We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +353 12338944 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Human Resource Accounting (HRA) is a valuable approach that recognises the significance of human capital in an organisation's financial performance. It involves quantifying and reporting the value of human resources in financial terms. By providing insights into the investment and effectiveness of human capital, HRA can assist organisations in making informed decisions regarding their workforce. However, like any methodology, it has its advantages and disadvantages that should be carefully considered. In this blog, we will delve into the Advantages and Disadvantages of Human Resource Accounting.
Table of Contents
1) What is Human Resource Accounting
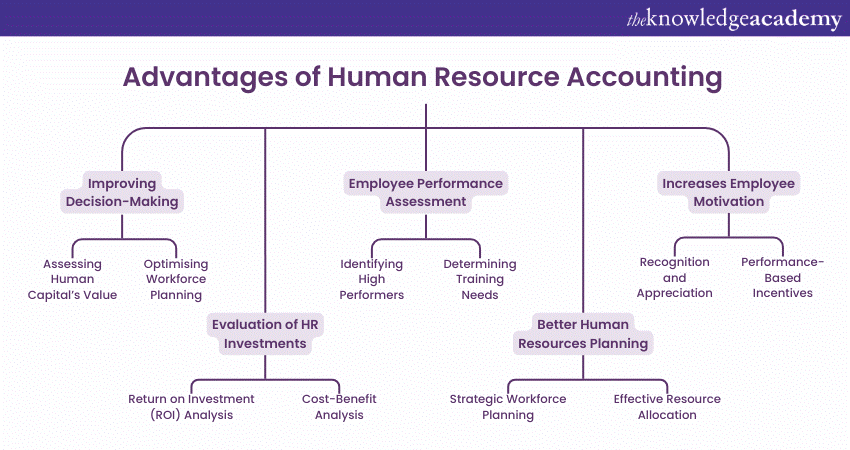
2) Advantages of Human Resource Accounting
a) Improving Decision-Making
b) Evaluation of HR investments
c) Employee Performance Assessment
d) Better Human Resources Planning
e) Increases Employee Motivation
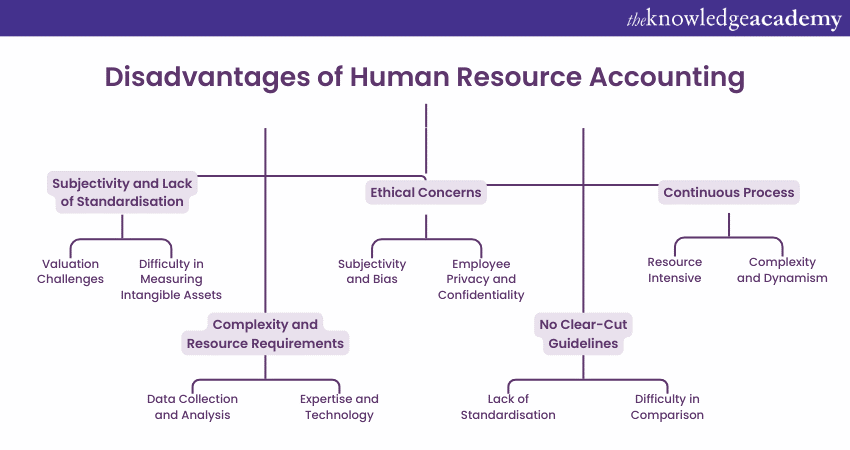
3) Disadvantages of Human Resource Accounting
a) Subjectivity and Lack of Standardisation
b) Complexity and Resource Requirements
c) Ethical Concerns
d) No Clear-Cut Guidelines
e) Continuous Process
4) Conclusion
What is Human Resource Accounting?
Before we enumerate the Advantages and Disadvantages of Human Resource Accounting, we will first define what it is. Human Resource Accounting (HRA) is an approach that involves quantifying and reporting the value of human resources in financial terms. It recognises that human capital, consisting of the knowledge, skills, experience, and abilities of employees, is a valuable asset that contributes to an organisation's overall performance and success. By assigning a monetary value to human resources, HRA provides organisations with insights into the investment and effectiveness of their workforce.
HRA goes beyond traditional accounting practices, which focus solely on tangible assets such as buildings, equipment, and inventory. It acknowledges that human capital is an intangible asset that plays a vital role in achieving organisational objectives. By valuing human resources, organisations can better understand their contributions, make informed decisions, and allocate resources effectively.
The importance of Human Resource Accounting lies in its ability to enhance decision-making processes within an organisation. By quantifying and assessing the value of human capital, organisations gain a deeper understanding of the impact employees have on their financial performance. This understanding allows management to make more informed decisions in various areas, including strategic planning, resource allocation, and performance management.
Advantages of Human Resource Accounting
Human Resource Accounting (HRA) offers several advantages that can significantly benefit organisations in managing their human capital and making informed decisions. By quantifying and assessing the value of human resources, HRA provides valuable insights into the investment and effectiveness of the workforce. Let us explore the key advantages of Human Resource Accounting:
Improving decision-making
One of the primary advantages of HRA is its ability to enhance decision-making processes within an organisation. By quantifying and evaluating the value of human capital, organisations gain a deeper understanding of the contribution employees make to their overall performance. This understanding enables management to make more informed decisions in various areas.
