We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344 203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

In today's data-driven world, GDPR compliance is more than just a legal requirement—it's essential for protecting customer trust and sensitive information. With 92% of companies still striving for full compliance, the GDPR Audit is a vital tool to tackle these challenges and strengthen your data protection strategies.
This blog will walk you through the GDPR Audit process, explaining key terms, common pitfalls, and the undeniable benefits of strict compliance. Whether you're new to GDPR or looking to refine your approach, we'll provide practical insights and tips to help you navigate the audit with confidence and clarity.
Table of Contents
1) What is a GDPR Audit?
2) Why Should a GDPR Audit be Conducted?
3) How to Conduct a Proper GDPR Compliance Audit
4) Basic Terminologies in GDPR
5) GDPR Audit Checklist
6) Is GDPR Audit Necessary for Businesses?
7) Benefits of a Data Privacy Audit
8) Conclusion
What is a GDPR Audit?
A GDPR Audit refers to identifying critical risks and gaps in an organisation's compliance with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). It assesses current processes, procedures, and policies to pinpoint areas for improvement and recommends strategies to address these issues. Some of the key Audit activities include:
1) Personal data management monitoring
2) Implementing data breach prevention measures
3) Training staff on GDPR obligations
Additionally, it covers conducting Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIA) for high-risk initiatives, ensuring GDPR-compliant consent practices, and managing Data Subject Access Requests (DSAR) efficiently.
By addressing these areas, a GDPR Audit strengthens compliance and builds a robust data protection framework. This framework helps to mitigate risks and enhances overall organisational trust in their data management practices, especially with respect to GDPR after Brexit.
Why Should a GDPR Audit be Conducted?
Conducting a GDPR Audit is crucial for organisations to adhere to the requirements. Below listed are some of the key reasons that highlight the importance of regularly conducting these audits:
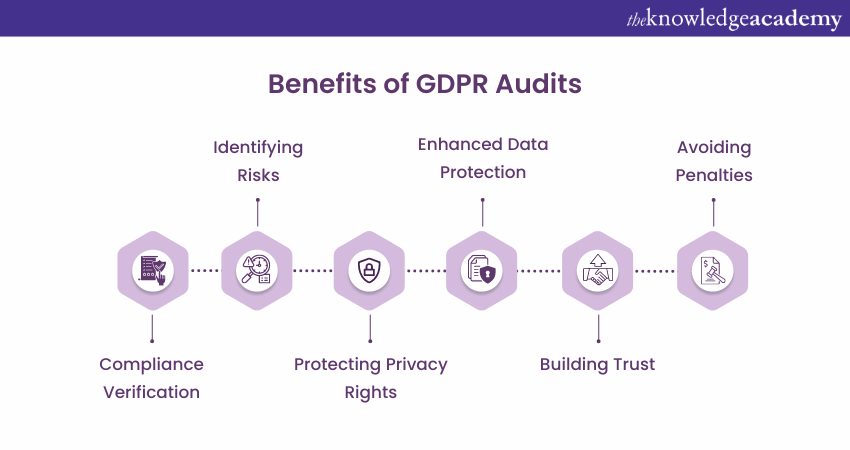
1) Compliance Verification: The GDPR has developed an extensive concept of rules and regulations for issues in personal information processing. Organisations can perform the audits to realise how well they have complied with the GDPR requirements and where they are actors of non-compliance.
2) Identifying Risks: The auditing process clarifies the extent to which the organisations have implemented their Data Protection provisions to recognise any system loopholes. By understanding GDPR and its vulnerabilities, organisations can implement essential practices to secure personal data from unauthorised access, loss, and disclosure.
3) Protecting Privacy Rights: Regular audits ensure that organisations are improving their data protection practices continuously by equipping their employees with new tools for the security of personal data. Organisations can build customers, employees, and stakeholders’ trust by demonstrating a commitment to transparency.
4) Enhanced Data Protection: An audit can assess whether the data protection measures are effective for an organisation. Additionally, audits can ensure the availability of tools such as encryption, access controls, and incident response plans.
5) Building Trust: In an era where it's a common practice to breach data and privacy scandals, organisations that prioritise data protection and privacy have a competitive edge. Moreover, regular audits demonstrate a data privacy and security commitment, which further builds trust among customers, partners, and stakeholders.
