among other revolutionised innovations, are continually shaping ecommerce’s future. These technologies enhance personalisation, create immersive shopping experiences, and ensure the security of transactions, driving the evolution of the digital marketplace.
What is an Ecommerce Website?
An ecommerce website is an online store where customers can look for their desired products, browse offerings, and make relevant purchases. This approach facilitates transactions between buyers and sellers.
A digital storefront acts as the virtual counterpart to the product shelves, sales staff, and cash register of a physical shop. Other online store elements may include listings of products, categories, and customer reviews.
How Does Ecommerce Work?
Ecommerce or electronic commerce, involves buying and selling goods and services over the internet. Here’s how it works:
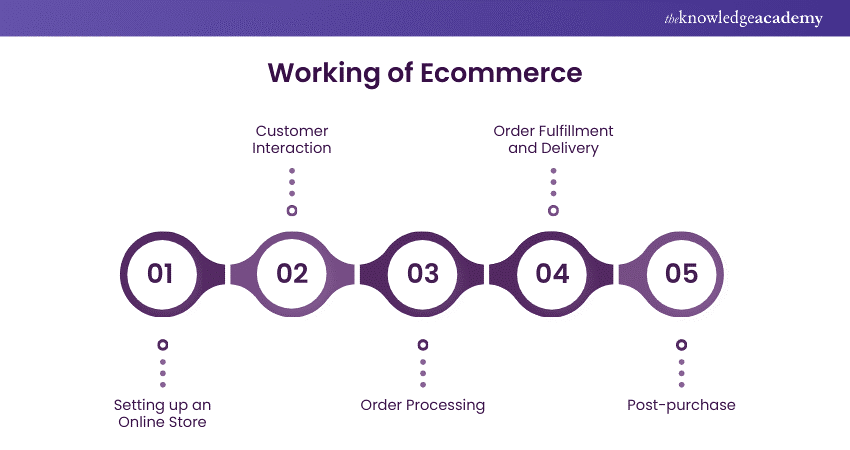
1) Setting up an Online Store
a) Website Creation: Businesses create a website for ecommerce using Shopify, WooCommerce, or Magento 2, among other platforms. These platforms provide tools for product listing, inventory management, and payment processing.
b) Product Listings: Products are listed along with their prices, descriptions, and images in a detailed manner, making it easier to browse for customers and select their desired purchasing. This information helps shoppers not only make well-informed decisions but also helps in their overall shopping experience.
2) Customer Interaction
a) Browsing: Customers visit the online store, browse through various categories of products, and add their chosen items to the shopping cart. This process allows them to select multiple products before checkout. This approach ensures a seamless and convenient shopping experience.
b) Payment: Once ready to purchase, customers proceed to checkout. They enter their shopping details and choose a payment method, such as credit/debit cards, digital wallets (like PayPal), or other online payment systems. This step ensures the processing of their order and shipment preparation.
3) Order Processing
a) Order Confirmation: The order is confirmed post-payment, and the customer receives an email for confirmation with the details of the orders. This email typically includes items purchased, the shipping address, and the expected delivery date, among other vital information. This ensures that customers are well-informed about what purchases they make from the ecommerce platform.
b) Inventory Management: The system works for inventory updates to reflect the sale of items, ensuring stock levels and overselling prevention accurately. This inventory management in real-time helps with smooth operations maintenance and customer satisfaction.
4) Order Fulfillment and Delivery
a) Shipping: The business prepares the shipping order, which involves product packaging and shipping label generation. This step ensures the delivery-readiness of the items, which can be tracked until they reach the customer.
b) Delivery: The order has been shipped to the customer's address. Some businesses also offer store pickup or local delivery, providing customers with additional convenience and flexibility. Moreover, this ensures the products reach customers in a timely manner.
5) Post-purchase
a) Customer Service: Businesses provide support for customers for any issues related to the order, such as returns or exchanges. This ensures that customers have a rewarding shopping experience and can resolve any problems quickly and efficiently.
b) Feedback: Customers have the opportunity to leave reviews and feedback, which not only aids other shoppers in making informed decisions but also allows the business to improve its services. This feedback loop is important for maintaining high standards and customer satisfaction.
Boost your ecommerce success through compelling content creation- Sign up for our Product Content for Ecommerce Training now!
Different Types of Ecommerce
Ecommerce can be categorised into several types on the basis of their transactional nature. Understanding this category is crucial for businesses that are aiming to enter the space of ecommerce.
