We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +39 800580270 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

A business plan is often a terminology referred to by aspiring entrepreneurs on account of a vision for their venture. This document acts in a similar fashion to that of a plan of a housing project. As mentioned, a business plan acts as a roadmap for the business enumerating parameters such as market analysis, financial projections, and organisational structure.
Table of Contents
1) What is a Business Plan?
2) Why is a Business Plan Important?
3) Why Should I Write a Business Plan?
4) What to Consider When Writing a Business Plan?
5) Steps to Write a Business Plan
6) Business Plan Types
7) Tips for Writing a Business Plan
8) Conclusion
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan encompasses the core objectives of an organisation and strategies to achieve the same. It is a crucial document to any organisation regardless of its size and nature. For startups, a well-formulated business plan is essential for attracting potential investors. Whereas established entities apply business plans to be in a loop with the company’s objectives. Banks and lending firms typically rely on a business plan which is often presented in pitch decks for providing capital.
Business Plans are reviewed periodically to review and evaluate it’s alignment with the company’s recent goals and objectives.
Why is a Business Plan Important?
A well-written Business Plan is the first step in starting a new venture and a vital document for attracting investors. It helps them assess the business's potential and decide if it's worth their investment.
Typically, Business Plans include detailed information that can enhance the chances of success, such as:
a) Market Analysis: Gathering data on factors and conditions affecting the industry.
b) Competitive Analysis: Assessing the strengths and weaknesses of competitors.
c) Customer Segmentation: Dividing customers into groups based on specific characteristics to improve marketing.
d) Marketing Strategies: Using research to promote the business effectively.
e) Logistics And Operations Plans: Planning and executing efficient production processes.
f) Cash Flow Projections: Preparing for the inflow and outflow of money.
g) Long-term Growth Path: Establishing an overall strategy for sustained growth.
Why Should I Write a Business Plan?
Writing a Business Plan is essential for several reasons, from clarifying your Business Idea to securing funding. Here are some key benefits:
a) Clarify Your Business Idea
Creating a Business Plan helps you refine and strengthen your initial concept, providing a detailed and robust proposition. It also offers a detailed overview of your needs and the required funding.
b) Set Out Your Goals
Drafting a Business Plan encourages you to set tangible goals for different growth stages. Your objectives for the first year will differ from those for the fifth year, and a Business Plan helps you engage with both short- and long-term targets.
c) Spot Potential Problems
A well-crafted Business Plan sharpens ideas, sets goals, and helps identify potential issues that may have been apparent with thorough research.
d) Measure Your Progress
A Business Plan is a starting point, providing targets to measure your progress. These benchmarks help evaluate your organisation’s development at various stages.
e) Secure Funding
A Business Plan is crucial if you need a Business Loan or Credit. Investors and banks will want to see it before committing funds. It can also help convince suppliers, customers, and employees to support your venture.
What to Consider When Writing a Business Plan?
When writing a Business Plan, you must consider the following essential steps:
Step 1: Understand Your Target Market
Begin by identifying your target market. Ask yourself questions like- Who are your potential customers? What are their needs? How will your product or service meet these needs? Conduct thorough market research and include this data in your plan to ensure it is tailored for your audience.
Step 2: Define Your Business Goals
Clearly outline your business goals. What do you aim to achieve in the next year, five or ten years? Setting clear, measurable objectives will guide your Business Plan and keep you focused on your long-term vision.
Step 3: Know Your USP
Determine your unique selling proposition (USP), which sets you apart from the competition. Highlighting your USP in your Business Plan will help you stand out and attract potential investors.
Steps to Write a Business Plan
Reviewing examples from your industry can be beneficial when creating a Business Plan. While there is no one-size-fits-all template, many Business Plans typically include the following elements:
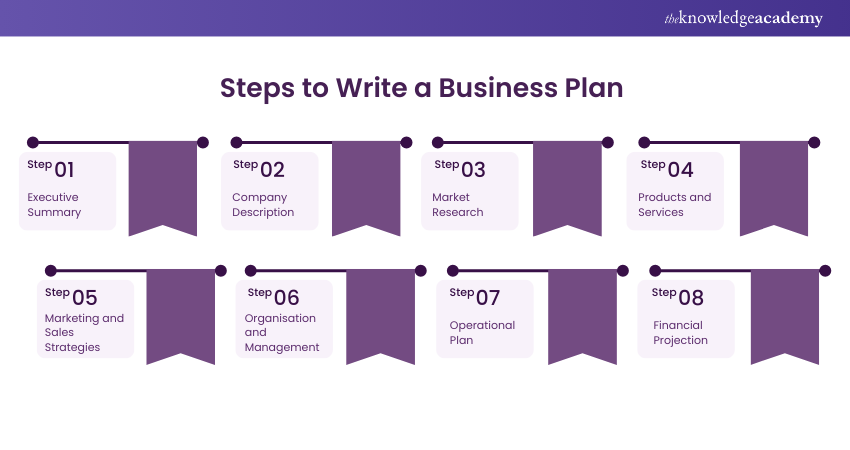
1) Executive Summary
Your Business Plan should begin with a concise summary highlighting the key points and making a solid first impression. This overview should be compelling enough to engage readers and encourage them to delve deeper into the plan.
2) Company Description
The Company Description provides an in-depth overview of your business’s identity and purpose, starting with a clear mission statement. It outlines the legal structure, industry landscape, market trends, and critical milestones, offering insights into your business’s history and cultural values.
3) Market Research
The Market Research section demands a comprehensive understanding of your industry, target market, and competitors. You should showcase your knowledge of market trends, customer needs, and the competitive landscape.
4) Products and Services
The Products and Services section highlights your offerings’ features and benefits, addressing the needs of your target audience. It emphasises your Unique Selling Proposition (USP) and illustrates the value customers can derive, helping them envision the practical impact on their lives.
5) Marketing and Sales Strategies
The Marketing and Sales Strategies section outlines your plan to attract customers and details your channels, such as social media or traditional advertising. It also highlights your pricing strategy and sales approach, demonstrating how you’ll convert leads into paying customers and showcasing your revenue generation potential.
