We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344 203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

The term "Trojan Horse" has transcended its origins in ancient Greek mythology to become a widely recognised metaphor in the world of cybersecurity. In the digital realm, a Trojan Horse is a deceptive and cunning form of malware. It disguises itself as something benign or desirable but conceals malicious intent beneath its surface.
According to Eftsure, Trojan virus attacks account for 65% of all malware attacks on Windows systems. With such high risks, it is always better to be prepared by understanding the nature of the threat. In this blog, we will discuss everything about What a Trojan Horse is and its various forms. We will also learn how it operates and how to protect your devices against this insidious threat.
Table of Contents
1) What is a Trojan Horse?
2) Types of Trojan Horses
3) How did Trojan Horses spread?
4) Notable Trojan Horse Examples
5) How to Detect Trojan Horses?
6) How to Prevent Trojan Horse Infections?
7) How to Remove a Trojan Horse?
8) Conclusion
What is a Trojan Horse?
A Trojan Horse Virus is a rank of malware that saturates a computer by disguising itself as a legitimate program. Attackers often use social engineering tactics to embed malicious code within seemingly harmless software, aiming to gain unauthorised access to users' systems.
In simple terms, a Trojan is a malware that typically hides as an email attachment or a free-to-download file. Once downloaded, it executes its intended malicious function, such as granting attackers backdoor access to corporate systems, spying on users’ online activities, or stealing sensitive data.
Signs of an active Trojan on a device may include unexpected changes to computer settings or other unusual activities.
Origins of the Trojan Horse
According to ancient Greek legend, the war began when the Greeks besieged the city of Troy. For ten long years, they were unable to breach its formidable walls. In a desperate bid to overcome this impasse, the Greeks resorted to subterfuge, hatching a cunning plan.
The Greek hero Odysseus devised a stratagem involving a colossal wooden horse, symbolising surrender and peace. The Greeks constructed this massive equine structure, hollowed it out, and concealed a select group of elite warriors inside. They left the horse at the gates of Troy as an apparent offering to the gods. Along with it, they spread a fabricated story of their departure.
The Trojans, deceived by the apparent withdrawal of the Greek forces, accepted the enigmatic wooden horse as a token of victory. They then dragged it within the city's walls to symbolise their triumph. Little did they know that the horse concealed a deadly secret.
Under cover of night, the Greek warriors hidden within the horse emerged and opened the city gates from the inside. This allowed the waiting Greek army to infiltrate and sack Troy. The city fell to this ingenious ruse, leading to the end of the legendary Trojan War.
The tale of the Trojan Horse serves as a timeless reminder of the power of deception. Its devastating consequences offer a lesson that resonates even in the digital age of cybersecurity.
Trojan Horse Definition
A Trojan Horse in Cybersecurity is a cunning and malevolent malware designed to deceive and infiltrate digital systems. Like its ancient Greek namesake, it conceals its true intent beneath an innocuous facade, luring unsuspecting users into a trap. At its core, the Trojan Horse definition hinges on a two-faced strategy. It masquerades as a legitimate and harmless program or file, enticing users to willingly install or execute it. All the while, it harbours malicious code and sinister objectives.
Once a Trojan Horse infiltrates a device or network, it can wreak havoc. Its capabilities range from stealing sensitive data, such as login credentials and financial information, to enabling unauthorised remote access. This effectively grants cybercriminals control over the compromised system. It can also contribute as a delivery mechanism for additional malware, expanding the scope of the attack.
The Trojan Horse definition underscores its deceptive nature. It does not replicate like viruses or self-propagate like worms but relies on the art of deception. This insidious malware can be distributed through various means, including email attachments, infected software downloads, or compromised websites. Its success often hinges on social engineering tactics that exploit human trust and curiosity.
Unlock the world of cybersecurity – Join our Ethical Hacking Training today and defend against cyber threats ethically!
How did Trojan Horses Spread?
Unlike computer viruses, a Trojan Horse requires user interaction to activate. It cannot manifest on its own and needs the user to download and install the server side of the application. The Trojan’s attack begins once the executable (.exe) file is implemented and the program is installed.
1) Email and File-based Distribution
Trojans often spread through legitimate-looking emails with attached files, spammed to reach as many inboxes as possible. Once the email is opened by the user and they downloaded the malicious attachment, the Trojan virus installs itself and runs automatically every time the infected device is turned on.
