We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on + 1-866 272 8822 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Have you ever wondered What are Greenhouse Gases and what keeps our planet comfortably warm, allowing life to flourish? The secret lies in a group of atmospheric gases known as Greenhouse Gases (GHGs). These invisible protectors form a thermal blanket around Earth, trapping just the right amount of heat to sustain life. But there's a twist: the gases nurturing our existence are now driving the global crisis of climate change.
Are we doing enough to combat the rise in Greenhouse Gases? As we delve into this blog, we'll explore What are Greenhouse Gases, the major types of Greenhouse Gases, their sources, and their profound environmental effects. We'll explore strategies to reduce emissions and emphasise the importance of collective action to protect our future generations.
Table of Contents
1) What are Greenhouse Gases?
2) Major Greenhouse Gases
3) How to Reduce Greenhouse Gases?
4) What Human Activities Contribute to the Increase in Greenhouse Gases?
5) Are All Greenhouse Gases Equally Potent?
6) Conclusion
What are Greenhouse Gases?
Greenhouse Gases are components of the atmosphere that trap heat, keeping the Earth's surface warmer than it would be if these gases were not present. This natural phenomenon is known as the Greenhouse Effect. Without Greenhouse Gases, the Earth's average temperature would become extremely cold, making it difficult for life to thrive.
The primary Greenhouse Gases in Earth's atmosphere include water vapour, Carbon Dioxide (CO2), Methane (CH4), Nitrous Oxide (N2O), and Ozone (O3). These gases absorb Earth's infrared radiation and re-radiate it, warming the planet by directing heat back to the surface.
Which are the Primary Greenhouse Gases?
The primary Greenhouse Gases in Earth's atmosphere include:
1) Water vapour
2) Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
3) Methane (CH4)
4) Nitrous Oxide (N2O)
5) Ozone (O3)
These gases are explored in detail below
Major Greenhouse Gases
Understanding the key players in the Greenhouse Effect is essential to grasping how our climate is changing. Here are the major Greenhouse Gases driving this global phenomenon.
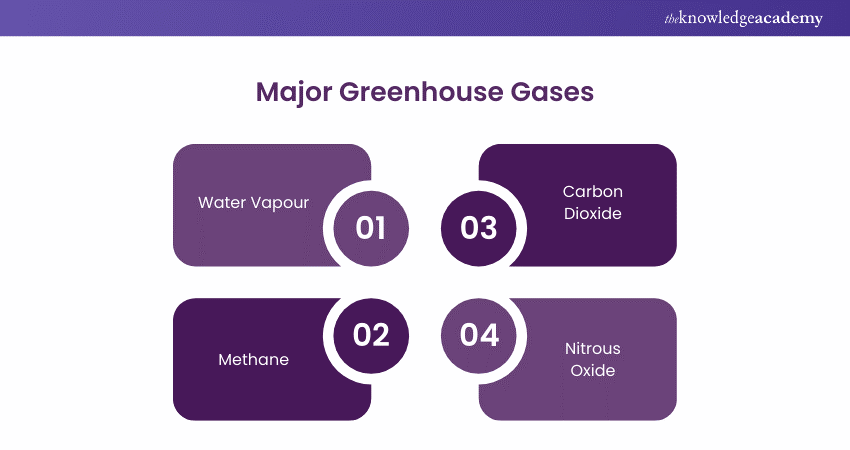
1) Water Vapour
The major constituent of Greenhouse Gases is water vapor which occurs autonomously through evaporation of water and transpiration of plants. It is important for the processes of natural greenhouse effect and reinforces increasing temperatures due to other artificial gases. As the climate gets warmer the humidity in the atmosphere increases that leads to an enhancement of global warming.
2) Carbon Dioxide
Greenhouse Gases, minimally water vapor and carbon dioxide, are hydrogen produced through activities which include burning of fossil fuel, deforestation, industrial processes as well as respiration. Currently, it accounts for a 20% percentage of the human initiated greenhouse effect and its effect on climate lasts centuries in the atmosphere.
3) Methane
Methane is much less plentiful than carbon dioxide, and although less stable, it is a much more powerful GHG with a much higher GWP for the shorter term. Among them, enteric fermentation by the cattle, the paddy fields, the landfill, and natural gas are notable sources of the emissions. Methane is much more effective in terms of heat capture over a period of 20 years compared to CO2, in fact the GWP is about 25 times more in the 100-year timescale.
4) Nitrous Oxide
Laughing gas or nitrous oxide is a very active greenhouse gas which sources include soil and other organic farming practices, synthetic fertilisers, processes and electricity production, burning of fossil and biomass. It has a GW potential of approximately 298 times that of CO2 over 100 years and depletes the ozone layer.
Start your ISO 14001 Foundation Certification Training today and enhance your Environmental Management skills!
How to Reduce Greenhouse Gases?
Emissions of Greenhouse Gases should be reduced in order to help minimise climate change. Below are some effective strategies and actions:

