We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Effective management is essential for an organisation’s success, where a significant contributing factor is the selection of a Management Model. The model must be best suited to the organisation’s business requirements.
More importantly, the choice selection of a model helps them tackle challenges, foster growth, and optimise their business performance. The Management Model is a framework that guides decision-making, planning, & resource allocation for businesses to help them achieve their goals efficiently. Read more.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding what is a Management Model
2) Importance of a Management Model
3) Exploring the various types of Management Models
a) Kurt Lewin’s Change Management Model
b) Situational leadership Model
c) Bridges Transition Model
d) SMART Management Model
e) Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
f) PDCA Management Model
4) Conclusion
Understanding what is a Management Model
A Management Model is a structured and comprehensive framework that guides organisations in effectively managing their resources, operations, and people. It serves as a strategic blueprint, providing clear direction for decision-making and setting goals. This essential tool enables businesses to navigate the complexities of the modern business landscape with efficiency and confidence.
Additionally, the model encompasses various processes, practices, and methodologies that support organisational success. It contains the defined roles and responsibilities of different stakeholders, outlines communication channels, and sets performance metrics. By doing so, it fosters a cohesive and unified approach, ensuring all team members are aligned with the organisation's objectives.
Furthermore, a key advantage of the Model lies in its ability to promote consistency and standardisation across diverse functions. It streamlines operations, reduces redundancies, and enhances overall productivity. Moreover, a well-developed Model encourages adaptability, enabling organisations to respond promptly to evolving market dynamics and emerging challenges.
Now, the Model is a solution that is customisable according to the specific needs of an organisation. Businesses can continually refine and update their Management Model to stay relevant, agile and resilient, especially in times of uncertainty. Organisations are thereby empowered to achieve their goals with optimal efficiency.
Importance of a Management Model
Managing an organisation effectively is a complex task that requires a structured approach. A well-defined Model plays a pivotal role in ensuring the smooth functioning and success of an organisation. Let's explore the importance of this Model in an organisation through the following six key points:
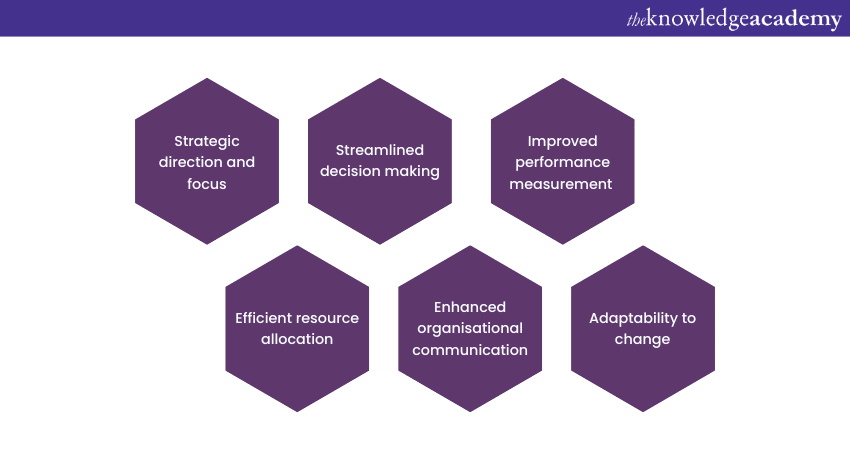
Strategic direction and focus
A Management Model provides a clear strategic direction for the organisation. It outlines the mission, vision, and long-term objectives, helping all stakeholders align their efforts towards common goals. With a focused approach, the organisation can avoid distractions and work towards achieving its mission.
Efficient resource allocation
A Management Model also facilitates efficient resource allocation. It identifies the critical areas that require investment and optimises the allocation of financial, human, and technological resources. The optimisation thereby ensures that resources are utilised effectively to maximise productivity and minimise wastage.
Streamlined decision making
Numerous decisions are made daily in any organisation. The model establishes a systematic decision-making process, providing guidelines for evaluating options and choosing the most viable solutions. This minimises ambiguity and enhances the speed and accuracy of decision-making.