2) Social Engineering Tactics
Cybercriminals incorporate social engineering to trick users into downloading malicious applications. Trojans can be hidden in banner ads, pop-ups, or links on websites, making it easy for unsuspecting users to infect their devices.
3) Zombie Computers and Botnets
An infected device can be turned into a zombie computer, giving cybercriminals remote control without the user's knowledge. This allows the hacker to advance malware across a network of multiple devices, known as a botnet.
4) Deceptive Email Attachments
A user might receive an email from a familiar contact with an attachment that appears legitimate. However, this attachment contains malicious code that installs the Trojan, often without any immediate signs of infection.
5) Hidden and Delayed Activation
The malware remains undetected until triggered by specific actions, like visiting a particular website or banking app. Once activated, the Trojan virus carries out the hacker’s desired task and may either delete itself, go dormant, or stay active.
6) Mobile Device Vulnerability
Trojans can also target smartphones and tablets via mobile malware. Attackers may redirect traffic on a Wi-Fi network to launch cyberattacks, compromising mobile devices connected to that network.
Do you have a high level of experience and understanding in a variety of Cyber Security related fields? Then you should take this Microsoft Cybersecurity Architect SC100 Training!
Types of Trojan Horses
Trojan Horses come in various forms, each designed for specific malicious purposes. Understanding these types is important in recognising and combating these digital threats. Here are some prominent categories:
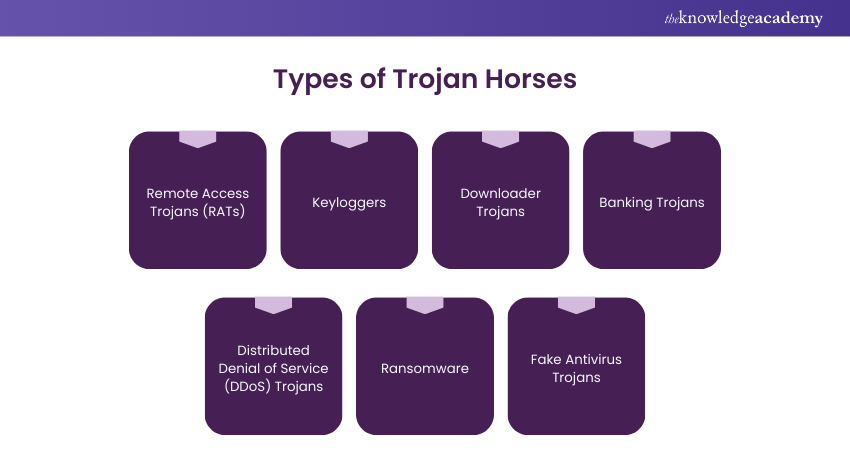
a) Remote Access Trojans (RATs): These insidious Trojans grant cybercriminals unauthorised access to a victim's device. Once infiltrated, the attacker can control the victim's computer and steal sensitive data. They can also use the compromised device as part of a botnet to propel further attacks.
b) Keyloggers: Keylogger Trojans are crafted to record a user's keystrokes. It enables hackers to capture login credentials, personal messages, and other sensitive information. This stolen data is often used for identity theft and financial fraud.
c) Downloader Trojans: As the name suggests, these Trojans are primarily focused on downloading and installing additional malware onto the victim's system. They serve as a gateway for other malicious software to infiltrate the device.
d) Banking Trojans: These Trojans target online banking and financial transactions. They manipulate web sessions and redirect funds, often leading to financial losses for victims.
e) Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Trojans: DDoS Trojans turn infected devices into bots that work together to launch massive DDoS attacks on targeted websites or networks. This coordinated assault can cripple the functionality of the affected systems.
f) Ransomware: While often considered a separate category, ransomware can be delivered through a Trojan Horse. These Trojans encrypt a victim's data, demanding a ransom for decryption keys.
g) Fake Antivirus Trojans: Masquerading as legitimate antivirus software, these Trojans convince users to pay for their services while providing no real protection. They often infect the victim's computer with additional malware.
Notable Trojan Horse Examples
Trojan attacks represent a category of malware that camouflages itself as a legitimate program or file. The intention is to deceive users into installing it on their computer systems.
