We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +353 12338944 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Imagine a tool that helps you unravel the art of market competition, guiding you through the complex interplay of choices made by individuals and firms alike! That's the power that game theory has equipped the field of Economics with. Understanding the role of Game Theory in Economics can help illuminate market behaviours, negotiations, and every strategic manoeuvre that shapes our economic reality.
This blog digs deep into Game Theory in Economics, encompassing this framework's history, principles, examples, applications and more. So read on and master the art of predicting market dynamics!
Table of Contents
1) What is Game Theory?
2) Types of Game Theory in Economics
3) How Game Theory Works in Economics
4) Applications of Game Theory in Economics
5) Famous Game Theory Examples in Economics
6) Benefits and Limitations of Game Theory in Economics
7) Historical Background of Game Theory in Economics
8) Conclusion
What is Game Theory?
Game theory refers to a mathematical framework used to analyse interactions between rational decision-makers and conceive social scenarios among competing players. It explores how these actors anticipate and respond to others' actions, aiming to identify optimal strategies in diverse scenarios.
In a way, game theory is the science of strategy. Founded on the works of scholars like John Nash and John Von Neumann, game theory has transcended its mathematical roots and found profound applications across diverse disciplines, including Economics.
Types of Game Theory in Economics
Game theory in Economics primarily serves as a tool that enables the fundamental analysis of various industries and the relationships between organisations. There are five types of game theory as detailed below:
Cooperative vs Non-cooperative Games
Cooperative game theory involves the study of players forming binding agreements and allocating payoffs between themselves. Meanwhile, players can't get into binding agreements in non-cooperative game settings.
A non-cooperative game analyses how rational individual players decide on their strategy to fulfil objectives. Non-cooperative game theory analyses how rational economic agents deal with each other to reach their goals.
Symmetric vs Asymmetric Games
In the case of symmetric games, the payoffs are dependent on each player’s strategy. Conversely, in asymmetric game settings, payoffs differ among the players. That's why the payoff will vary if all players pick an identical strategy.
Simultaneous vs Sequential Games
A simultaneous game is one in which players come to a decision without knowing other players’ decisions or where all players make their decisions simultaneously. Meanwhile, in sequential games, players are aware of the decisions made by the other players or take turns to decide.
Zero-sum vs Non-zero-sum Games
In the case of zero-sum games, a participant’s gains or losses balance the gains or losses of other participants. On the contrary, in a non-zero-sum game, a player’s gains or losses don't result in other players’ gains or losses.
Investing and trading stocks are often considered zero-sum games because one market participant buys a stock, and another sells that stock for the same price. However, since different investors have different investing goals and risk appetites, it may be mutually beneficial for both parties to participate in a transaction.
Perfect Information vs Imperfect Information Games
In a perfect information setting, all participants can access the same information, and they can make decisions based on it. However, in an imperfect information setting, the data available to one player isn't available to other participants.
How Game Theory Works in Economics
In the field of Economics, individuals, firms, and governments strategise their choices based on their objectives and expectations of how others might act. Game theory provides a structured approach for understanding these strategic interactions, providing insights into pricing strategies, competitive behaviours, negotiations, and more. By structuring economic interactions as games, economists can analyse diverse scenarios and predict outcomes more precisely.
The Role of Nash Equilibrium
Nash equilibrium refers to an outcome upon reaching which no player can increase the payoff by changing decisions unilaterally. This equilibrium is typically reached over time; once it's reached, it'll not be deviated from.
Strategic Decision-Making in Economic Models
Game theory revolutionised Economics by addressing critical problems in prior mathematical economic models. For example, neoclassical Economics couldn't explain entrepreneurial anticipation or handle imperfect competition. Game theory siphoned attention away from steady-state equilibrium and toward the market process.
Economists often utilise game theory to explain oligopoly firm behaviour, which helps predict likely outcomes when firms engage in behaviours, including price-fixing and collusion.
Gain deeper insight into the diverse procedures of costing and pricing in our detailed Costing and Pricing Course - Sign up now!
