We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +353 12338944 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Welcome to the world of ITIL Service Management (ITIL), isn’t just another tech keyword —it’s a robust framework that transforms how modern businesses navigate the complex IT landscape. Imagine it as a GPS for your IT services, guiding you through the twists and turns of service strategy, transition, design, operation, and continual improvement.
This blog delves into the concept of ITIL Service Management in detail, unravelling its essential elements, importance, and job roles. Read on and learn how it's the secret sauce turns your IT department from a chaotic jumble of networks and cables into a well-oiled machine.
Table of Contents
1) What is Service Management in ITIL?
2) Importance of ITIL Service Management
3) What is ITIL Service Lifecycle?
4) How is Service Management Helpful in ITIL?
5) What are the Roles Within Service Management for ITIL?
6) How does Governance Relate to Management of Services?
7) Conclusion
What is ITIL Service Management?
Information Technology Service Management (ITSM) is a concept of the Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL). It comprises various cycles of designing, managing, delivering and improving IT services for end customers. The internal or external IT service provider works with organisations, taking responsibility for the associated costs and risks.
ITSM is based on a set of key principles and concepts that together make up a cultural mindset to ensure that the desired objectives of the business are achieved. It involves processes and practices from various management approaches, including Lean manufacturing, organisational change management, ITIL Change Management, system analysis, and risk management.
Therefore, ITIL Service Management enables organisations to maximise business value using Information Technology. As a result, ITSM has become one of the most widely recognised bodies of knowledge.
Importance of ITIL Service Management
ITIL Service Management is important for several reasons. We explore the some of these reasons below:
a) It provides a comprehensive and flexible framework that helps organisations in effective IT Service Management.
b) It emphasises the importance of swift product delivery to customers.
c) It helps organisations understand the importance of continuous collaboration and good liaison between different parts of the organisation.
d) It helps in aligning customer needs with expectations and helps organisations to improve customer service and maintain customer loyalty.
e) It provides easy and flexible methods for organisations that can be personalised to modern business environments.
f) It helps organisations to identify and then address the gaps that exist in service delivery.
g) ITIL Service Management helps in reducing miscommunication and improves the alignment of different stakeholders in an organisation.
h) It reduces costs by enhancing the service delivery process.
i) ITIL Service Management plays a huge role in managing and mitigating different risks, for example, Incident Management, problem management, service utility management, etc. This helps organisations minimise the impact of disruptions on service delivery and ensure that business operations are continuing without any disruption.
j) ITIL Service Management monitors services over time so that they can be improved. This helps organisations adapt to constant changes in customer needs and innovate new services adapted to the dynamic market.
Gain in-depth knowledge of the IT Service Management system with our Certified IT Service Manager (CITSM) Certification Course – join today!
What is ITIL Service Lifecycle?
The delivery of a product or service entirely depends upon the lifecycle of ITIL Service Management. The Lifecycle in ITSM comprises various stages to effectively launch and maintain products and services for the end consumer. Therefore, it is vital to follow each stage and principle of the ITIL Service Lifecycle.
The stages in the ITSM Lifecycle are centred around a common goal and make together a cross-functional system for providing consistent and quality IT services. These stages of the ITIL Service Management Lifecycle are as follows:
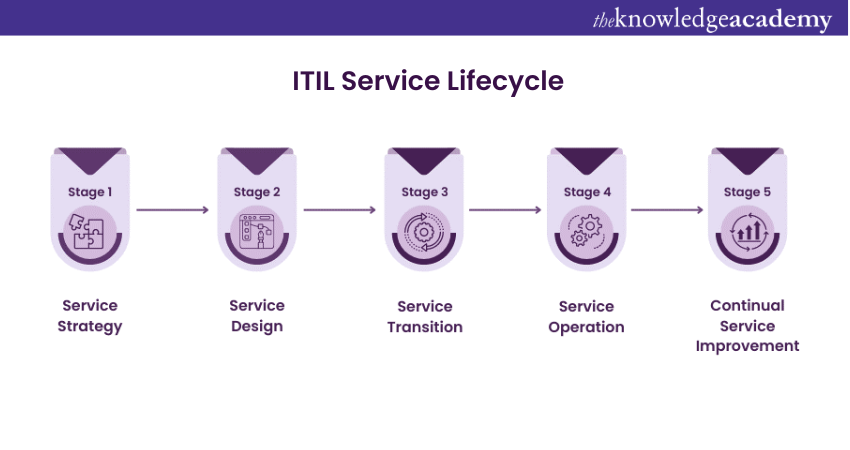
1) Service Strategy
The service strategy stage is the first and core stage of the ITSM Lifecycle. The creation of service begins at this stage, listing the steps to be followed and outlining business goals and customer requirements. While outlining the business goals, one must ensure that the services are aligned with the organisation’s goals. This stage involves the following processes:
a) Strategy Management for IT service
b) Financial Management
c) Service Portfolio Management
d) Demand Management
e) Business Relationship Management
Service Design
Service design is the stage to plan and design new or improved IT services and convert them into actionable items. It helps organisations achieve business vision and strategy. The following are the key activities involved in this stage:
a) Design Coordination
b) Service-level Management
c) Supplier management processes
d) Availability management
e) IT Continuity management
f) Information Security Management
g) Service Catalogue Management
h) Supplier Management
Learn IT Service Management as a key strategic capability with our ITIL Certification Training now!