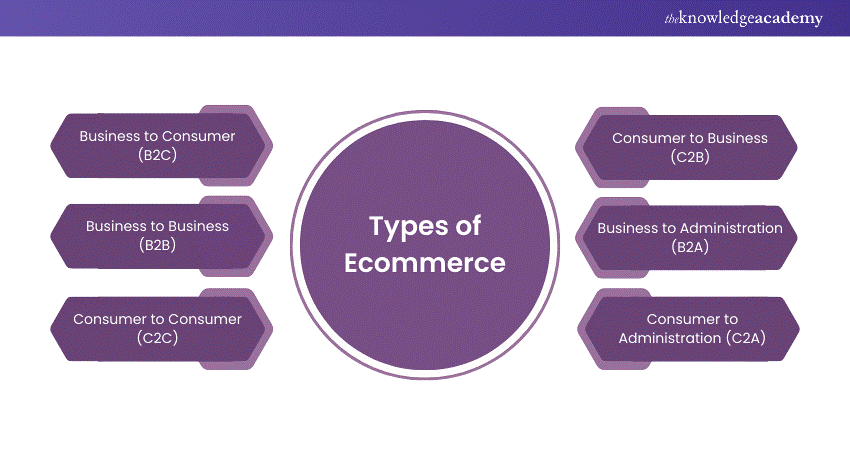
1) Business to Consumer (B2C): This is the most common type, where businesses perform products or services selling directly to consumers. The key examples include Amazon, ASOS, and Tesco, among other retailers.
2) Business to Business (B2B): In this model, businesses perform products/services selling to other businesses and brands. The key examples include Alibaba and other bulk suppliers.
3) Consumer to Consumer (C2C): This involves consumers’ transactions, often facilitated by a third-party platform. The key examples of C2C include eBay, Gumtree, and Depop.
4) Consumer to Business (C2B): Here, individual's sell products or services selling to businesses. Prominent examples in this category include freelance platforms like Upwork and Fiverr.
5) Business to Administration (B2A): This model involves transactions between businesses and public administration or government bodies. Examples include government procurement systems.
6) Consumer to Administration (C2A): In this model, consumers interact with government or public administration. The key examples include paying taxes or applying for government services online.
Learn to build, manage, and optimise your WooCommerce store with our comprehensive, hands-on WooCommerce Training – sign up now!
How to Launch an Ecommerce Business on an Online Marketplace?
ecommerce businesses launching in an online marketplace can be rewarding ventures; however, it requires careful planning and strategic steps. Here are the steps to help you with the process navigation, ranging from business model defining to launching your store successfully.

Step 1 - Define Your Business Model
Begin by identifying a potentially profitable business idea that aligns with your skills and interests. Having products or services with detailed knowledge you plan to sell will give you a competitive edge.
Step 2 - Select an Online Marketplace
Select an online marketplace where you will set up your store. Popular options provide access to a large customer base, growth tools, and customer relationship services. While creating your own website is an option, many sellers prefer established marketplaces for their convenience and reach.
Step 3 - Register Your Business on the Marketplace
Create an account on your chosen marketplace. Most platforms offer a straightforward sign-up process. Carefully follow the instructions and have your documents ready, as you may need to provide your name and bank details, among other personal information.
Step 4 - Create and Optimise Your Product Listings
Start with your online store setting by listing your products in appropriate categories. Ensure there are detailed and informative product listings, giving potential buyers a clear knowledge of what they are purchasing. Well-crafted listings can attract more customers and help increase sales.
Step 5 - Determine and Set Your Pricing Strategy
Pricing your products can be challenging due to competition. Utilise pricing tools to adjust prices automatically based on your set rules. This helps you stay competitive without constantly revisiting your listings. Ensure your prices are reasonable to attract and retain customers.
Step 6 - Develop a Marketing Plan
Effective marketing is crucial for sales generation. Leverage social media, among other inexpensive tools, to create a robust marketing strategy. Plan both a launch strategy and a post-launch strategy to maintain a steady flow of customers.
Step 7 - Execute a Successful Launch
With everything in proper order, it’s time for business to launch officially. You must make sure your inventory is well-stocked and ready to meet fluctuating demands. However, you must remember that making a strong first impression is vital for long-term success.
Elevate your brand with advanced digital marketing tools with our Digital Marketing Tools Training – join now!
Benefits and Drawbacks of Ecommerce
Ecommerce offers numerous benefits, but it also comes with its own set of challenges. Understanding these can help you with easy ecommerce navigation.