Applications of Game Theory in Economics
From modelling competing behaviours between economic agents in business to areas such as mergers and acquisitions, capital structure, corporate governance and asset pricing, game theory has tremendous applications in Economics. Its applications also include analysing strategic behaviour and formulating optimum responses and understanding voting paradoxes.
Examples in Market Competition
Game theory can help model market competition. Consider these examples of market competition using game theory:
a) Two firms can either compete or collude. If they compete, they generate high quantities and realise small profits, and in case of collusion, they reduce total production and enhance profits. However, if any of these firms undercut the collusive price and set a low price, it can sell more and benefit from the best of both worlds.
b) Two companies in the machinery market are facing an attack from Country A and are therefore planning to open their own multipurpose factory. Depending on assumptions about customer demand, cost structures, market growth, among other factors, the best strategy in one scenario could be to cut prices.
c) Game theory helps determine the optimal price at which to sell products or services when facing competition.
Game Theory in Oligopoly Markets
Let’s say that the oligopoly market comprises two rival competitors, Firm A and Firm B. The table below summarises strategies and rewards, depending on the firms' cooperation in price setting. After playing the game simulation, the following outcomes were noticed:
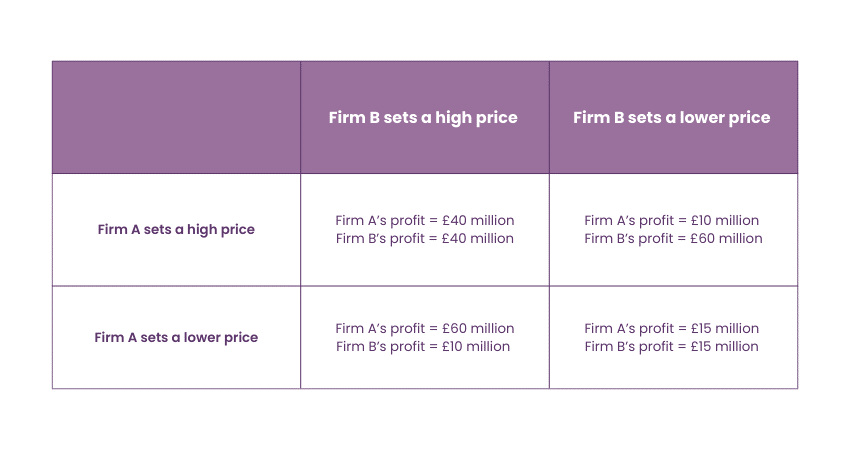
When Firm A sets a high price, and Firm B sets a lower price, most consumers will buy Firm B’s products, making it more profitable than Firm A. The opposite is true when Firm B sets a high price, and Firm A sets a lower price.
If both firms set high prices, neither firm will carry a market share advantage, but the high price will create a moderately high profit for each firm. Meanwhile, if both firms set a low price, neither firm will achieve a market share advantage.
Use in Auction Design and Bidding Strategies
Auction design refers to the process of choosing the rules and type of an auction to achieve an objective, such as efficiency or maximising revenue. Game theory can help compare and assess various auction formats based on their incentives and expected outcomes. Factors such as entry fee, reserve price, information disclosure and number of items can all affect the auction design.
Meanwhile, in game theory, a bidding strategy tells a bidder how much to bid based on the item's valuation, as well as the number and type of other bidders. The optimal bidding strategy maximises the bidder's expected payoff (The difference between the item's value and the price paid).
Game Theory in Negotiations and Bargaining
By analysing the interactions between parties, game theory can help identify effective bargaining strategies and predict potential negotiation outcomes. By adapting game theory strategies to a specific negotiation context, parties can spotlight opportunities for mutually beneficial agreements rather than engaging in risky win-loose scenarios.
Hone your skills of collecting and analysing historical data for financial information in our Financial Modelling and Forecasting Training - Sign up now!
Famous Game Theory Examples
The following widely-regarded examples of game theory illustrate the significance of this framework in analysing and predicting human behaviour and strategic outcomes.