Once successfully installed, these Trojans can execute various malicious activities. These activities may include data theft, the installation of additional malware, or even gaining control over the compromised computer. A few notorious examples of Trojan virus attacks include:
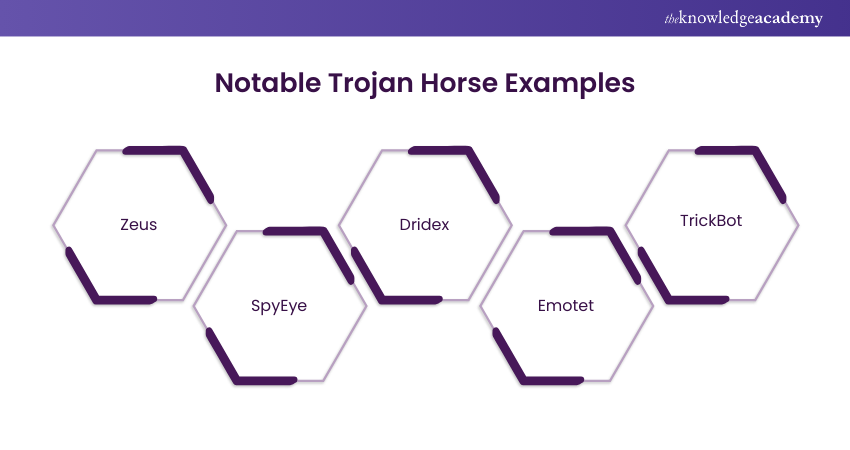
a) Zeus: First identified in 2007, Zeus is a Trojan notorious for its capacity to steal personal and financial information. This includes bank account details and passwords. It has played a role in several high-profile cyberattacks. One such attack is the 2011 Citibank heist, where over $100 million was stolen.
b) SpyEye: This Trojan, similar to Zeus, specialises in the theft of personal and financial data. It gained prominence in 2011 and can bypass certain security measures employed against Zeus. SpyEye contributed to major cyber incidents, including the 2013 theft of over $100 million from Bank of America.
c) Dridex: Targeting banking credentials, Dridex excels in infiltrating financial institutions. It was first identified in 2014 and has been implicated in substantial cyberattacks. One notable incident is the 2015 theft of over $100 million from the Royal Bank of Scotland.
d) Emotet: Discovered in 2014, Emotet is a Trojan that specialises in the theft of personal and financial data. It also facilitates the installation of additional malware on infected computers. It is particularly adept at spreading through email attachments and phishing attacks. Emotet has been associated with significant incidents, such as the 2019 theft of over $100 million from the city of Baltimore.
e) TrickBot: Emerging in 2016, TrickBot is a Trojan designed for stealing personal and financial data and facilitating the installation of additional malware. It primarily targets financial institutions and has been involved in notable cyberattacks. One significant incident includes the 2018 theft of over $100 million from the US Department of Energy.
How to Detect Trojan Horses?
Trojan Horses often masquerade as legitimate system files. This makes their detection and removal challenging for conventional virus and malware scanners. Identifying and eliminating these discreet Trojan Horses usually requires specialised software tools.
However, it is possible to detect the presence of a Trojan Horses by observing unusual behaviours exhibited by the computer. These anomalies may include:
a) Alterations to the computer's display, like changes in colour or resolution. There might also be unexpected upside-down screen flips.
b) Excessive influx of pop-up ads offering solutions to various errors, enticing users to click on them.
c) Spontaneous movement or freezing of the computer mouse, with the mouse buttons' functions possibly reversed.
d) Changes in the browser, such as a modified homepage or consistent redirection to an unintended website, are common signs of infection. These sites are often laden with offers that, if clicked, lead to further malware installation.
e) Disabling antivirus and antimalware programs prevents users from taking the necessary steps to remove malware.
f) The appearance of mysterious messages and abnormal graphic displays.
g) Unfamiliar programs are running in the task manager.
h) Altered appearance or disappearance of the taskbar.
i) Changes to the computer's desktop wallpaper, desktop icons, and application formats.
j) The user's email service sends spam messages to contacts, potentially spreading the Trojan Horses to other computers.
How to Prevent Trojan Horse Infections?
For everyday users, the best defence against Trojan virus attacks is practising responsible online behaviour and implementing basic preventive measures. Best practices for responsible online behaviour include:
1) Avoid clicking on unsolicited links or downloading unexpected attachments.
2) Use strong, unique passwords for all the online accounts and devices you own.
3) Only access URLs that begin with HTTPS.
4) Log into your accounts through a new browser tab or official app — not via links in emails or texts.
