We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344 203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Nanotechnology is often heralded as the frontier of modern science, but What is Nanotechnology exactly? Imagine a world where materials are manipulated at the tiniest scales, creating stronger, lighter, and more reactive products. This isn’t the realm of science fiction—it’s the reality of Nanotechnology. Read ahead to learn more!
How does this cutting-edge technology work, and what sets it apart? In this blog, we will explore What is Nanotechnology, the production of nanomaterials, their astonishing applications, and the potential risks and ethical dilemmas. Ready to dive into the nanoscale universe? Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
1) What is Nanotechnology?
2) The Importance of Nanotechnology
3) How is Nanotechnology Produced?
4) Risks and Challenges of Nanotechnology
5) Use Cases of Nanotechnology
6) The Future of Nanotechnology
7) Conclusion
What is Nanotechnology?
Nanotechnology is an exciting area of science and engineering that involves the modification of matter at the atomic and molecular levels. Essentially, it involves working with materials that have dimensions measured in nanometres (one billionth of a metre). To put this in viewpoint, a human hair is around 80,000 nanometres wide. This technology allows scientists and engineers to develop new materials and devices with unique features and functions.
Nanotechnology enables the development of stronger, lighter, and more chemically reactive products by operating at an extremely small scale. These developments have the capacity to revolutionise several industries, from healthcare to electronics, by offering solutions that were previously unattainable.
The Importance of Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology holds immense potential across various fields due to its ability to revolutionise how we approach problems and develop solutions. Here are key points highlighting its importance:
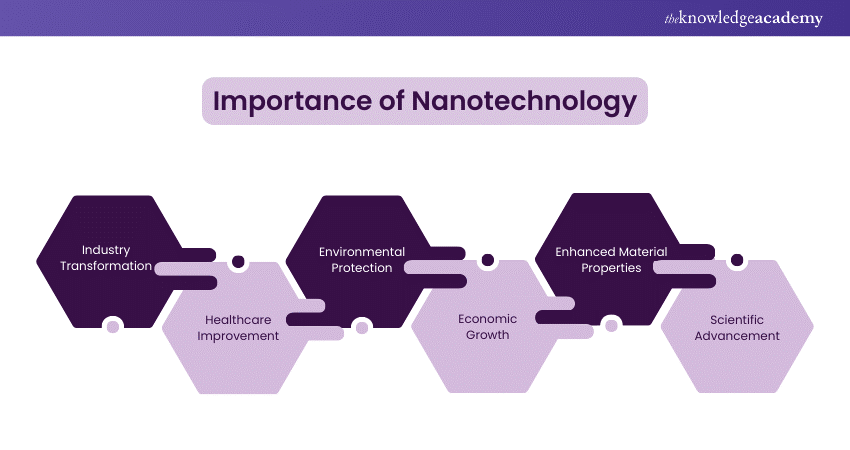
1) Industry Transformation: Nanotechnology revolutionises industries by developing stronger, lighter, and more chemically reactive materials.
2) Healthcare Improvement: Nanotechnology advances diagnostics, drug delivery, and treatments, leading to more effective, personalised healthcare solutions.
3) Environmental Protection: Nanotechnology aids environmental protection by improving pollution control, waste management, and creating sustainable energy solutions.
4) Economic Growth: Nanotechnology drives economic growth by creating markets and jobs, fostering innovation, and enhancing industry competitiveness.
5) Enhanced Material Properties: Nanotechnology develops materials with superior conductivity, thermal resistance, and strength that are applicable in various fields.
6) Scientific Advancement: It drives scientific research, leading to new discoveries and expanding our understanding of matter at atomic and molecular levels.
Discover cutting-edge Advanced Technologies Courses - start learning today for professional growth and development!
How is Nanotechnology Produced?
Here are several approaches used to produce nanomaterials:
Top-down Approaches
1) These methods involve breaking down larger materials into smaller components or structures at the nanoscale.
2) Techniques like lithography, laser ablation, chemical etching, and mechanical milling are employed to precisely remove or carve out material from a bulk sample.
3) This approach is widely used in the fabrication of integrated circuits and nanoelectronics.
Bottom-up Approaches
1) These methods involve building up nanomaterials from smaller components, such as atoms or molecules.
2) Chemical synthesis and self-assembly techniques are used to create nanostructures by arranging individual atoms or molecules in a controlled manner.
3) Examples include the synthesis of nanoparticles, quantum dots, and carbon nanotubes through chemical reactions or self-assembly processes.
Self-assembly
1) This approach relies on the intrinsic properties of materials to spontaneously organise themselves into desired nanostructures.
2) Techniques like template-assisted self-assembly and directed self-assembly are employed to guide the self-organisation process.
3) Self-assembly is observed in the production of block copolymers, where different polymer chains organise into distinct nanodomains.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)
1) In this method, a material is vaporised and then deposited onto a surface to form a thin film.
2) PVD techniques include sputtering, evaporation, and pulsed laser deposition.
3) PVD is commonly used for coating cutting tools, creating thin-film coatings, and depositing nanostructured films.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
1) This approach involves the reaction of gaseous precursors with a surface, leading to the deposition of a thin film or nanostructured material.
2) CVD is widely used in the production of thin films for solar cells, semiconductor devices, and protective coatings.
Enhance your skills with Internet Of Things IoT Systems and Applications Training – sign up now for expert guidance!
Risks and Challenges of Nanotechnology
Despite its promising potential, Nanotechnology comes with its share of risks and challenges that need careful consideration.