Elevate your business acumen with our Business Administration Course - Sign up now!
6) Organisation and Management
The Organisation and Management section delves into the core of your team dynamics. It introduces key team members and outlines their roles, qualifications, and expertise. It also outlines the business structure, hierarchy, and responsibilities. Highlighting strong leadership and a competent team assures investors and partners that your business can navigate challenges and seize opportunities.
7) Operational Plan
The Operational Plan details daily business operations, covering production, inventory management, customer service, and quality control. It highlights supply chain relationships with suppliers and vendors and addresses the technology and facilities needed. A well-structured plan ensures efficient delivery of products or services, supporting seamless growth.
8) Financial Projection
The Financial Projection section outlines future financial performance, including revenue forecasts, expense estimates, and profit and loss projections. It demonstrates financial viability and an understanding of revenue streams and costs. This section also includes cash flow projections, which are essential for investors to assess ROI and long-term sustainability.
Business Plan Types
Business plans can vary in length and detail, from a single page to multiple pages with detailed graphs and reports. The key is to convey the most essential information about your company to the readers. Here are some common types of Business Plans:
Traditional Business Plans
These are the most common and detailed Business Plans that venture capitalists and lenders often require. They can be dozens of pages long and take considerable time to write. If you don’t plan to seek outside funding, a traditional Business Plan may not be necessary.
Lean Business Plans
A Lean Business Plan is a shorter version of a traditional plan, including only the most essential information. It helps onboard new hires or modify existing plans for specific target markets. A lean Business Plan is often sufficient for internal planning for small businesses starting out.
Tips for Writing a Business Plan
Creating a Business Plan is important if you are looking to start or expand your business. To ensure that your plan meets your objectives, follow these tips:
1) Have a Clear Goal
Before you start, define what you want to achieve with your Business Plan. Are you seeking funding, partners, customers, or employees? Your goal will shape your plan's structure, format, and focus. For instance, if you’re looking for investors, emphasise your market opportunity, competitive advantage, and financial projections. If recruiting talent, highlight your vision, values, and company culture.
2) Know Your Audience
Craft your Business Plan to cater to your target audience's needs and expectations. For potential investors, use a formal and professional tone, provide data and evidence to support your claims, and address their concerns. For potential customers, adopt a friendly and engaging tone, highlight your product's or service's benefits and features, and include testimonials and reviews to build credibility.
3) Do Your Research
A good Business Plan is based on thorough research and analysis.
1) Gather reliable information about your
a) Industry
b) Market
c) Competitors
d) Customers, and
e) Suppliers
2) Conduct a Strength, Weakness, Opportunity, Threat (SWOT) analysis.
This research will show your expertise, validate your assumptions, and help you identify and tackle risks.
Keep Things Concise and Consistent
Your Business Plan should be concise, to the point, and complete. Aim to avoid appendices and attachments. Maintain consistency in style, tone, format, and terminology. Use headings, subheadings, bullet points, tables, charts, and graphs to organise and present your information logically and aesthetically.
Check Your Spelling and Grammar
Spelling and grammar errors can undermine your credibility and professionalism. Proofread and edit your plan carefully or hire a professional editor or proofreader. Use spell check and grammar check tools to catch any missed mistakes.
Unlock your potential as a leader with our Business Development Training and pave the path to strategic growth and success!
Conclusion
A Business Plan is important for building a successful and sustainable venture. This strategic blueprint shows the essence of your business, guiding its journey from concept to realisation. A well-crafted Business Plan aligns your team and resources. It also helps communicate your vision to potential investors and partners. We hope we have answered all your questions about “How to Develop a Business Plan” with our blog!
Elevate your leadership potential with our Leadership Skills Training – Sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions

Writing a Business Plan demonstrates strategic thinking, organisational skills, and a deep understanding of market dynamics. It showcases your ability to plan for growth and manage resources effectively, making you a more attractive candidate for leadership roles.

When writing a Business Plan, include an executive summary, company description, market analysis, organisational structure, product line or services, marketing and sales strategies, funding request, financial projections, and an appendix. These elements ensure a comprehensive and effective plan.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Leadership Courses, including the Leadership Skills Course, Agile Leadership Training, and Design Thinking Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Innovative Thinking.
Our Business Skills Blogs cover a range of topics related to Leadership Skills, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Business Skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Business Development Training
Business Development Training
Fri 29th Nov 2024
Fri 21st Feb 2025
Fri 25th Apr 2025
Fri 20th Jun 2025
Fri 22nd Aug 2025
Fri 17th Oct 2025
Fri 19th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