5) Use a password manager to automatically enter saved passwords into recognised sites, avoiding spoofed sites.
6) Enable a spam filter to prevent most spoofed emails from reaching your inbox.
7) Enable two-factor authentication whenever possible, making it harder for attackers to gain access.
8) Ensure that software programs and operating systems are updated promptly.
9) Regularly back up files to help restore your computer in the event of an attack.
Additionally, users should invest in cybersecurity software to protect their devices from all types of malware. Such software can detect threats or block them before they infect the device.
Unlock the world of cybersecurity with our Ethical Hacking Professional Course and become a guardian of the digital realm today.
How to Remove a Trojan Horse?
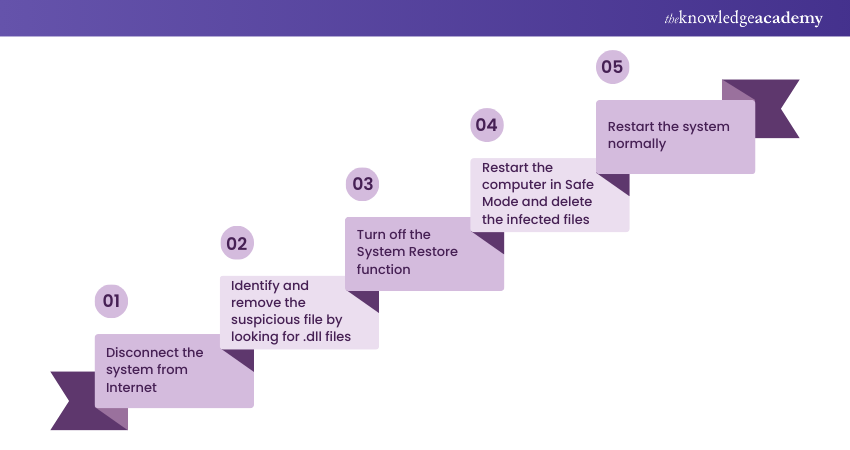
When a Trojan Horse is detected on a computer, immediate action is crucial.
a) Start by disconnecting the system from the Internet to prevent further communication with malicious servers. Then, remove the suspicious files associated with the Trojan virus.
b) Identifying infected files is the most challenging part. Look out for error messages like Dynamic Link Library (DLL) errors, which often indicate a Trojan's presence. Copy and search these errors online to identify affected .exe files.
c) Turn off the System Restore function to prevent the restoration of deleted malicious files.
d) Restart the computer in Safe Mode by pressing the F8 key during startup. In Safe Mode, access the "Add or Remove Programs" feature in the control panel to uninstall and delete infected programs. To ensure a thorough removal, delete all associated program files.
e) Finally, restart the system in normal startup mode to complete the Trojan Horse removal process.
This diligence and attention to detail are essential to eradicate the Trojan and fully prevent potential reinfection.
Conclusion
In this blog, we've traced the Trojan Horse's journey from its mythological origins to its current role as a serious cybersecurity threat. Understanding What is a Trojan Horse virus and recognising its various forms is important for every business. By adopting proactive cybersecurity practices, you can strengthen your digital defences against these stealthy invaders.
Accelerate your security professional career by attending our Mastering Metasploit Framework Course – Register today!
Frequently Asked Questions

The first known Trojan Horse attack was the "Animal" program in the early 1970s, created by John Walker. It disguised itself as a game that guessed animals but secretly copied itself onto other systems without the user's knowledge. This marked the beginning of using deception in software to breach security.

To check if a Trojan virus is installed, look for signs like slow computer performance, unexpected pop-ups, or unauthorised changes to settings. Use antivirus or antimalware software to run a full system scan. Reviewing active processes in the Task Manager or Activity Monitor can also help identify suspicious activities.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Ethical Hacking Training, including the Ethical Hacking Professional and Mastering Metasploit Framework. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Ethical Hacker Roles and Responsibilities.
Our IT Security & Data Protection Blogs cover a range of topics related to Ethical Hacking, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your IT Security & Data Protection skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Certified Cyber Security Professional (CCS-PRO)
Certified Cyber Security Professional (CCS-PRO)
Fri 17th Jan 2025
Fri 7th Mar 2025
Fri 23rd May 2025
Fri 18th Jul 2025
Fri 12th Sep 2025
Fri 14th Nov 2025
Fri 12th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


