We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on + 1-866 272 8822 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Professionals using the Scrum methodology often require tracking methods to measure their project’s state. They resort to extensive documentation, make notes and whatnot! However, they forget to do the smart work; you know what it is. The answer is using Sprint Burndown Charts.
These Charts are essential components of Scrum Methodology, providing teams with a visual representation of their progress throughout a sprint. They serve as a guiding compass, enabling teams to track their daily progress, adjust their course when necessary, and ensure they're on track to meet sprint goals.
So, if your organisation is still depending upon extensive documentation and files to track project progress, it’s time to get familiar with these Charts. In this blog, you will learn everything about a Sprint Burndown Chart. Also, explore its importance in the Scrum framework and how to create one.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding What is a Sprint Burndown Chart in Scrum
2) Steps to create a Sprint Burndown Chart in Scrum
a) Create your estimate effort
b) Track your daily process
c) Calculate the actual effort
d) Acquire the final dataset
e) Make a Burndown plot using the Dataset
3) Conclusion
Understanding What is a Sprint Burndown Chart in Scrum
The Sprint Burndown Chart is a fundamental visual tool in the Scrum Framework, designed to provide teams with a clear and brief view of their progress during a sprint. This Chart serves as a valuable instrument for tracking and managing work, promoting transparency, and helping teams achieve their sprint goals. Here's what an ideal Sprint Burndown Chart looks like:
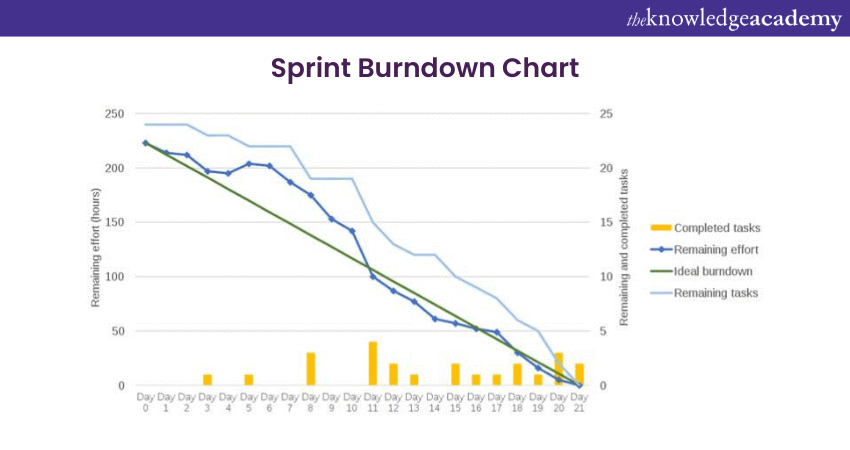
Additionally, the Sprint Burndown Chart is a graph that plots the amount of work remaining on the vertical axis against the passage of time on the horizontal axis. The central idea is to illustrate how much work remains to be completed in a Sprint, typically measured in Story Points or other relevant units. This Chart features two key Lines:
a) Ideal Burndown Line: This is a straight line connecting the total work at the start of the Sprint to zero work at the end, representing the planned rate of work completion. It serves as a benchmark for measuring the team's actual progress against the plan.
b) Actual Burndown Line: This line tracks the team's real progress, depicting how much work remains at each point in time during the Sprint. It is based on daily updates and helps in identifying deviations from the ideal path.
The Sprint Burndown Chart plays a critical role in Scrum by offering real-time insights into the team's performance, encouraging collaboration, and facilitating quick responses to any issues or impediments that may arise during the Sprint. It is an essential tool for enhancing predictability and ensuring that Sprint's goals are met effectively and efficiently.

Steps to Create a Sprint Burndown Chart in Scrum
The Sprint Burndown Chart in Scrum is a dynamic and versatile tool that serves several important functions throughout a Sprint. Here's a list of the key steps involved in creating and using this Chart:
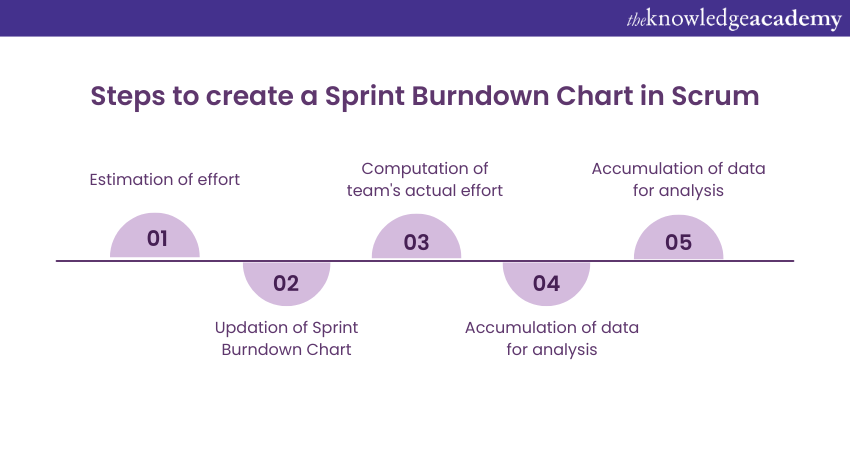
Create your estimate effort
At the start of the Sprint, the team estimates the effort required for each item in the Sprint Backlog, typically using Story Points or other relevant units. These estimates are recorded as the initial "work remaining" for each task.
Track your daily process
Every day during the Sprint, the team updates the Sprint Burndown Chart. This involves reducing the work remaining for each task as they make progress. The updated data is recorded on the Chart, which visually illustrates the daily changes.
Calculate the actual effort
The Chart captures the actual effort expended by the team each day. The Actual Burndown Line represents how much work remains in real-time, taking into account the work completed and any additional work added during the Sprint.
Acquire the final dataset
As the Sprint progresses, the Chart accumulates data that reflects the team's daily updates. This dataset includes the initial estimates, daily reductions in work remaining, and any fluctuations caused by changes in scope, impediments, or unexpected events.
Make a Burndown plot using the dataset
Once the Sprint is complete, the data collected throughout the Sprint is used to create the Sprint Burndown Chart. The Chart plots the rest of the work on the vertical axis against the passage of time on the horizontal axis. It typically includes two lines: the ideal burndown line (representing the planned rate of work completion) and the actual burndown line (reflecting the team's real progress).
Want to be a Scrum Master? Sign up for our Scrum Master Certification today!
Conclusion
We hope that after reading this blog, you have understood the concept of a Sprint Burndown Chart and how it stands as an indispensable asset within the Scrum framework. It offers real-time insights, promotes collaboration, and ensures the predictability and success of Sprints. It serves as a compass, guiding teams toward their goals and helping stakeholders make informed decisions.
Understand the ecosystem of a Scrum team by signing up for our Scrum Overview Course now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Project Management Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Scrum Master Certification
Scrum Master Certification
Thu 23rd Jan 2025
Thu 27th Feb 2025
Thu 27th Mar 2025
Thu 29th May 2025
Thu 3rd Jul 2025
Thu 4th Sep 2025
Thu 6th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