1) Renewable Energy Sources Saves Electricity
a) Use more natural sources of energy such as solar energy, wind energy, and hydro energy.
b) Maximise the efficiency of the generating power stations.
2) Enhance Energy Efficiency
a) Replace current appliances and utilities in homes and industries with energy-efficient equipment.
b) Increase insulation and use passive designs for heating and cooling in buildings.
3) Adopt Sustainable Transportation
a) It also called for the use of cleaner automobiles and has recommended that everyone should own an electric or a hybrid vehicle.
b) Another option is to better should encourage public transport, cycling and walking.
c) The Utilisation of fuel-efficient technologies for aerplanes, ships and other means of transport vehicles.
4) Improve Waste Management
a) Avoid wasting material, and where possible, reinforce the use of the principles of the 3Rs which are; recycle, reuse and recycle.
b) Methane can be captured and used from the landfills.
c) Another method is to ensile organic waste since composting is known to produce methane gas.
5) Support Sustainable Agriculture & Forestry
a) The best and most tested Agronomic practices include Agroforestry and No tillage farming with an aim of increasing the carbon stocks.
b) To reduce the emission of Greenhouse Gases and fund reforested programmes.
c) Diet formulation can also be used to minimise fresh content of methane through management of livestock diet and waste production.
The Impact of Climate Change on Agriculture necessitates a shift towards sustainable agricultural practices that enhance soil health, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and increase resilience to climate-related challenges.
6) Encourage Energy Conservation
a) Switch off lights and appliances when not needed.
b) Adjust temperature settings with the help of electronic boards known as programmable thermostats.
c) To yield results that foster positive energy behaviour change in households as well as business entities.
Transform with ISO 14097 - start your ISO 14097 Greenhouse Gas Management Training - sign up now!
What Human Activities Contribute to the Increase in Greenhouse Gases?
Human activities such as burning fossil fuels for energy, deforestation, industrial processes, and agriculture contribute to higher levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, particularly carbon dioxide and methane.
Are All Greenhouse Gases Equally Potent?
No, different greenhouse gases have varying levels of heat-trapping ability. For example, methane (CH₄) is much more effective at trapping heat than carbon dioxide (CO₂) over a shorter period, though CO₂ persists in the atmosphere much longer.
Conclusion
Understanding Greenhouse Gases is key to tackling climate change. By uncovering What are Greenhouse Gases, their roles and impacts and taking bold steps to reduce emissions, we can collectively fight the global climate crisis. Similarly, understanding the benefits of a Greenhouse can also contribute to sustainable agricultural practices by optimizing plant growth and reducing energy consumption. Let's unite in this mission for a sustainable future, making every effort count towards saving our planet. For those preparing for a role as a climate change analyst, reviewing Climate Change Analyst Interview Questions can help you deepen your understanding of these crucial topics and how they’re applied in real-world scenarios.
Master Environmental Management with expert ISO 14097 Training – join now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Which Greenhouse Gas is Most Affected by Human Activities?

The most affected greenhouse gas by human activities is carbon dioxide. Its levels have significantly increased due to burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes that drive climate change.
Do Greenhouse Gases Affect Climate?

Yes, Greenhouse Gases affect climate change by trapping heat in the Earth's atmosphere. This causes the Greenhouse Effect, altering weather patterns, increasing global temperatures, and contributing significantly to climate change.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various ISO 14097 Training, including ISO 14097 Greenhouse Gas Management Training. This course caters to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Environmental Aspects and Impacts Register.
Our Health & Safety Blogs cover a range of topics related to Greenhouse Effect, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Health and Safety skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Health & Safety Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 ISO 14097 Greenhouse Gas Management Training
ISO 14097 Greenhouse Gas Management Training
Fri 11th Apr 2025
Fri 13th Jun 2025
Fri 8th Aug 2025
Fri 26th Sep 2025
Fri 21st Nov 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


