We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +971 8000311193 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
As the world grows more connected, thanks to the ubiquitous hold of the internet, additional spaces are needed to accommodate the growing number of devices connected to the internet. Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6) emerged as the ideal answer to this challenge. Designed to replace IPv4, it offers an enormous address space, capable of easily supporting billions of devices. With smarter, faster, and more secure connections, IPv6 continues to shape the future of networking. This blog explores What is IPv6, outlining its benefits, drawbacks, key features, and more. So read on and be part of this continuing and exciting evolution in the realm of the internet!
Table of Contents
1) What is Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6)?
2) Different Types of IPv6 Address
3) How Does IPv6 Work?
4) Key Features of IPv6
5) Benefits of IPv6
6) Drawbacks of IPv6
7) How to Check if IPv6 is Enabled or not?
8) What are the Challenges of IPv6?
9) Conclusion
What Is IPv6 (Internet Protocol Version 6)?
IPv6 is the most recent iteration of the Internet Protocol devised by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). It identifies and localises endpoint systems within a computer network, directing online traffic. This is aimed at mitigating the issue of IPv4 address exhaustion resulting from prolonged global internet usage.
IPv6 Interview Questions often focus on how Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) operates as a network layer protocol facilitating communication across the network. Each internet-connected device possesses a unique IP address, enabling its identification and location. In the 1990s digital revolution, it became evident that the IP addresses employed by Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) to link devices would fall short of meeting escalating demand.
Consequently, the IETF embarked on developing the next generation of Internet Protocols. IPv6 achieved draft standard status for the IETF in December 1998, and on July 14, 2017, it gained approval as an internet standard for global implementation.
Different Types of IPv6 Address
The following are the different types of IPv6 addresses:

1) Unicast Addresses: It denotes a singular node within a network, typically signifying either a lone sender or receiver.
2) Multicast Addresses: It signifies a collective of IP devices and can solely serve as the designated destination for a datagram.
3) Anycast Addresses: It is allocated to a group of interfaces, typically associated with distinct nodes.
Want to master internet security in various domains? Our Online Internet Security Specialist Training will guide you - Register now!
How Does IPv6 Work?
The work of IPv6 relies on several key concepts such as IPv6 addresses, network and node addresses, IPv6 address types and scope and IPv6 loopback. Let’s explore them in detail:
1) Decoding IPv6 addresses
a) An IPv6 address consists of 128 bits. This is four times the size of an IPv4 address, which has 32 bits.
b) IPv6 addresses are expressed in hexadecimal format, unlike IPv4, which uses dotted decimal notation.
c) A full IPv6 address comprises 32 hexadecimal digits, with each digit representing 4 bits.
d) The address is organised into eight groups of four digits, separated by colons (e.g., group1:group2:group3:...group8).
e) IPv6 addresses can be abbreviated to simplify their representation.
f) Leading zeros in each group can be removed during abbreviation.
g) Consecutive segments of zeros can be replaced with two colons (::).
h) Abbreviation methods should be used sparingly to avoid ambiguity in interpreting the address.

Improve your networking skills with our Troubleshooting and Maintaining Cisco IP Networks Course - visit the link to join!
2) Network and Node Addresses in the IPv6 Landscape
a) In IPv4, address classes were originally used to divide an address into a network and node section, later replaced by subnet masking.
b) In IPv6, an address is split into two 64-bit portions: the network section (upper 64 bits) and the node section (lower 64 bits).
c) The upper 64-bit network segment is used for routing purposes.
d) The lower 64-bit node segment identifies the interface or node address.
e) The node section is generated from the physical or MAC address using the IEEE’s EUI-64 format.
f) The computer network component is further divided into two blocks:
i) 48 bits for internet routing and global network addresses.
ii) 16 bits for subnetting within an internal network, managed by a network administrator.