Service Transition
The new services designed and planned in the Service Design stage are built, tested, implemented, proved and transferred to operate in this stage. The Transition stage is crucial since the plan and design are finally executed here. The primary focus in this stage is to manage the following:
a) Service Assets and Configuration
b) Transition planning and support
c) Change Management
d) Validation and testing evaluation
f) Deployment management
4) Service Operations
The fourth stage of the ITSM Lifecycle is called service operations. Here, the services designed in earlier stages are placed in live environments for the end-user to utilise. This is the stage where the created services are finally tested to see if they meet the user's requirements. The Service Operations stage comprises the following processes:
a) Incident Management
b) Problem Management
c) Access Management
d) Event Management
e) Request Management
f) Service Desk
g) Technical Management
h) Application Management
i) IT Operations Management
5) Continual Service Improvement (CSI)
The last stage of the ITSM Lifecycle is one of the protector stages in the ITSM Lifecycle. Effectively using processes in the CSI stage can help deliver long-lasting services in the market. It involves bringing all four stages of the lifecycle together to examine and identify the successes and areas of improvement in these stages. This is done by implementing enhancement plans to identify the key areas of pain and mitigate them to improve the efficiency of IT services. The CSI stage includes a seven-step process, which is as follows:
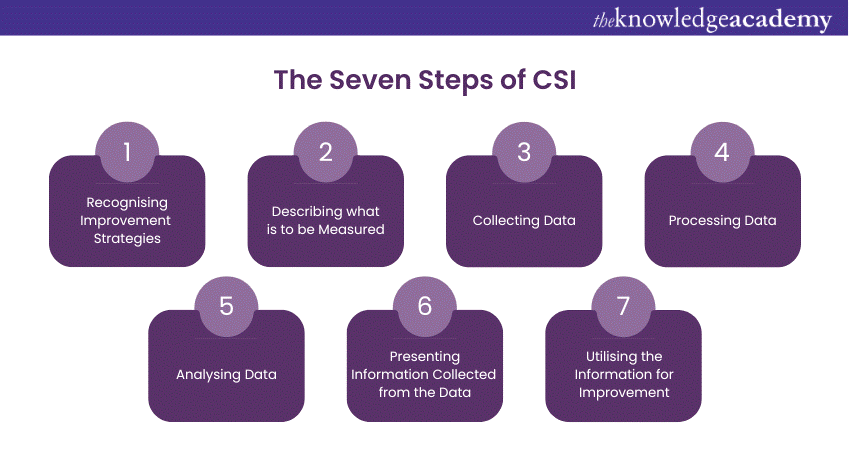
a) Recognising improvement Strategies
b) Describing what is to be Measured
c) Collecting Data
d) Processing Data
e) Analysing Data
f) Presenting information Collected from the data
g) Utilising the Information for Improvement
Get a practical understanding of how to run IT-enabled services, teams, and workflows with our Complete ITIL 4 Managing Professional (MP) Certification Path Course now!
How is Service Management Helpful in ITIL?
Understanding the role of Service Management in ITIL is crucial for effective IT service delivery. Service Management is a key component within ITIL, it plays a significant role in ensuring the successful implementation of service management practices. Therefore, implementing ITSM effectively can prove helpful in various ways. Some of are a few ways Service Management can help you:
a) ITSM uses superior expertise in providing services to enhance customer experience
b) It provides improved IT services using best practices and processes
c) Increases Return on Investment (ROI) from IT services
d) Improves service delivery quality using ITIL processes
e) Encourages IT staff competence, skills, and productivity
f) Cut shorts spendings on training
g) Decreases useless spending by providing visibility into costs and assets
h) Minimises business threats, bottlenecks, and failures
i) Provides enhanced services to the end consumer, thus building long-lasting customer relationship
j) Enhanced utilisation of resources by eliminating redundant and repetitive tasks
Learn about various guiding principles of ITIL in Digital and IT strategy with our ITIL 4 Leader: Digital and IT Strategy DITS Course now!
What are the Roles Within Service Management for ITIL?
