We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203 999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Is your organisation truly compliant, or are you at risk of missing crucial details? In a world where regulations and standards constantly evolve, Process Compliance is more than just a checklist—it’s the key to maintaining operational integrity. This vital practice ensures that every procedure within your organisation meets both internal and external requirements, from industry regulations to company policies.
But how can you guarantee that your processes are up to standard? It’s not just about creating rules; it’s about actively managing and refining them. Dive into the essentials of Process Compliance in the sections ahead and discover how it can enhance your organisation’s performance and reliability.
Table of Contents
1) What is Process Compliance?
2) Process Compliance vs. Process Adherence
3) What are the Main KPIs for Tracking Process Compliance?
4) How do you Ensure Process Compliance?
5) Key Components of Process Compliance
6) Implementing Process Compliance
7) Benefits of Process Compliance
8) Role of Automation in Process Compliance
9) Conclusion
What is Process Compliance?
Process Compliance involves adhering to established procedures, standards, and regulations within an organisation to ensure effective and consistent operations. It requires following predefined protocols to meet both internal and external requirements, including regulatory and industry standards.
By maintaining Process Compliance, organisations can ensure quality control, minimise risks, and achieve operational efficiency. This practice helps maintain consistency, reduce errors, and foster trust among stakeholders. Process Compliance ensures reliable outcomes and adherence to guidelines and legal requirements, which is crucial for consistent and error-free operations.
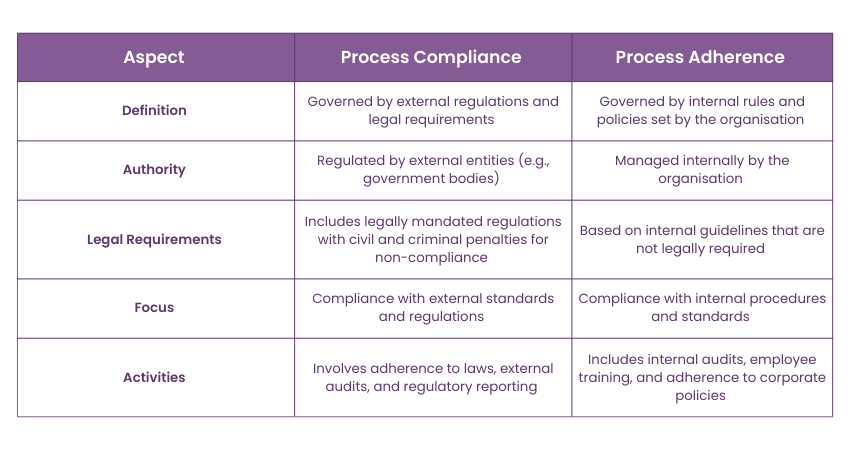
Process Compliance vs. Process Adherence
The following table highlights the key differences between Process Compliance and process adherence, clarifying their distinct roles and requirements.
What are the Main KPIs for Tracking Process Compliance?
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to track Business Process Compliance include:
1) Compliance Rate: Measures the percentage of processes that adhere to established standards and regulations. A high rate indicates effective compliance.
2) Audit Findings: Tracks the number and severity of issues identified during compliance audits. Fewer findings suggest better adherence to processes.
3) Non-compliance Incidents: Records the frequency and nature of deviations from established processes. A lower number of incidents indicates better compliance.
4) Corrective Action Frequency: Monitors how often corrective actions are taken to address compliance issues. Frequent corrective actions may signal ongoing compliance challenges.
5) Training Completion Rates: Assesses the percentage of employees who have completed mandatory compliance training. Higher rates indicate better preparation for maintaining compliance.
6) Regulatory Reporting Timeliness: Measures how promptly compliance reports are submitted to regulatory bodies. Timely reporting indicates effective compliance management.
How do you Ensure Process Compliance?