1) Assessing human capital’s value: Human Resource Accounting allows organisations to assign a monetary value to their human capital. By evaluating factors such as skills, experience, and knowledge, companies can quantify the worth of their employees. This valuation helps in determining the optimal allocation of resources and aids in strategic planning. Organisations can identify the specific areas where human capital creates the most value and focus their efforts and investments accordingly.
2) Optimising workforce planning: HRA provides valuable insights into the strengths and weaknesses of the workforce. By quantifying the value of human resources, organisations can identify critical skills gaps and areas of expertise that need improvement. With this information, they can strategically plan their recruitment, training, and development programs using a Workforce Planning Model to ensure a competent and well-rounded workforce. By aligning their Workforce Planning with the organisation's strategic objectives, companies can maximise the effectiveness of their human capital.
Evaluation of HR investments
Another advantage of Human Resource Accounting is its role in evaluating investments made in human resources. It allows organisations to assess the returns generated from their HR-related initiatives, which helps justify future investments and allocate resources effectively.
1) Return on Investment (ROI) analysis: Through HRA, companies can determine the return on investment for various HR initiatives. Whether it's recruitment, training, or employee development programs, HR professionals can evaluate their effectiveness by comparing the costs incurred with the benefits derived. This analysis aids in decision-making and ensures that resources are allocated to initiatives that yield the highest returns. By quantifying the impact of HR investments, organisations can make data driven decisions and focus on activities that generate the most significant value..
2) Cost-benefit analysis: HRA enables organisations to conduct cost-benefit analyses for HR interventions. By quantifying the costs associated with HR activities and comparing them to the expected benefits, organisations can make informed decisions regarding the feasibility and potential outcomes of their HR investments. This analysis helps organisations optimise their resource allocation, ensuring that investments are made in initiatives that provide the most significant value for the organisation.
Employee performance assessment
Lastly, Human Resource Accounting plays a crucial role in assessing employee performance and identifying high performers within an organisation.
1) Identifying high performers: By assigning value to human capital, organisations can differentiate high-performing employees from average performers. This distinction helps in identifying and rewarding individuals who consistently contribute to the organisation's success. It enables companies to recognise and retain talent, creating a positive work environment while also motivating employees to perform at their best.
2) Determining training needs: HRA aids in determining the training and development needs of employees. By assessing the current value of human capital and identifying skill gaps, organisations can design targeted training programs that enhance the competencies of their workforce. This approach ensures that employees receive the necessary training to excel in their roles and contribute to the organisation's objectives. By investing in training and development initiatives based on the identified needs, organisations can enhance employee performance and drive overall organisational growth.
Elevate your HR career to new heights with our Certified HR Manager course – register today!
Better Human Resources Planning
Better human resources planning refers to the benefits that arise from having a systematic approach to assessing and accounting for human resources within an organisation.
1) Strategic Workforce Planning: Human Resource Accounting provides valuable insights into the skills, capabilities, and potential of employees within an organisation. This information helps in Strategic Workforce Planning by identifying the current and future talent needs of the organisation. It enables management to proactively address skill gaps, succession planning, and recruitment strategies to ensure a competent and skilled workforce aligned with organisational goals.
2) Effective Resource Allocation: Human Resource Accounting helps organisations allocate their resources effectively by assessing the value and contribution of human capital. It provides a basis for decision-making regarding investments in employee training and development programs, talent retention initiatives, and workforce optimisation. By understanding the value of human resources, organisations can allocate resources in a manner that maximises employee productivity, engagement, and overall organisational performance.
Increases Employee Motivation
Increases employee motivation" refers to the positive impact that accurately accounting for human resources can have on the motivation and engagement of employees within an organisation.
1) Recognition and Appreciation: Human Resource Accounting recognises and quantifies the value of employees as valuable assets to the organisation. This recognition and appreciation of their contributions can significantly boost employee motivation by creating a sense of worth, validation, and job satisfaction.
2) Performance-Based Incentives: Human Resource Accounting provides a basis for performance-based incentives and rewards. When employees see that their efforts and achievements are accurately assessed and rewarded, it serves as a motivating factor to excel in their work. This can include bonuses, promotions, or other forms of recognition tied to their performance, further enhancing their motivation and commitment to their roles.
Get your free HR Audit PDF to understand best practices and evaluate your HR practices effectively.
Disadvantages of Human Resource Accounting
While Human Resource Accounting (HRA) does offer numerous benefits, it also comes with several disadvantages that organisations need to consider. These disadvantages highlight the challenges and limitations of Human Resouces Accounting associated with quantifying and valuing human capital. Let us explore the key disadvantages of Human Resource Accounting:
Subjectivity and lack of standardisation
One of the primary challenges associated with HRA is the subjectivity and lack of standardisation in measuring human capital. Unlike financial assets, the value of human resources is difficult to quantify accurately. Different approaches and assumptions can lead to inconsistent results, making it challenging to compare data across organisations.