Enhanced organisational communication
Clear communication is vital for a well-functioning organisation. The model defines communication channels, ensuring a seamless flow of information between different departments and hierarchical levels. Effective communication fosters collaboration and teamwork.
Improved performance measurement
Measuring performance is essential to track progress and identify areas for improvement. A Management Model sets Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and performance targets, enabling the organisation to gauge its success and make data-driven decisions.
Adaptability to change
Adaptability is of absolute essence in the current business climate. A Management Model promotes flexibility, allowing the organisation to respond swiftly to market changes, technological advancements, and other external factors. This adaptability enhances the organisation's resilience and competitiveness.
Run your operations effectively, by signing up for our Introduction to Management course now!
Exploring the various types of Management Models
There are seven common Management Models that demonstrate the chain of command in an organisation. The models help recognise the responsibilities and management of efficient team workflow. Here is a list that explains the various models of Management to help you select the one that best fulfils your business needs:

Kurt Lewin’s Change Management Model
Kurt Lewin's change model basically emphasises the importance of creating a supportive environment for change and involves the active involvement of employees throughout the process. The model comprises three key stages, described as follows:
a) Unfreeze stage: The first step involves preparing the organisation for change by creating awareness about the need for change. This is done by breaking down existing mindsets and attitudes that resist change.
b) Transition stage: In this phase, the actual change is implemented. It involves introducing new processes, systems, or structures to replace the old ones. This may lead to uncertainty and resistance, requiring strong leadership and support.
c) Refreeze stage: Once the change has been implemented, this stage aims to stabilise the new processes and ensure they become the new norm. It involves reinforcing the change through proper training, support, and rewards.
Situational leadership Model
The situational leadership Model emphasises the importance of flexibility and responsiveness in leadership. Here are the four key aspects of this model, explained as follows:
a) Adaptable leadership style: The situational leadership Model, developed by Paul Hersey and Ken Blanchard, focuses on the leader's ability to adapt their leadership style based on the readiness level of their followers.
b) Four leadership styles: The model identifies four leadership styles - directing, coaching, supporting, and delegating - each suited for different levels of follower readiness.
c) Directing: Used when followers have low readiness, the leader provides clear instructions and closely supervises tasks.
d) Coaching: Applied when followers' readiness improves, the leader continues to provide guidance and support, encouraging skill development.
e) Supporting: When followers reach moderate to high readiness, the leader becomes more supportive, offering encouragement and involvement.
f) Delegating: For highly ready followers, the leader takes a hands-off approach, giving autonomy and responsibility.
g) Readiness levels: Readiness is determined by the follower's ability and willingness to perform tasks, requiring the leader to assess and adjust their leadership style accordingly.
Adapt, delegate and motivate your team, by signing up for our Leadership Training courses now!
Bridges transition Model
The Bridges transition Management Model provides valuable insights for leaders to support their teams. Here are the six key aspects of the model, explained in detail as follows:
a) Understanding transitions: Developed by William Bridges, this model focuses on managing transitions during times of change. It differentiates between change (external events) and transition (internal psychological process).
b) Three stages of transition: The model consists of three stages, namely ‘Ending’, ‘Neutral zone’, and ‘New beginning’. Each of these stages requires different approaches from leaders and organisations. Here are the stages described briefly as follows:
i) Ending: In this stage, individuals must acknowledge and let go of the old ways, which can be emotionally challenging. Leaders must provide support and communication to help people navigate through loss and uncertainty.
ii) Neutral zone: The Neutral Zone is a period of ambiguity and discomfort, where the old is gone, but the new is not yet fully established. Leaders should encourage experimentation and innovation during this phase.
Iii) New beginning: In the third and final stage, individuals begin to embrace the new reality and find their place in it. Leaders should celebrate successes and reinforce the benefits of the change.
The Bridges Management Model basically emphasises that successful change depends on effectively managing the psychological and emotional aspects of transition that individuals experience during times of change.