Ensuring Process Compliance involves a systematic approach to maintaining adherence to established procedures and regulations. Here are key steps to achieve this:
a) Develop Clear Policies and Procedures: Draft comprehensive Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) detailing required processes and compliance standards. Ensure these are consistently followed across the organisation.
b) Conduct Regular Training: Offer ongoing training to employees to ensure they understand compliance requirements and can apply them correctly. Update training as needed to reflect changes.
c) Implement Monitoring Systems: Use technology to continuously monitor compliance with established standards. Quickly detect and address any deviations or non-compliance issues.
d) Perform Regular Audits: Schedule periodic internal and external audits to evaluate compliance. Identify any gaps and make necessary improvements to enhance process reliability.
e) Establish Corrective Actions: Create and execute plans to address identified compliance issues. Ensure corrective measures are effectively implemented to resolve and prevent future problems.
f) Maintain Up-to-Date Documentation: Ensure all compliance-related documentation is current and accurate. Update records to reflect changes in regulations and procedures.
g) Engage in Continuous Improvement: Regularly review and refine processes based on audit results and feedback. Adapt to new challenges and changes to improve overall compliance.
h) Ensure Regulatory Alignment: Keep abreast of relevant regulations and update processes accordingly. Ensure all procedures comply with current legal requirements and industry standards.
Key Components of Process Compliance
The following outlines the key components of Business Process Compliance, detailing the essential elements needed to ensure adherence to regulatory and internal standards.
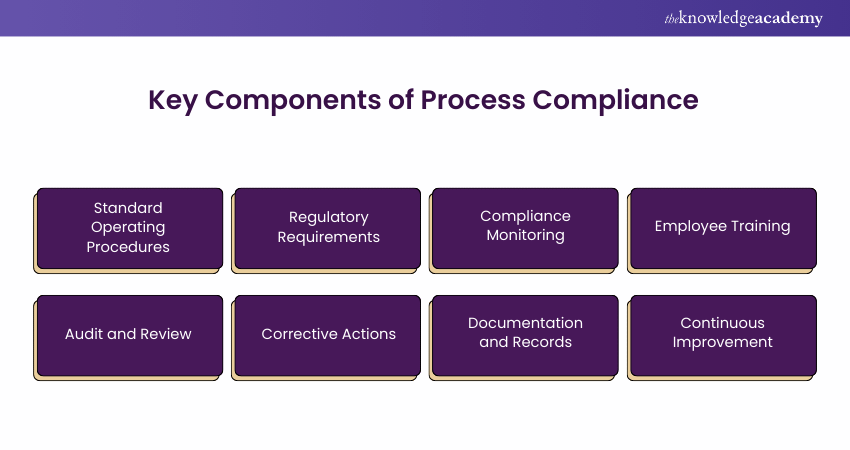
1) Standard Operating Procedures: Detailed documents outlining processes and guidelines required for compliance. SOPs ensure consistency and adherence to both regulatory and internal standards.
2) Regulatory Requirements: Specific laws and regulations that organisations must follow. These include industry standards and legal obligations that ensure compliance and avoid legal issues.
3) Compliance Monitoring: Systems and tools used to track adherence to standards continuously. These tools detect deviations and ensure timely resolution of compliance issues.
4) Employee Training: Regular training programs ensure employees understand and follow compliance requirements. Training is updated to reflect changes in regulations and procedures.
5) Audit and Review: Periodic internal and external audits assess compliance with standards. Audits help identify gaps and suggest improvements to maintain process integrity.
6) Corrective Actions: Procedures to address and resolve compliance issues. These actions involve developing and implementing plans to correct problems and prevent future occurrences.
7) Documentation and Records: Accurate, up-to-date records of processes and compliance activities. Documentation ensures transparency and accountability and provides evidence of adherence to compliance requirements.
8) Continuous Improvement: Regular assessment and refinement of processes based on feedback. This approach adapts to changing requirements and enhances overall compliance effectiveness.
Master ESG essentials with our Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Training Course - elevate your skills and drive sustainable change today!
Implementing Process Compliance
Process Compliance doesn't remain theoretical; it transforms into action through meticulous implementation. Let’s look at the essential steps that organisations need to take to ensure that their operations align with established processes, rules, and regulations:
Assessing Current Processes
Begin by thoroughly evaluating existing processes to identify any gaps or inefficiencies. This assessment involves reviewing procedures, workflows, and compliance with current regulations.
Understanding how well current practices align with compliance standards is crucial. It helps pinpoint areas needing improvement and ensures that the organisation meets both internal and external requirements. Regular assessments provide valuable insights into potential risks and compliance issues, enabling proactive adjustments and refinements to enhance overall process effectiveness.