1) Valuation challenges: Assigning a financial value to human capital is a complex task. Factors such as skills, experience, and knowledge are intangible and not easily measured. This subjectivity can create discrepancies in the valuation process and impact the overall accuracy of the results. Organisations may employ different methodologies or make different assumptions, leading to variations in the valuation outcomes.
2) Difficulty in measuring intangible assets: Human Resource Accounting aims to capture the value of intangible assets, such as employee skills and knowledge. However, accurately measuring and quantifying intangible assets is inherently challenging. It requires robust methodologies and reliable data sources, which may not always be readily available. As a result, organisations may struggle to capture the full extent of the value generated by their human capital.
Complexity and resource requirements
Implementing and maintaining a Human Resource Accounting system requires substantial resources, including time, expertise, and technology. These resource requirements can pose challenges for organisations, especially those with limited capabilities or budgets.
1) Data collection and Analysis: Collecting and analysing data related to human capital can be a time-consuming process. Organisations need to gather relevant information from various sources, such as performance evaluations, training records, and employee surveys. This data then needs to be processed and analysed to generate meaningful insights. It requires a systematic and rigorous approach to ensure the accuracy of the results.
2) Expertise and Technology: Applying Human Resource Accounting requires specialised knowledge and expertise. HR professionals need to understand the complexities of valuation methodologies and possess the necessary analytical skills. Moreover, implementing HR software and technology solutions can incur additional costs and require ongoing maintenance. Organisations need to invest in training their HR teams and ensuring they have access to suitable technology platforms to effectively implement and maintain an HRA system.
Learn effective recruitment strategies and best practices for success with our Recruitment Training!
Ethical Concerns
Human Resource Accounting raises ethical concerns related to objectivity, transparency, and privacy. These concerns need to be addressed to ensure fairness and protect employee rights.
1) Subjectivity and Bias: Human Resource Accounting involves assessing and assigning monetary values to intangible assets such as employee skills and knowledge. This subjective process can lead to biases and subjective judgments, potentially resulting in unfair treatment or discrimination among employees. Ethical concerns arise when there is a lack of transparency, objectivity, and fairness in the valuation and treatment of human resources within the accounting framework.
2) Employee Privacy and Confidentiality: Human Resource Accounting requires collecting and analysing sensitive employee data, including performance evaluations, skills assessments, and potential for future contributions. Maintaining employee privacy and confidentiality becomes crucial to ensure ethical practices. If employee data is mishandled, misused, or accessed without proper consent, it can violate ethical principles and erode trust between employees and the organisation.
Master the intricacies of employment law with our Employment Law Training – Sign up now!
No Clear-Cut Guidelines
No clear-cut guidelines" refers to the lack of standardised or universally accepted principles or guidelines for implementing Human Resource Accounting (HRA) practices.
1) Lack of Standardisation: "No clear-cut guidelines" implies that there is no universally accepted framework or methodology for valuing human resources. This absence of standardised practices leads to inconsistency and subjectivity in how organisations assess and report the value of their human capital.
2) Difficulty in Comparison: Without clear guidelines, it becomes challenging to compare or benchmark human resource values across companies or industries. This lack of comparability undermines the reliability and transparency of Human Resource Accounting (HRA) practices, making it difficult for stakeholders to assess the true value of an organisation's workforce.
Continuous Process
Human Resource Accounting (HRA) offers valuable insights into the quantifiable worth of an organisation's human capital, but its implementation comes with several challenges
1) Resource Intensive: "Continuous process" suggests that implementing Human Resource Accounting (HRA) requires ongoing effort and resources. This continuous nature means organisations must dedicate significant time and manpower to gather, update, and maintain data on human capital, leading to increased administrative burden and operational costs.
2) Complexity and Dynamism: Human Resources are dynamic and complex, with factors like skills, experience, and performance constantly changing. As a continuous process, HRA must adapt to these changes, requiring regular updates and adjustments to accurately reflect the value of human capital. This complexity adds layers of intricacy to the accounting process, potentially leading to errors or inaccuracies in valuing human resources over time.
Conclusion
All in all, Human Resource Accounting offers several advantages that can enhance decision-making, evaluate HR investments, and assess employee performance. However, it also faces challenges related to subjectivity, lack of standardisation, complexity, and ethical considerations. Organisations should carefully consider the Advantages and Disadvantages of Human Resource Accounting when implementing HRA and seek to strike a balance between the financial valuation of human capital and the intrinsic value of their employees.
Unlock your full potential with our HR Courses – Sign up today!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Scope of Human Resource Accounting?

Human Resource Accounting (HRA) quantifies the value of human capital in financial terms, aiding in decision-making regarding workforce management, investment, and performance evaluation.
How do you Measure Human Resource Accounting?

Human Resource Accounting is typically measured using methods such as the Replacement Cost Method, the Historical Cost Method, and the Opportunity Cost Method. These approaches help quantify the value of human capital within an organisation.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various HR Courses, including Certified HR Advisor Training, Certified HR Manager Course and Certified Training & Development Manager Course .These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Top 25 HR Interview Questions.
Our Business Skills Blogs covers a range of topics offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course




 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