Benefits
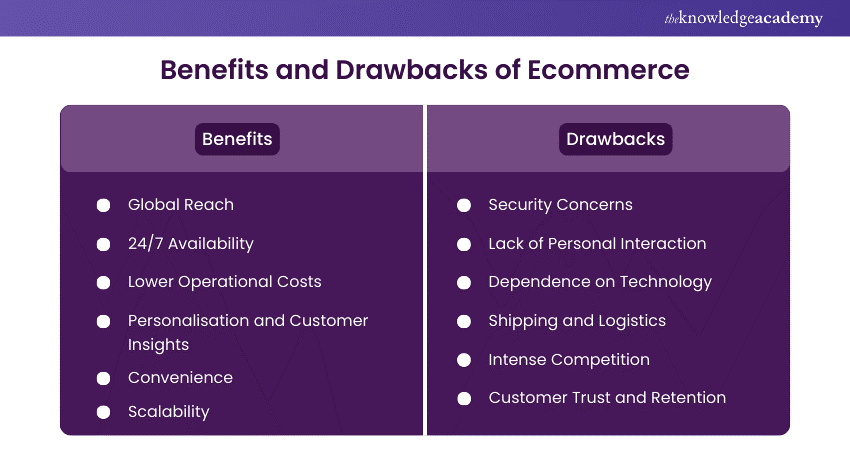
a) Global Reach: E-commerce allows businesses to global audience expansion, breaking geographical barriers and expanding their customer base.
b) 24/7 Availability: Online stores are open at all times of the week, providing customers with shopping at any time, leading to an increase in sales.
c) Lower Operational Costs: An online store often incurs lower costs in comparison to a physical store. Expenses such as rent, utilities, and in-store staff can be reduced significantly.
d) Personalisation and Customer Insights: ecommerce platforms can collect data on customer behaviour, preferences, and purchase history. This enables personalised marketing and improved customer service.
e) Convenience: Customers can shop from their homes comfort easily compare prices, and have products delivered to their doorstep.
f) Scalability: Ecommerce businesses can scale more easily than physical stores. Adding new products or expanding into new markets can be done with minimal additional costs.
Drawbacks
a) Security Concerns: Online transactions can be vulnerable to security breaches. These include hacking and fraud, which can undermine the trust of the customers.
b) Lack of Personal Interaction: The personal interaction lack can make it challenging to build customers’ personal relationships and provide assistance on an immediate level.
c) Technology Dependency: ecommerce is technology-reliant on a heavy basis, and any technical issues, such as downtime of the website or payment gateway failures, can disrupt the operations of the businesses.
d) Shipping and Logistics: Managing shipping and logistics can be complex and costly, especially for orders on an international scale. Delays and errors in shipping can negatively impact customer satisfaction.
e) Intense Competition: The online marketplace is competitive at a large scale, with several businesses vying for the same customers. This situation can result in price wars and diminishing profit margins.
f) Customer Trust and Retention: Building trust with customers can be more challenging online, and retaining customers requires consistent effort and excellent service.
Applications of Ecommerce
Ecommerce applications are essential for customer experience enhancement and driving usage of the platform. They employ various strategies and technologies to achieve these goals. Here are some key components:
1) Online Marketing Strategies
Many ecommerce apps utilise online marketing strategies to enhance the customer experience and encourage platform usage. These strategies include email, shopping carts, online catalogues, web services, Electronic Data Interchange (EDI), file transfer protocol, and mobile applications.
2) B2C and B2B Activities
These approaches are utilised in both B2C and B2B ecommerce activities, as well as other outreach types. They involve emailing targeted ads to subscribers and sending text messages to mobile devices. To avoid being considered spam, companies now use tools like digital coupons, social media marketing, and targeted advertisements to attract consumers online.
3) Security Focus
Consumers need to feel confident that their personal as well as their financial information is protected when they shop online. Invest in secure payment gateways and SSL certificates to safeguard customer data. All Shopify plans include these security features.
Challenges of Ecommerce
Running an online business has its benefits, but it also comes with challenges. If you're looking to start an ecommerce business, be prepared for these potential pitfalls:
1) Security Concern
Consumers need to feel confident that their personal and financial information is protected when they shop online. Invest in secure payment gateways and SSL certificates to safeguard customer data. All Shopify plans include these security features.
2) Increased Competition
Ecommerce is a highly competitive space, with many businesses vying for the same customers. Online businesses need to differentiate themselves by offering unique products, competitive prices, and exceptional customer experiences.
3) Shipping Challenges
Shipping impacts customer satisfaction. Use reliable shipping services to ensure timely and safe delivery of products and minimise lost orders.
4) Customer Service Demands
Effective customer service is crucial for maintaining customer satisfaction. Implement strong return policies and customer service strategies to address any issues efficiently. This ensures that customers feel supported and valued, leading to a positive shopping experience and fostering customer loyalty.
Explore Shopify's features and build your online presence with expert guidance in our Introduction To Shopify – join now!
Difference Between Ecommerce Business and Traditional Business Models
Ecommerce and traditional business models differ significantly in various aspects, each offering unique advantages and challenges.