3) Navigating IPv6 Address Types and Their Scope
There are three categories of IPv6 addresses:
1) Global Unicast Addresses: These can be routed on the internet and commence with 2001:.
a) Routers convey network announcements to determine the prefix for international unicast addresses.
b) These prefixes are equivalent to IPv4 public addresses.
c) Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (SLAAC) requires a block of 64 addresses.
d) Internet authorities allocate address blocks to ISPs for distribution to their customers.
e) It is recommended to allocate more than one block of 64 addresses to home sites
2) Unique Local Addresses: Local addresses are intended for usage within an internal network, such as a local area network; these addresses are routable within the internal network but not on the Internet.
a) The address allocation space in IPv6 is divided into two /8 spaces:
i) fd00::/8 for globally assigned addresses.
ii) fc00::/8 for locally assigned addresses.
b) Organisations can manually configure addresses using the fd00::/8 prefix.
3) Link-local Addresses: These addresses are reserved for use within an internal network; these addresses are routable within the internal network but not on the internet.
a) Link-local addresses in IPv6 are analogous to the IPv4 address range 169.254.0.0/16, used in the absence of a DHCP server.
b) Link-local addresses in IPv6 begin with the prefix fe80.
c) Every IPv6 interface must have a link-local address configured, even if routing is not in use.
Master the basics of networking concepts by signing up for our Cisco Certified Network Professional Boot Camp Week 1 Course now!
4) Integrating IPv6 addresses into uniform resource locators
When utilising an IPv4 network, users can connect to a network resource like a webpage through HTTP://192.168.121/webpage. Webpages can also be reached via IPv6, albeit with a modification in the format. IPv6 addresses employ a colon as a separator and must be enclosed in square brackets.
5) Unveiling the Functionality of IPv6 Loopback
a) The loopback address corresponds to the same interface as the computer.
b) The TCP/IP protocol stack redirects packets back to the same interface in both IPv4 and IPv6.
c) In IPv4, the 127.0.0.0/8 network is reserved for loopback addresses.
d) In IPv6, the loopback address is 0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0001/128, simplified to ::1/128.
e) Routers in both IPv4 and IPv6 will not forward packets with an undefined address.
f) The unspecified address in IPv6 is ::/0.
Key Features of IPv6
IPv6 has been redesigned to address the limitations of its predecessor, IPv4, while retaining the core functionalities of Internet Protocol (IP) addressing. Below are the key features of IPv6 that make it a game-changer in internet communication:
1) Larger Address Space
The key eason for developing IPv6 was to offer a solution for the exhaustion of addresses in IPv4.
a) IPv6 uses four times more bits than IPv4 to address devices on the internet.
b) The extended address space supports approximately 3.4 x 10^38 unique devices.
c) IPv6 allows for around 1,564 addresses to be allocated per square meter of the planet.
d) The larger address space satisfies the growing demand for addressing almost everything globally.
e) With IPv6, address conservation techniques like Network Address Translation (NAT) become unnecessary.
2) End-to-end Connectivity
a) IPv6 ensures that every machine has a unique IP address.
b) Devices can traverse the internet without the need for Network Address Translation (NATs) or other translation mechanisms.
c) Once IPv6 is fully implemented, every host can directly communicate with other hosts on the internet.
d) Restrictions may still apply in the form of firewalls and organisational policies to maintain security and control.
Learn about Frame-Mode MPLS implementation on Cisco IOS platform in our comprehensive Cisco MPLS Training - Sign up now!
3) Smooth Transition
The transition from IPv4 to IPv6 is a critical step to ensure the sustained growth of the internet.
a) IPv6 provides an extensive address system for assigning universally unique IP addresses to devices.
b) This system enables devices to communicate seamlessly and receive data efficiently.
c) IPv6 features a lighter header, allowing routers to make quicker forwarding decisions.
4) Simplified Header
a) The IPv6 header features a simplified design for reduced complexity and easier processing compared to IPv4.
b) Optional and non-essential fields are moved to extension headers that follow the main IPv6 header.
c) Despite IPv6 addresses being four times larger than IPv4 addresses, the IPv6 header is only twice as large as the IPv4 header.
5) Stronger Security Through IPSec
a) IPv6 incorporates IP Security (IPSec) as a fundamental part of its design, unlike IPv4, which was optional.
b) Mandating IPSec ensures a higher level of security for data transmitted over the internet.