6) Avoiding Penalties: GDPR non-compliance can result in significant fines and penalties. Organisations can identify and rectify non-compliance issues through regular audits before they lead to legal consequences. This proactive approach reduces the penalty risks and ensures the legalised operation of the enterprises with regard to the Data Protection regulations.
Elevate your understanding of GDPR Regulations and ensure compliance with our GDPR Courses.
How to Conduct a Proper GDPR Compliance Audit?
Conducting a GDPR Audit involves several crucial steps to ensure personal data compliance and protection. Here are some of the key steps to follow:
1) Understand the GDPR Requirements: Thorough regulations should be performed to create a comprehensive action plan and implement changes that are highly necessary.
2) Appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO): A DPO ensures compliance and oversees strategies for data protection within the organisation.
3) Implement Necessary Changes: Adjust your data processing activities to align with the requirements of GDPR.
4) Perform Regular Audits: Regularly audit your data processing activities to identify and address any issues at an early stage.
5) Consider All Types of Data: Be thorough in considering all data types within your organisation to ensure comprehensive compliance.
6) Work with Third-Party Service Providers: Identify potential risks and solutions in third-party service providers collaboration.
7) Develop a Plan of Action: Create a detailed plan to ensure ongoing GDPR compliance.
8) Train Your Employees: Educate your employees on GDPR requirements and your data protection program.
9) Maintain Records: Keep all the detailed records of data processing activities as required by GDPR.
10) Ensure Compliance with Legal Professionals: Work with legal professionals to address any ongoing compliance concerns.
Take control of data privacy and enhance your understanding of GDPR compliance with our Data Privacy Awareness Course now!
Basic Terminologies in GDPR
Some of the basic GDPR terms you need to understand include Personal Data, Sensitive Personal Data, Anonymous Data, and Pseudonymous Data. Here are the definitions and their associated abbreviations:
1) Personal Data: Any information that can identify a living person is considered Personal data. This can be a combination of different pieces of information that can single out a specific person.
2) Sensitive Personal Data: Sensitive Personal Data are the Special Personal data that require extra protection. Generally, organisations need stronger reasons to process Sensitive Personal data than regular Personal data.
3) Anonymous Data: Data sets that are modified so nobody can recognise any person(s) (directly or indirectly) by any means or by anyone are known as Anonymous Data.
4) Pseudonymous Data: Pseudonymous Data is the data that is altered by using a reference number or other identifier to replace names or other identifiers that are easily linked to individuals.
5) Controller: The controller is the legal person, agency, public authority, or other organisation that decides the purposes and means of processing personal data alone or with others.
GDPR Audit Checklist
GDPR standards compliance using this checklist ensures that organisations accurately meet GDPR requirements and effectively protect their data. Here are the steps involved in conducting a GDPR Audit:
1) Review Data Processing Activities
The very initial step is analysing an organisation's data processing operations, which involves identifying different Personal Data types, the purposes behind processing, lawful processing grounds, and the retention periods.
It is your responsibility to ensure that personal data is handled in a lawful manner, fairly, and transparently, as provided for in the personal data processing regulations.
2) Assess Data Protection Policies and Procedures
Verifying data protection policies and procedures is essential for a GDPR Risk Assessment. This includes privacy notices reviewing provided to Data Subjects and assessing the consent mechanism’s effectiveness. It also ensures that necessary contractual agreements with data processors are in place.
Additionally, it is important to regularly audit these policies and procedures to ensure they remain highly effective and GDPR-compliant. This involves checking that privacy notices are clear and accessible, consent mechanisms are robust and verifiable, and contractual agreements with data processors are comprehensive and up-to-date.
3) Evaluate Data Breach Response Plan
Examining an entity's data breach plan is a crucial part of auditing to ensure the comprehensiveness and effectiveness of the plan. This involves verifying proper procedures for detecting, investigating, and reporting GDPR data breaches.
Additionally, it's important to check that the organisation has an accessible and actionable response plan for breaches. Assessing the adequacy of notifications to both the data protection authority and affected individuals is also essential.