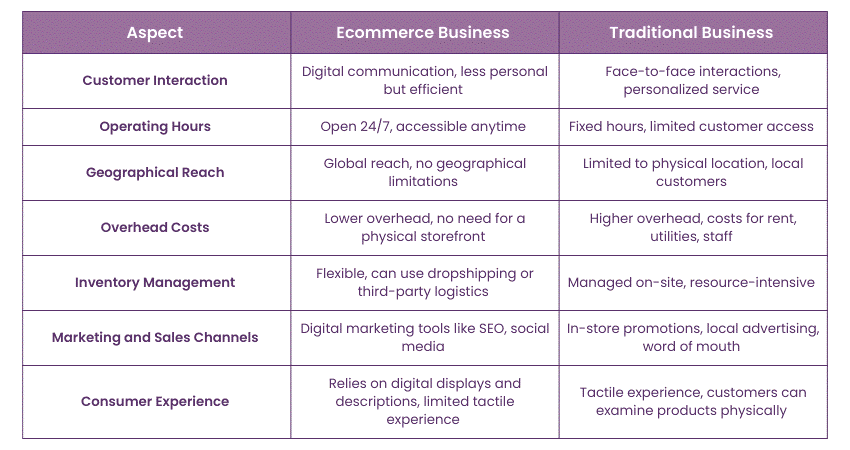
1) Customer Interaction: Traditional businesses involve face-to-face interactions, allowing for personalised customer service. In contrast, Ecommerce businesses rely on digital communication, which can be less personal but more efficient.
2) Operating Hours: Traditional businesses typically operate during fixed hours, limiting customer access. Ecommerce stores, on the other hand, are open 24/7, providing customers with the convenience of shopping anytime, anywhere.
3) Geographical Reach: Traditional businesses are often limited by their physical location, serving customers in a specific area. Ecommerce businesses, however, have the ability to reach a global audience, breaking down geographical barriers.
4) Overhead Costs: Traditional businesses usually incur higher overhead costs, such as rent, utilities, and staffing for a physical storefront. Ecommerce businesses often have lower overhead, as they don't require a physical location, reducing property and in-person staff expenses.
5) Inventory Management: Traditional businesses manage physical inventory on-site, which can be resource-intensive Ecommerce businesses can use various models like dropshipping or third-party logistics, allowing for more flexible and often cost-effective inventory management.
6) Marketing and Sales Channels: Traditional businesses rely heavily on in-store promotions, local advertising, and word of mouth. Ecommerce businesses have access to a wide array of digital marketing tools, including social media, SEO, and email marketing, enabling them to reach a larger and more targeted audience.
7) Consumer Experience: Traditional businesses offer a tactile experience where customers can physically examine products before purchasing. Ecommerce uses digital displays, but detailed images, reviews, and return policies help reduce potential customer disconnect.
What’s the Best Ecommerce Platform?
Selecting the optimal ecommerce platform depends on your business's specific needs, technical expertise, and budget. Shopify is a popular all-in-one solution that offers a user-friendly interface, scalability, and a wide range of features suitable for businesses of all sizes. Its extensive app ecosystem and 24/7 customer support make it a reliable choice for many entrepreneurs.
For those seeking flexibility and customisation, Wix provides an intuitive drag-and-drop website builder with over 500 pre-designed templates. It is particularly suitable for small businesses with a limited product range, offering features like multilingual support and various payment methods. However, it may have limitations in scalability for larger inventories.
Unlock the secrets to ecommerce success with our ecommerce Strategy Course and elevate your digital business strategy today!
Conclusion
After exploring the concept of ecommerce, it's evident that this digital marketplace is more than a passing trend—it's a fundamental transformation in how we engage with businesses and shops. Whether you're a consumer or an entrepreneur, grasping the nuances of ecommerce is crucial for thriving in today's fast-paced, online-driven economy.
Leverage analytics to optimise your marketing campaigns- Join our Data-driven Marketing Course today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is Ecommerce Used?

Ecommerce is used for its convenience, global reach, and cost-effectiveness. It allows businesses to operate 24/7, connecting with customers and selling products or services online efficiently.
Is Amazon an Ecommerce?

Yes, Amazon is a leading Ecommerce platform. It facilitates the buying and selling of a vast range of products online. Amazon connects millions of customers and sellers globally through its digital marketplace.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Digital Marketing Courses, including an ecommerce Strategy Course, Customer Acquisition Training, Product Content for Ecommerce Training and a Pinterest Marketing Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Dropshipping Tips.
Our Digital Marketing Blogs cover a range of topics related to Ecommerce, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Digital Marketing skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Digital Marketing Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Ecommerce Strategy Course
Ecommerce Strategy Course
Fri 28th Mar 2025
Fri 23rd May 2025
Fri 4th Jul 2025
Fri 5th Sep 2025
Fri 5th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


