We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344 203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
In this rapidly evolving digital world, data has become omnipresent, paving its way into our everyday conversations. Technological advancements are literally dependant on it and the very fabric of our interconnected world. But do you know What is Data, exactly?
How is it shaping our technological world? Worry no more. Read this blog to get the answers to all your queries. This blog will explain What is Data, the diverse forms it takes, and shed light on the vital role it plays in today's information age.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding What is Data
2) Different Types of Data
3) How to Analyse Data?
4) How is Data Stored?
5) Uses of Data
6) Jobs in Data
7) What is Data in a Computer?
8) What is Data vs Information?
9) Conclusion
Understanding What is Data
Data collection refers to any gathering of facts, statistics, or information stored for various purposes. In computing and technology, Data often consists of raw facts and figures that lack specific meaning. These raw Data points become valuable when processed, organised, or analysed to derive useful insights, make informed decisions, or perform specific tasks.
Data can take various forms, including text, numbers, images, audio, and video. It is the foundation for information and knowledge, enabling businesses, individuals, and systems to understand and interpret the world around them. It can be structured. In simple terms, it can be organised in a predictable format or unstructured, making it less organised and more challenging to work with.
The management, analysis, and utilisation of Data play a critical role in various fields, such as business, science, healthcare, and technology. With the advent of Big Data, Data Analytics, and Artificial Intelligence (AI), the importance of Data in our modern world has only grown. Thus, it has become a valuable resource for innovation, problem-solving, and decision-making.
Different Types of Data
After learning What is Data, let’s have a look at its various types. It comes in various types and forms, each serving a specific purpose in the world of information and analysis. Understanding these types is fundamental to making sense of their diverse nature. Here are a few key types of Data:
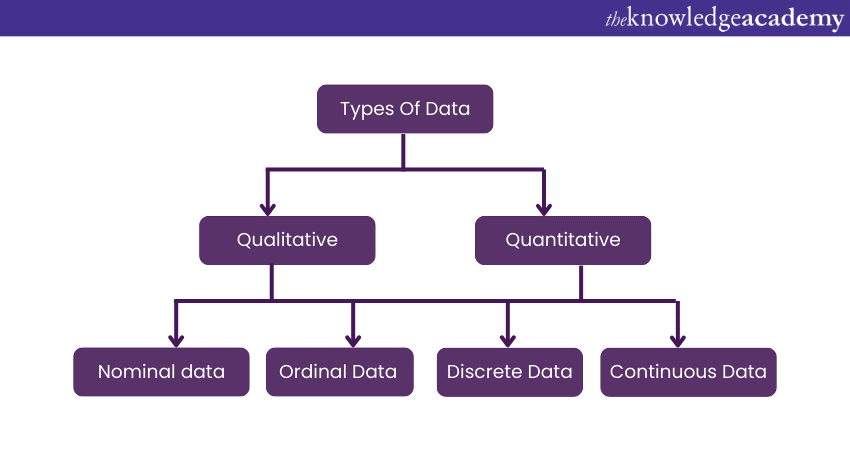
1) Qualitative Data
Qualitative, or Categorical Data, encompasses non-numerical information that falls into distinct categories. Categorical variables describe attributes like a person's gender or hometown and are defined using natural language rather than numerical values.
While Categorical Data can sometimes include numerical values, these numbers lack mathematical significance. Its examples include birthdates, favourite sports, or school postcodes. Although birthdates and school postcodes contain quantitative values, they do not hold numerical meanings. Within Qualitative Data, there are two subcategories: Nominal Data and Ordinal Data. Let's have a brief look at them:
a) Nominal Data:
Nominal Data, also referred to as Nominal Scale Data, serves to label variables without assigning numerical values. This type of Data cannot be ordered or measured. Examples of Nominal Data include letters, symbols, words, and gender. Analysis of Nominal Data involves grouping the Data into categories and calculating frequencies or percentages. Visual representations, such as pie charts, help illustrate Nominal Data distribution.
b) Ordinal Data:
Ordinal Data follows a natural order, unlike Nominal Data. In Ordinal Data, the difference between Data values is not determined, but there exists an inherent ranking. Ordinal Data is commonly encountered in surveys, finance, economics, and questionnaires. Bar charts and various visualisation tools are used to represent and interpret Ordinal Data. Information can be presented in tabular form, with each row displaying distinct categories.
2) Quantitative Data
Quantitative Data, often referred to as Numerical Data, involves measurements and numerical values. It provides precise information about quantities, frequencies, or measurements. Common examples of Quantitative Data include height, weight, temperature, and income. This type of data allows for mathematical operations and statistical analysis to derive meaningful insights and patterns. In the context of Discrete Mathematics, Quantitative Data is further classified into two types: Discrete Data and Continuous Data. Let's have a brief look at them: Quantitative Data is further classified into two types: Discrete Data and Continuous Data. Let's have a brief look at them:
a) Discrete Data:
Discrete Data can assume only distinct, finite values that cannot be meaningfully subdivided. These values are typically whole numbers and represent countable items. For instance, the number of students in a class is a Discrete Data point.
b) Continuous Data:
Continuous Data encompasses values that can be measured and possess an infinite number of possible selections within a defined range. Temperature range is an example of Continuous Data. This type of Data provides information on how much or to what extent its values can take any position within the specified range.
Unlock the power of data with our Data Science with R Training and propel your career to new heights!
How to Analyse Data?
Data Analysis is a pivotal research component. It is the linchpin for deriving valuable insights. It includes two primary ways: qualitative and quantitative Data Analysis, each offering distinct techniques tailored to their unique Data characteristics. Let's see how it can be analysed:
1) Data Analysis in Qualitative Research
Qualitative Data Analysis comes into play when dealing with non-numeric, often unstructured Data, such as text, images, or narrative descriptions. Researchers employ qualitative analysis to extract meaning and patterns from this rich, contextual information.
It is particularly valuable for exploratory research, where the objective is to gain a deeper understanding of a subject or phenomenon. The hallmark of Qualitative Data Analysis is its manual, interpretive nature.