SMART Management Model
The SMART Management Model is a powerful tool for organisations to set and achieve meaningful goals. Here are the seven key aspects of the SMART Model, described as follows:
a) Specific goals: The SMART model emphasises setting specific and well-defined goals that are clear and concise. This ensures a focused and unambiguous direction for the organisation.
b) Measurable objectives: Goals must be measurable, allowing progress to be tracked and evaluated effectively. Measurable objectives provide tangible evidence of success and help in identifying areas for improvement.
c) Achievable targets: The SMART model encourages setting challenging yet attainable goals. It ensures that goals are realistic and within the organisation's capabilities, preventing frustration and demotivation.
d) Relevant to the mission: Goals should align with the organisation's mission and vision. They must contribute to the overall strategic direction and add value to the organisation's growth.
e) Time-bound deadlines: Setting specific time frames for achieving goals adds a sense of urgency and accountability. Time-bound deadlines motivate teams to work efficiently and meet targets.
f) Flexibility and adaptability: The SMART model recognises the importance of flexibility in adjusting goals based on changing circumstances or new information. +
g) Clear communication: Effective communication of SMART goals to all stakeholders ensures everyone is on the same page and working towards the same objectives.
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Abraham Maslow's ‘Hierarchy of Needs’ Management Model highlights the significance of understanding and addressing individual needs for motivation and development in the workplace. The model comprises five key levels, which are described in the list below as follows:
a) Physiological needs: The foundational level includes basic necessities like food, water, shelter, and sleep. These must be met for survival and form the base of the pyramid.
b) Safety needs: Once physiological needs are satisfied, individuals seek safety and security in their environment, including employment, health, and protection from harm.
c) Love/Belonging needs: The third level involves the need for love, affection, and a sense of belongingness to family, friends, or community.
d) Esteem needs: The fourth level focuses on the need for recognition, respect, and self-esteem. It includes achievements and recognition from others.
e) Self-actualisation: At the peak of the pyramid, individuals strive for personal growth, realising their full potential and fulfilling their unique purpose.
f) Motivation and growth: The model suggests that as lower-level needs are met, individuals are motivated to pursue higher-level needs, leading to personal growth and self-improvement.
Plan, lead, monitor and set goals to accomplish tasks successfully, by signing up for our Introduction to Management course now!
PDCA Management Model
The PDCA (‘Plan’,’ Do’,’ Check’,’ Act’) Management Model is a continuous approach to improvement utilised in management and quality control procedures. It is segregated into four key stages, which are explained below as follows:
a) Plan: The first stage involves identifying the problem, setting objectives, and developing a detailed plan to achieve those goals. The procedure includes analysing the data, forecasting potential challenges, and formulating strategies for improvement.
b) Do: The second involves putting the plan into action and implementing the proposed changes on a small scale or as a pilot project. These two measures allow for testing and assessing the effectiveness of the proposed solutions.
c) Check: Once the changes are implemented, data is then collected and analysed to evaluate the outcomes. The third stage involves measuring performance against the set objectives and comparing the results with the expected improvements.
d) Act: Based on the evaluation in the previous ‘Check" stage, necessary adjustments and refinements are made to the plan. Lessons learned are then incorporated into a revised plan, which is then implemented on a larger scale. The cycle continues, promoting ongoing improvement and optimisation.
Conclusion
The Management Model principles discussed include ‘SMART’ goal-setting, situational leadership, ‘Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs’, PDCA’s continuous improvement, and Bridges transition management. These models offer valuable insights for effective organisational management. The implementation of these models can lead to enhanced performance, adaptability, and success for businesses.
Unlock your leadership potential, by signing up for our Management Courses courses now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Introduction to Management
Introduction to Management
Fri 18th Oct 2024
Fri 22nd Nov 2024
Fri 20th Dec 2024
Fri 14th Feb 2025
Fri 11th Apr 2025
Fri 13th Jun 2025
Fri 8th Aug 2025
Fri 10th Oct 2025
Fri 12th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