The Prisoner's Dilemma
In this well-known example of game theory, the prisoner's dilemma involves two arrested criminals. Prosecutors have no concrete evidence to convict them, and to get a confession, officials question the prisoners in separate chambers. The prisoners don't have the means to communicate with each other and the officials present four deals (often displayed as a 2 x 2 box). The results are summarised in the following table:
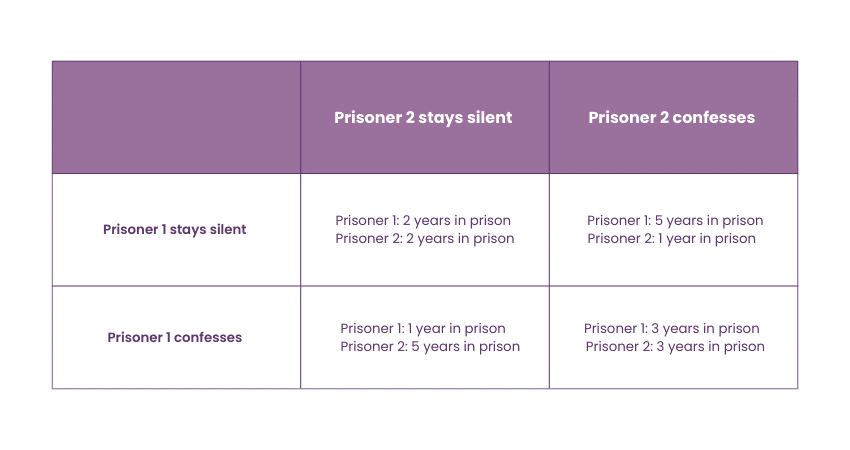
Since neither is aware of the other's strategy (and there's no certainty that one won't confess), both are likely to confess and receive a three-year prison sentence. The Nash equilibrium suggests that in this scenario, both players will make the move that's individually best for them but worse for them collectively.
The Dictator Game
This is a simple game involving one player deciding how to split a cash prize with another player who has no input in the decision. This provides fascinating insights into people’s behaviour. Experiments reveal that about 50% of people keep all the money to themselves, 5% split it equally, and the remaining 45% give the other player a smaller share.
The Volunteer's Dilemma
In a volunteer’s dilemma, someone undertakes a job for the common good. The worst possible outcome is realised if nobody volunteers. For example, consider an organisation where accounting fraud is rampant and top management is unaware of it.
Let's say some junior employees in the IT department are aware of the fraud. But they are hesitant to tell top management because they fear the employees involved in the fraud will be fired and prosecuted. Being labelled a whistleblower may have repercussions, but if nobody volunteers, the large-scale fraud can lead to the company’s bankruptcy and loss of everyone’s jobs.
The Centipede Game
The centipede game involves two players who alternately take the bigger share of a slowly increasing money stash. It's arranged so that if a player passes the stash to their opponent, the player receives a smaller amount compared to if they had taken the pot.
The game terminates as soon as a player takes the stash, with the player getting the more significant portion and the other getting the smaller portion. The total number of rounds is pre-defined, and each player knows it in advance.
Benefits and Limitations of Game Theory in Economics
Game theory is a powerful tool that revolutionised the field of Economics, offering several benefits as well as some limitations. Let's explore its benefits and drawbacks in detail:
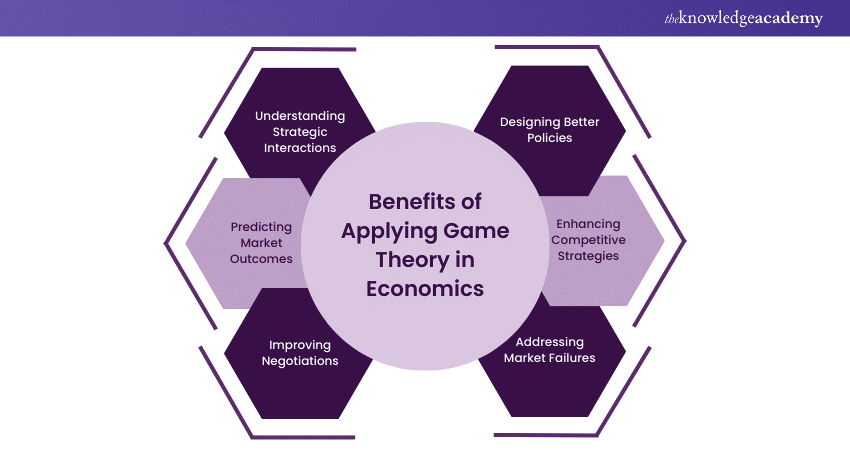
Benefits of Applying Game Theory
Game theory offers several benefits including the following:
a) Modelling Complex Interactions: Game theory helps economists model and analyse strategic interactions between agents, including consumers, firms, and governments.