4) Examine Consent Mechanisms
Reviewing the process of obtaining and managing Data Subjects' consent is essential to ensure compliance with GDPR principles. This involves verifying that subjects freely give consent without any subconscious influence. It's important to assess the organisation's ability to maintain consent for various processing activities and establish effective consent withdrawal mechanisms.
Furthermore, organisations should ensure that consent requests are clear and specific, detailing the purposes for personal data use. This transparency helps Data Subjects make informed decisions about their consent.
5) Assess Third-party Contracts and Compliance
Such clauses should specify the service provider’s roles and responsibilities, as well as their obligations to adhere to GDPR data protection principles. Your organisation must review third parties to ensure their compliance and verify the effectiveness of the measures they take to protect personal data.
Moreover, it is important to establish channels for clear communication with third-party service providers to address data protection concerns promptly. This includes setting up regular meetings and reporting mechanisms to monitor compliance with GDPR requirements.
6) Evaluate Data Subject Rights Processes
This is one of the central factors in creating GDPR, which is the increase of power of citizens with Data Subject rights. These rights let people establish themselves as the masters of their data and the means by which this data is handled.
The auditor must perform a control verification to check whether the organisation's Data Subject rights request procedures are in order. This ensures that individuals can exercise their rights effectively and the organisation is compliant with the regulations.
7) Review Security Measures
The GDPR mandates that organisations implement robust technical measures to safeguard personal data. This includes encryption and pseudonymisation to protect data integrity and strict access controls to limit data access to authorised personnel only.
Additionally, data minimisation practices ensure only necessary data is collected. Regular testing and monitoring of these security measures are essential to maintain their effectiveness and to promptly identify and address any vulnerabilities.
8) Implement Privacy Impact Assessments
Ensure that the organisation conducts Privacy Impact Assessments (PIAs) for high-risk processing activities. Evaluate the effectiveness of these PIAs in identifying and addressing privacy risks associated with data processing activities and confirm that appropriate mitigating measures are implemented when necessary.
Additionally, data minimisation practices ensure only necessary data is collected. Regular testing and monitoring of these security measures are essential to maintain their effectiveness and promptly identify and address any vulnerabilities.
9) Examine Data Retention and Disposal Practices
Review the organisation's data retention and disposal practices to ensure compliance with GDPR's storage limitation principle. It's crucial to verify that personal data is retained only for the necessary period and securely disposed of when no longer needed.
It's essential to check that the organisation has clear and well-defined policies and procedures for data retention and disposal, ensuring that personal data is not kept longer than necessary and is securely deleted or destroyed once it is no longer required. This helps to minimise the data breaches risks and ensures compliance with GDPR.
10) Evaluate Incident Response and Notification Procedures
One of the most important steps is to assess the incident response and notification procedures for data breaches of an organisation. Verify that the organisation has appropriate processes to detect, respond, and notify relevant parties in the event of a data breach.
Additionally, it is crucial to ensure that these procedures are tested and updated regularly to address any new kinds of threats and vulnerabilities. This includes periodic drills conducting and simulations to evaluate the response plan’s effectiveness and making outcome-based necessary adjustments.
11) Assess Accountability Measures
It is essential to determine the organisation’s leitmotif for data violations and notification so that the incidents can be responded to appropriately. Review the organisation's procedures, initiate a data breach simulation, and confirm timely notification to the authorised agencies.
A DPO functions as a liaison officer within an organisation charged with supervising Data Protection activities and maintaining discipline. Among the many things an organisation should guarantee while auditing its GDPR checklist is that it knows exactly what data it actually processes, why it processes it, and how it does it.
12) Regularly Review and Update Data Protection Measures
Ensure the organisation regularly reviews and updates its Data Protection measures to adapt to changes in GDPR requirements and emerging Data Protection best practices.
Furthermore, it is important to engage in regular training and awareness programs for employees to inform them about the latest data protection protocols and practices. This helps foster a data security culture within the organisation. This further ensures that all staff members are vigilant and proactive in personal data protection.
13) Personal Information Management System (PIMS)
A PIMS is a system that points out the protection of privacy as potentially affected by the processing of Personal data. A PIMS is based on ISO/IEC 27701 for Personal information management.