Establishing Robust Standard Operating Procedures
Develop comprehensive Standard Operating Procedures that clearly outline the necessary steps for compliance. SOPs should include detailed instructions, responsibilities, and regulatory requirements relevant to each process.
Ensure these documents are well-structured and easily accessible to all employees. Effective SOPs provide a consistent framework for performing tasks, help standardise operations and ensure that everyone follows the same procedures. Regularly review and update SOPs to reflect changes in regulations or organisational needs.
Ensuring Compliance with Regulations
Stay informed about relevant laws and regulations impacting your industry. Continuously monitor updates and changes in legal requirements to ensure that your processes remain compliant.
Implement procedures to integrate new regulatory standards into your operations promptly. This may involve updating policies, revising procedures, or conducting additional training for staff. Regularly review compliance with these regulations through audits and assessments to maintain adherence and avoid legal issues.
Quality Assurance (QA) and Control Measures
Implement robust Quality Assurance (QA) systems and control measures to ensure that processes consistently meet compliance standards. QA involves regularly inspecting and testing processes to verify their effectiveness and adherence to established guidelines.
Control measures, such as checkpoints and monitoring tools, help detect deviations and ensure corrective actions are taken. These practices help maintain high-quality standards, reduce errors, and ensure that processes comply with both internal and regulatory requirements. Regular QA checks and controls are essential for sustaining compliance.
Empower your organisation’s success – register for our Corporate Governance Training - sign up today!
Benefits of Process Compliance
Process Compliance transforms organisations by ensuring tasks are carried out consistently, minimising risks, and promoting operational excellence. Let’s understand some of the significant importance of Process Compliance:
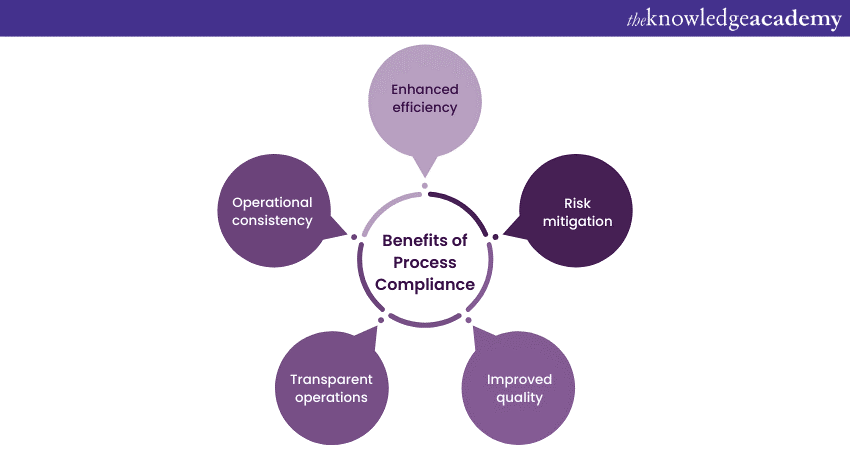
Enhanced Efficiency
Process Compliance establishes a framework where tasks are executed consistently and in line with established standards. This uniformity streamlines operations by eliminating guesswork and reducing variations.
As a result, redundancies and inefficiencies are minimised, leading to heightened overall efficiency. Resources are allocated optimally, and operational processes flow smoothly, contributing to improved productivity and performance.
Risk Mitigation
Process Compliance serves as a protective shield against potential risks and pitfalls. Adhering to regulations and industry standards mitigates the likelihood of legal penalties, fines, and reputational harm.
By following best practices and guidelines, organisations proactively safeguard themselves from financial liabilities and legal setbacks. This commitment to Compliance demonstrates a dedication to ethical conduct and responsible business practices, fostering trust with stakeholders and bolstering long-term sustainability.
Improved Quality
Process Compliance paves the way for elevated quality standards. When procedures are standardised, and Compliance guidelines are strictly adhered to, variations and errors decrease significantly.
This leads to consistently high-quality outputs that meet or even surpass customer expectations. By maintaining a stringent adherence to Compliance, organisations ensure that their products and services consistently deliver superior value and reliability.