Researchers immerse themselves in the Data, scrutinising text, images, and narratives and identifying recurring themes, codes, or keywords. A word-based approach is a common technique for finding these patterns, and various qualitative analysis methods are used, such as thematic or content analysis.
2) Data Analysis in Quantitative Research
Conversely, quantitative research hinges on numerical Data. The initial quantitative research phase involves Data preparation, a critical step encompassing Data validation, editing, and coding.
Once the Data is meticulously curated, researchers can apply various quantitative analysis techniques. This often leads to precise numerical outcomes, making it an ideal choice for research focused on quantifying relationships, variables, or phenomena.
However, Quantitative Data Analysis may not always reveal the underlying reasons or motivations behind the Data. It may require researchers to select the most appropriate analysis methods that align with their research objectives.
Unlock your potential with hands-on Data Engineering Projects. Start building today and advance your career!
How is Data Stored?
Computers store data like text, images, sound, and video using binary values, which are just 1s and 0s. The smallest piece of data is called a "bit," and it represents one value. Eight bits make up one byte. Memory and storage are measured in units like megabytes, gigabytes, terabytes, petabytes, and exabytes. As we generate more data, scientists keep creating new, larger measurements.
Data can be stored in different file formats using systems like ISAM and VSAM. There are also other formats for converting, processing, and storing data, like comma-separated values (CSV). These formats are used on many types of machines, even though more structured methods are becoming more popular in today's tech world.
Transform your data into valuable insights with our professional Data Cleaning services—get started now!
Uses of Data
Data is pivotal in our increasingly Data-driven world, offering diverse applications across various domains. Here are some critical uses of Data:
a) Business Intelligence: Companies leverage Data to gain insights into operations, customer behaviour, and market trends. This helps in making informed decisions, enhancing efficiency, and improving profits.
b) Healthcare: Data aids in patient diagnosis, drug development, disease monitoring, and personalised treatment plans. Electronic Health Records (EHRs) have revolutionised healthcare Data management.
c) Finance: Financial institutions use Data for risk assessment, fraud detection, investment strategies, and customer profiling. Algorithms analyse vast Datasets to make rapid trading decisions.
d) Marketing: Data-driven marketing allows businesses to target specific audiences, optimise campaigns, and measure their impact. Customer Data shapes personalised advertising and content.
e) Security: Data is used in surveillance, threat detection, and cybersecurity to protect against unauthorised access, cyberattacks, and other security risks.
Unlock the world of Data-driven opportunities with our comprehensive Data Science Training - join today to start your Data Science journey!
Jobs in Data
Here are a few in-demand jobs that require analytical skills:
1) Business Intelligence Analysts (BIA)
2) Database Developer
3) Database Administrator
4) Data Scientist
5) Data Analytics Manager
What is Data in a Computer?
Data in a computer is raw, unprocessed information like numbers, text, images, or audio stored digitally. It lacks context and requires processing by software or systems to become meaningful. Examples include files, databases, or binary code used for various tasks like analysis or storage.
What is Data vs Information?
Data refers to raw, unorganised facts like numbers or text, while information is processed data that provides context or meaning. For instance, "50, 100" is data, but "50 students scored above 100 marks" is information. Information is derived from data to make it useful and understandable.
Conclusion
Data and its diversity, from simple numbers to intricate narratives, empower us to explore, understand, and make informed decisions. From science and business to everyday life, Data is the compass guiding our choices. It carries the potential to illuminate patterns, reveal insights, and uncover hidden truths. Hopefully, this blog has helped you understand What is Data and grasp its fundamental concepts and nuances.
Unlock the world of data insights with our Data Science Analytics Course – start your journey to data mastery today!
Frequently Asked Questions
How Can Data Solve Problems?

Data solves problems by providing insights through analysis, identifying patterns, and enabling informed decisions. It helps optimise processes, predict outcomes, and design solutions. For example, analysing sales data can improve strategies, while healthcare data aids in better diagnosis and treatment.
What are the Common Threats to Data?

Common threats to data include hacking, malware, unauthorised access, phishing, and accidental deletion. Natural disasters, hardware failure, and insider threats also risk data security. Protecting data requires encryption, backups, strong passwords, and robust cybersecurity measures.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Data Analytics and AI Courses, including the Advanced Data Analytics Course, Advanced Data Science Course and AI and ML with Excel Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Data Reconciliation.
Our Data Analytics and AI Blogs cover a range of topics related to Data Analytics, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Data Analytical skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Data, Analytics & AI Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Python Data Science Course
Python Data Science Course
Mon 21st Jul 2025
Mon 8th Sep 2025
Mon 24th Nov 2025
Mon 8th Dec 2025
Tue 27th Jan 2026
Mon 4th May 2026
Mon 7th Sep 2026
Mon 2nd Nov 2026






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