A PIMS helps organizations establish, implement, maintain, and continually improve their privacy policies, procedures, and practices. Additionally, a PIMS aids organizations in demonstrating their compliance with GDPR, especially when preparing a GDPR Privacy Policy PDF to ensure transparency and accountability.
14) Establish a Staff Training Program on GDPR
Neglecting to train staff on the nuances of handling data can undo all GDPR compliance efforts through a single mishap. Thus, educating employees on GDPR compliance is crucial.
This includes understanding the core principles of data protection, recognising the rights individuals have under GDPR, and becoming familiar with the organisation's particular policies and procedures for data protection, including the implementation of a GDPR Privacy Policy Template.
Is GDPR Audit Necessary for Businesses?
Yes, performing a GDPR Audit on any business that handles personal data is necessary for any business. It helps ensure data protection regulations compliance, builds customer trust, and reduces the risk of severe financial penalties for non-compliance.
Moreover, regular audits also promote harmonised data privacy practices and maintain data integrity. This proactive approach not only safeguards personal data but also enhances the organisation's overall security posture.
Master data privacy laws with the GDPR Cheat Sheet—get it now!
Benefits of Data Privacy Audit
Conducting a GDPR Compliance Audit offers several significant benefits for businesses. Here are the key advantages:
1) Thorough Review of Data Handling Practices: A GDPR Compliance Audit provides a comprehensive assessment of your data handling practices, helping to identify any areas where you may be at risk.
2) Implementation of Technical Controls and Processes: The audit facilitates the implementation of technical controls and processes to protect data. By establishing robust security measures, businesses can safeguard personal data against unauthorised access, loss, or breaches, thereby enhancing overall data security.
3) Development of Corrective Action Plans: A GDPR Compliance Audit aids in developing corrective action plans to address any identified risks. These plans outline steps to mitigate vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with GDPR requirements.
4) Mitigation of Financial and Legal Risks: Conducting regular audits helps mitigate financial and legal risks associated with GDPR compliance. By proactively addressing data protection issues, businesses can avoid severe financial penalties and legal repercussions.
5) Building Customers and Stakeholders Trust: Regular audits demonstrate a data privacy and security commitment, building trust with customers and stakeholders. This proactive approach enhances the organisation's reputation and fosters confidence in its data protection practices.
Wish to enhance your knowledge of Data Protection? Register for our Certified EU GDPR Foundation and Practitioner Course now!
Conclusion
Conducting a comprehensive GDPR Audit is crucial for organisations to ensure compliance with regulations for data protection and safeguard individuals' privacy rights. Regular GDPR Audits help protect your business from potential risks and help cultivate a strong culture of data privacy and security. We hope you found this information useful. The insights shared in this blog will equip you with the knowledge to identify gaps in the data privacy framework of your organisation and build trust with your stakeholders.
Take control of data privacy and enhance your understanding of GDPR compliance with our Data Privacy Awareness Course now!
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Consequences of Not Conducting a GDPR Audit?

Failing to conduct a GDPR Audit can lead to non-compliance, resulting in fines of up to £17 million or 4% of global annual turnover. It also risks data breaches, legal action, and reputational damage. In addition, companies may face operational restrictions, losing customer trust and market credibility.
Are There Specific Tools for Conducting a GDPR Audit?

Yes, there is a wide array of tools that can help with GDPR Audits by streamlining compliance checks, data mapping, and documentation. The key examples include OneTrust, TrustArc, BigID, Vanta, and Netwrix Auditor. These tools assist in identifying gaps, managing data, ensuring proper consent, and maintaining audit trails.
What are the other resources and offers provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is Knowledge Pass, and how does it work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are related courses and blogs provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various GDPR Courses, including the Certified EU General Data Protection Regulation (EU GDPR) Foundation And Practitioner Course and the EU General Data Protection Regulation Awareness Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into the Benefits of GDPR.
Our IT Security & Data Protection Blogs cover a range of topics related to GDPR, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your GDPR skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Certified Data Protection Officer (CDPO)
Certified Data Protection Officer (CDPO)
Fri 16th May 2025
Fri 11th Jul 2025
Fri 19th Sep 2025
Fri 21st Nov 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