b) Predicting Strategic Behaviour: It offers insights into the behaviour of rational agents in competitive situations. This helps predict outcomes in negotiations and markets.
c) Informing Decision-Making: Game theory can help decision-makers understand potential strategies and their payoffs. This helps them make informed choices and optimise strategies to achieve better outcomes.
d) Analysing Risk and Uncertainty: Game theory enables the consideration of various scenarios and the impact of different variables, aiding in processes such as risk assessment and management.
Criticisms and Limitations in Economic Contexts
Game theory comes with a significant baggage of limitations including the following:
a) Assumption of Rationality: Game theory often assumes that every player is rational and has complete information, which may not always be true in real-world scenarios.
b) Complexity of Real-world Applications: Real-life situations can display far greater complexity than the models used in game theory, making it a challenge to apply theoretical results directly.
c) Multiple Equilibria: Many games have multiple equilibrium states, making it difficult to predict which one will occur.
d) Limited Predictive Power: While game theory can suggest possible outcomes, it often fails to accurately predict human behaviour, especially in situations involving irrational decisions or emotions.
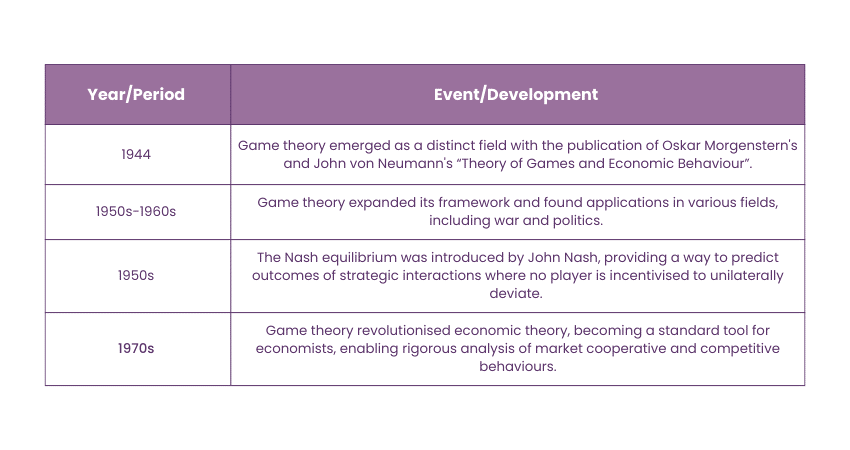
Historical Background of Game Theory in Economics
Here’s a summary of game theory’s history:
Conclusion
In conclusion, game theory is a powerful lens through which economists can analyse strategic interactions in diverse contexts. Through a firm grasp of the dynamics of decision-making, economists can devise more effective strategies, policies, and interventions to navigate the intricacies of the economic landscape.
Master advanced financial modelling and quantitative risk assessment with our comprehensive Quantitative Finance Course – Sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions

Decision theory analyses individual decision-making in scenarios where an the choice of one individual neither affects nor is affected by the choices of others. On the other hand, game theory studies decision-making in situations where individuals' choices affect each other.

Traditional game theory goes with the assumption that individuals are perfectly rational. Conversely, behavioural game theory acknowledges that human behaviour deviates from perfect rationality due to social preferences, psychological factors, and bounded rationality.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Management Courses, including Costing and Pricing Training and the Business Sustainability Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into What is Revenue Management.
Our Business Skills Blogs cover a range of topics related to Economics, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your expertise on Economics, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Economics for Managers Course
Economics for Managers Course
Fri 13th Dec 2024
Fri 10th Jan 2025
Fri 14th Mar 2025
Fri 9th May 2025
Fri 11th Jul 2025
Fri 12th Sep 2025
Fri 14th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