There are various roles in the ITIL Framework including the following:
1) Process Owner
A Process Owner oversees designing, implementing, and managing a specific ITIL process for an organisation. A Process Owner must make sure that the process is effective and efficient, and that it satisfies the needs of its users and the organisation’s overall aims and objectives. The Process Owner’s responsibilities include:
a) Setting the process Scope, Objectives, and Performance Measures: The Process Owner must specify the boundaries, goals, and indicators of the process and how to measure its success.
b) Creating and Applying Process Policies and Procedures: The Process Owner must establish and enforce the rules and guidelines that regulate the framework implementation process, and make sure they follow industry standards and the organisation’s overall aims and objectives.
c) Tracking and Reporting on Process Performance: The Process Owner must keep an eye on how the process is performing, find areas for improvement, and report on process performance to senior management and other stakeholders.
2) Process Manager
A Process Manager oversees running and improving a specific ITIL process for an organisation.
They must ensure that the process works well and efficiently, and that it satisfies the needs of its users and the organisation’s overall aims and objectives. The Process Manager’s responsibilities include:
a) Applying Process Policies and Procedures: The Process Manager must apply the rules and guidelines that regulate the process, and make sure they follow industry standards and the organisation’s overall aims and objectives.
b) Tracking Process Performance: The Process Manager must track how the process is performing, using measures and indicators to find areas for improvement.
c) Finding and Managing Process Risks: The Process Manager must find and manage process risks, ensuring that suitable controls are in place to reduce them.
d) Checking Process Compliance: The process manager must check that the process is compliant with relevant laws, regulations, and standards, such as ISO 20000 and ITIL.
3) Process Practitioner
A Process Practitioner should make sure that the process is done right and efficiently, and that it satisfies the needs of its users and the organisation’s overall aims and objectives. The Process Practitioner’s responsibilities include:
a) Adhering to Process Policies and Procedures: The Process Practitioner needs to adhere to the rules and guidelines that regulate the process, ensuring that they are done correctly and on time.
b) Carrying out Process Activities: The Process Practitioner should carry out the activities that constitute the process, ensuring that they are done well and effectively.
c) Raising Issues and Exceptions: The Process Practitioner should raise issues and exceptions to the process manager or other relevant stakeholders, when needed.
d) Giving Feedback on Process Performance: They need to give feedback on how the process is performing, identifying areas for improvement and proposing changes that could be made to improve its effectiveness and efficiency.
How does Governance Relate to Management of Services?
Governance is an essential element of the ITIL 4 Service Value System, encompassing controls, management, and processes. It ensures responsible and effective use of an organisation's resources to achieve its goals and objectives.
Governance establishes a framework for decision-making, accountability, and responsibility throughout an organisation. It offers guidance on resource allocation, risk management, and performance measurement.
ITIL 4 defines three primary types of governance:
a) Corporate Governance: Corporate Governance involves the management, controls, and processes used to direct and manage an organisation's overall performance. It includes defining strategic objectives, ensuring compliance and managing risk.
b) IT Governance: IT Governance ensures that IT resources are utilised effectively to meet the organisation's goals and objectives. It covers managing IT investments, risks, and compliance, as well as aligning IT with the organisation's overarching goals.
c) Service Governance: Service Governance ensures that services are delivered effectively and efficiently to meet the expectations of customers and stakeholders. It includes managing service performance, risk, and compliance, and aligning services with the organisation's overall strategy.
Conclusion
ITIL Service Management is helpful for IT organisations as it helps yield efficient outcomes if implemented effectively. It is an amalgamation of various principles, concepts, and processes that together ensure quality delivery of services and help the organisation achieve the predetermined objectives. It is the reason why businesses are extensively adopting and implementing ITSM in their enterprise environments.
Gain in-depth knowledge of using a value stream to design, develop and transition new services. Register for our ITIL® 4 Specialist: Create Deliver And Support Certification Course now!
Frequently Asked Questions

ITIL Service Management plays a crucial role in minimising downtime and service disruptions by establishing standardised processes for incident management, problem resolution, and Change Management. These practices ensure quick restoration of services and proactive identification of potential issues, leading to improved reliability and continuity of IT services.

IT Service Management (ITSM) in ITIL enhances the overall customer experience by streamlining service delivery processes, ensuring timely response to issues, and maintaining high service quality. It focuses on understanding customer needs, providing effective communication, and continuously improving services, leading to increased customer satisfaction and trust in IT services.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

Discover an array of ITIL Certification Courses, including the ITIL® 4 Specialist: Drive Stakeholder Value Course and ITIL® 4 Specialist: IT Asset Management Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into ITIL 4 Guiding Principles.
Our IT Service Management Blogs cover a range of topics related to ITIL, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your ITIL proficiency, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming IT Service Management Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 ITIL® 4 Foundation Certification Course
ITIL® 4 Foundation Certification Course
Thu 1st Jan 1970







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