c) IPSec in IPv6 provides authentication, integrity, and confidentiality, enhancing the protocol's security posture.
d) IPSec operates at the network processing layer to secure the network effectively.
6) No Broadcast
a) IPv6 uses multicast addresses for communication with multiple hosts, as it does not support broadcast addresses.
b) Multicast addresses are used for one-to-many communication.
c) These addresses are allocated to a collection of interfaces across multiple nodes.
d) When IPv6 sends a payload to a multicast group, it is delivered to all interfaces associated with that address.
e) Multicast addresses in IPv6 begin with ""FF"", making them easily identifiable.
Master IPv6 Networking – Download the CCNA IPv6 PDF and enhance your networking skills today!
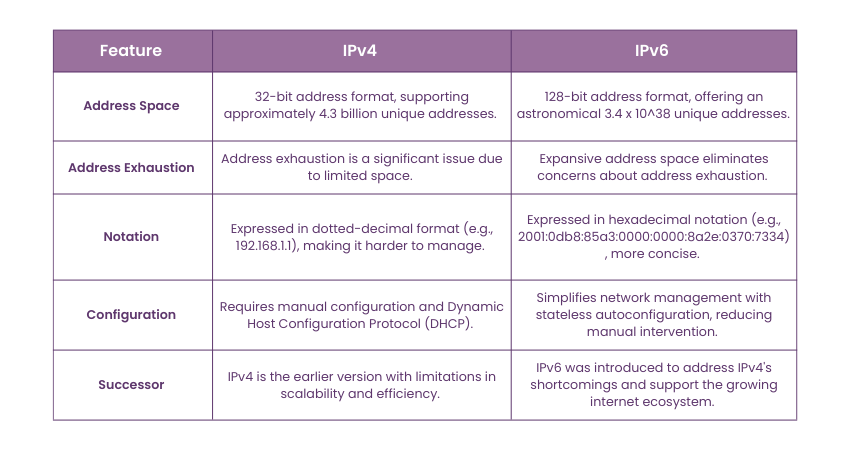
Differences Between IPv4 and IPv6
IPv4 is the Internet Protocol's fourth version, serving as the workhorse of Internet communication for decades. However, as technology advances and the demand for unique IP addresses skyrockets, IPv4 reveals its limitations. This is where the Advantages of IPv6 Over IPv4 become clear, addressing the growing need for more efficient and scalable solutions. The following table summarises the differences between IPv4 and IPv6:
Benefits of IPv6
IPv6 introduces many advantages, positioning it as a crucial upgrade in the networking domain. The following are the benefits of IPv6:
1) IPv6 addresses the global shortage of IP addresses caused by increasing demand.
2) It offers reliability and faster speeds.
3) It supports multicast addresses for efficient delivery of bandwidth-intensive packet flows (such as media streams) to multiple destinations.
4) IPv6 enforces stronger network security with built-in IPSecurity. This ensures data privacy and integrity, while increasing routing efficiency.
5) It supports both stateless and stateful address configuration, functioning effectively with or without a DHCP server.
6) The larger address space of IPv6 allows for more efficient packet handling and improved scalability.
Drawbacks of IPv6
While IPv6 brings many improvements, it has its challenges, such as the following:
1) IPv6 is not backwards compatible with IPv4. This makes communication between networks and devices using different protocols challenging.
2) Despite its limitations, IPv4 remains more widely used than IPv6 due to familiarity and existing infrastructure.
3) Transitioning fully to IPv6 is a lengthy process because of protocol incompatibilities.
4) Upgrading infrastructure to support IPv6 involves significant expenses, hindering widespread adoption.
Explore the fundamentals of IPv6 with IPv6 Basics Course. Join today!
How to Check if IPv6 is Enabled or not?
If you are using an Android phone, try the following steps:
1) Go to the system settings and tap on 'Network & Internet'.
2) Tap on 'Mobile network'.
3) Tap on 'Advanced' and then on 'Access Point Names'.
4) Tap on the APN currently being used.
5) Tap on 'APN Protocol'.
6) Tap on 'IPv6' and save the changes.
What are the Challenges of IPv6?
Some of the challenges associated with IPv6 are:
1) Security issues such as flooding, header manipulation and dual-stacking.
2) High costs
3) DNS issues
4) Challenges in network adaptation
Conclusion
IPv6 emerged as the next step in internet evolution and the ideal solution to meet the demands of a connected world. Understanding What is IPv6 is essential for any IT professional, as it's paving the way for future innovations with expansive address space, increased security, and efficient performance. Opting for IPv6 is being ready for a smarter, faster digital future.
Explore our expert-led Cisco Training courses for advanced networking skills. Sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is My IPv6 address Example?

An IPv6 address is expressed as a series of 16-bit hexadecimal values separated by colons. It is divided into eight groups, with each 16-bit group represented by four hexadecimal digits.
How do I Enable an IPv6 Address?

You can follow these steps:
a) From the Control Panel, click 'Network and Internet’.
b) Open 'Network and Sharing Center'.
c) Click 'Change Adapter Settings'.
d) Right-click on 'connection' and go to 'Properties'.
e) Check the box right next to Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6).
f) At the screen’s bottom right, pick OK to confirm the change.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Cisco Courses, including the IPv6 Basics Course and the CCNP Wireless Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into What is a Network Security Key.
Our IT Infrastructure & Networking Blogs cover a range of topics related to IPv6, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your IT Networking skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming IT Infrastructure & Networking Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 IPv6 Basics
IPv6 Basics
Thu 8th May 2025
Thu 3rd Jul 2025
Thu 4th Sep 2025
Thu 6th Nov 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