Transparent Operations
Compliance injects transparency into an organisation's operations. By documenting Processes and adhering to regulatory requirements, companies offer stakeholders, including customers, regulators, and investors, a clear view of how tasks are executed.
This transparency instils confidence in the organisation's integrity and ethical practices. It facilitates open communication and accountability, fostering a positive reputation and creating a foundation for sustainable relationships.
Operational Consistency
The bedrock of Compliance lies in consistency. Irrespective of changes in personnel or external circumstances, compliant processes remain steadfast. This operational consistency acts as a buffer against disruptions and uncertainties.
The organisation can maintain its operations smoothly, delivering reliable products and services while upholding Compliance standards. The ability to ensure uniformity and reliability contributes to the organisation's resilience and adaptability in a dynamic business environment.
Interested in Regulatory Analyst positions? Discover the Regulatory Analyst Salary and see if this career path aligns with your financial goals.
Role of Automation in Process Compliance
Automation plays a crucial role in enhancing Business Process Compliance by streamlining and simplifying compliance-related tasks. Here are some key ways automation contributes to Process Compliance:
1) Efficiency and Accuracy
a) Reduced Manual Errors: Automation minimises human errors by ensuring tasks are performed consistently and accurately.
b) Faster Processes: Automated systems can execute compliance tasks much faster than manual processes, improving overall efficiency.
2) Continuous Monitoring
a) Real-time Tracking: Automated tools provide real-time monitoring of compliance activities, allowing for immediate detection and correction of issues.
b) Consistent Audits: Automation ensures regular and consistent audits, helping maintain ongoing compliance.
3) Data Management
a) Centralised Data: Automation tools centralise compliance-related data, making it easier to manage and access information.
b) Accurate Reporting: Automated systems generate accurate and timely compliance reports, aiding in better decision-making.
4) Regulatory Updates
a) Automatic Updates: Compliance automation tools can automatically update processes and protocols in response to changes in regulations.
b) Adaptability: These tools can quickly adapt to new compliance requirements, ensuring the organisation remains compliant.
5) Risk Management
a) Proactive Risk Identification: Automation helps in identifying potential compliance risks early, allowing for proactive mitigation.
b) Consistent Implementation: Ensures that risk management strategies are consistently implemented across the organisation.
6) Cost Savings
a) Reduced Labor Costs: By automating routine compliance tasks, organisations can reduce labour costs and allocate resources more effectively.
b) Avoidance of Penalties: Ensuring compliance through automation helps avoid expensive fines and penalties associated with non-compliance.
7) Enhanced Compliance Culture
a) Employee Engagement: Workers can focus on more strategic compliance initiatives by assigning difficult work to automation.
b) Training and Awareness: Automated systems can also be used to deliver compliance training and track completion rates.
Register for our Effective Compliance Training and navigate regulations with confidence!
Conclusion
Mastering Process Compliance is crucial for maintaining operational excellence and ensuring adherence to standards. Understanding the distinction between Compliance vs Risk Management is key; while compliance ensures adherence to rules and regulations, risk management focuses on identifying and mitigating potential threats to business objectives. By implementing a robust compliance framework, organisations can enhance efficiency, mitigate risks, and achieve long-term success. Embrace these strategies to elevate your processes and secure a reliable, future-proof operation.
Unlock the power of Compliance; Register for our Compliance Training today!
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does a Strong Understanding of the Compliance Process Contribute to Career Success?

A strong understanding of the Compliance Process enhances career success by showcasing expertise in regulatory adherence. This boosts job performance and opens opportunities for advancement in roles requiring meticulous operational oversight.
Are There Specialised Career Paths for Professionals with Compliance Process Skills?

Yes, professionals with Compliance Process skills can pursue specialised career paths. These include roles such as Compliance Officer, Risk Manager, and Regulatory Specialist. Their expertise in adherence and regulation is highly valued.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Compliance Trainings, including Corporate Governance Course and Security Governance and Compliance Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing Compliance Frameworks.
Our ISO & Compliance Blogs covers a range of topics related to ISO and Compliance, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Compliance skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming ISO & Compliance Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 PCI DSS Implementer
PCI DSS Implementer
Thu 3rd Apr 2025
Thu 5th Jun 2025
Thu 7th Aug 2025
Thu 2nd Oct 2025
Thu 4th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