Potential Health and Environmental Hazards
The small size of nanoparticles allows them to communicate with biological systems in ways that larger particles cannot. This poses potential health risks, as nanoparticles can enter cells and tissues, potentially causing harmful effects. Moreover, their impact on the environment is not fully understood, raising concerns about their safe disposal and long-term ecological effects.
Economic Implications
The economic implications of Nanotechnology are significant. While it can drive economic growth by creating new markets and industries, it can also disrupt existing ones. The cost of developing and commercialising Nanotechnology can be high, and the benefits may not be immediately apparent, posing financial risks to investors and companies.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations are also paramount. The potential for Nanotechnology to alter the fabric of society, from enhancing human capabilities to creating new forms of surveillance, raises important ethical questions. Ensuring that Nanotechnology is developed and used responsibly requires robust regulatory frameworks and ethical guidelines.
Take your Quantum Computing skills further by joining Quantum Computing Training to harness the power of technology!
Use Cases of Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology’s integration into daily life is profound, with its applications spanning various industries. Here’s an overview of its practical uses:
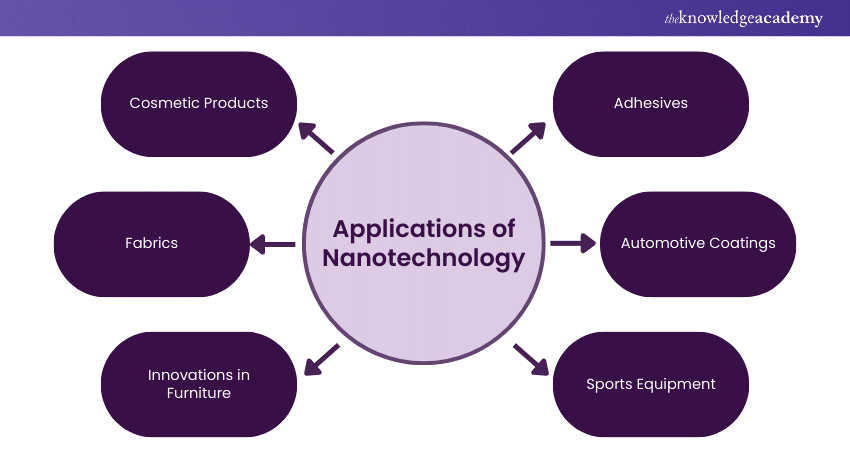
1) Cosmetic Products
Sunscreens incorporate nanoparticles like titanium dioxide and zinc oxide to effectively block UV rays while remaining sheer and lightweight on the skin.
2) Fabrics
Water-resistant clothing and accessories benefit from silica nanoparticles, which repel moisture. Additionally, silver nanoparticles are used for their antimicrobial properties, keeping garments fresher for longer and reducing the need for frequent washing. Titanium dioxide is employed to render cotton fabrics resistant to wrinkling.
3) Innovations in Furniture
Nanoparticles of silver, copper, and zinc are applied to furniture to combat pests and fungi. Titanium dioxide is sometimes used to repel dust and contaminants, enhancing furniture longevity and reducing maintenance needs. Notably, carbon nanofiber coatings can decrease the flammability of upholstered furniture by 35%.
4) Adhesives
High-temperature-resistant nano-adhesives have been developed, maintaining their adhesive properties even under extreme heat. These adhesives, measuring just 1 nm in thickness, are ideal for applications in electronics and machinery.
5) Automotive Coatings
Nano-ceramic coatings are applied to vehicles to protect against UV radiation and environmental pollutants. They also provide a barrier against corrosive substances like bird droppings. For instance, Nano Repel has created a high-performance coating that shields cars from such damage and prevents stains on upholstery.
6) Sports Equipment
The sports sector utilises nanomaterials like carbon nanotubes and silica nanoparticles to enhance the performance and durability of equipment. Nanomaterials enhance sports gear, making it durable, lighter, and stronger for better athletic performance.
The Future of Nanotechnology
Nanotech is poised to revolutionise medicine with precise drug delivery and enhanced diagnostic tools. In the realm of electronics, it promises breakthroughs in miniaturised transistors and the advent of Quantum Computing, potentially unlocking extraordinary processing capabilities.
Furthermore, nanotech is set to be instrumental in tackling pressing global issues like energy sustainability and environmental conservation. Nanotech advances are shaping future energy solutions with enhanced storage and solar cells.
Dive into the world of Nanotechnology through our detailed Nanotechnology Training - join us today and expand your knowledge!
Conclusion
You’ve learned What is Nanotechnology: an exciting venture into manipulating matter at the tiniest scales, transforming industries with stronger, lighter, and more advanced materials. Despite its risks and ethical challenges, Nanotechnology's boundless innovative potential promises a future of incredible advancements. Embrace the future of innovation with Nanotechnology!
Gain proficiency in Reverse Engineering methods - register today for comprehensive Reverse Engineering Training and practical insights!
Frequently Asked Questions

a) Nanotechnology improves drug delivery systems, enhancing medical treatments.
b) It facilitates the creation of ultra-thin electronic displays for advanced devices.
c) Nanomaterials are integral to developing lightweight, high-performance sports equipment.

The biggest problem in Nanotechnology is managing potential health and environmental risks. This necessitates rigorous safety assessments and regulatory frameworks to ensure safe deployment and disposal of nanomaterials.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Advanced Technologies Courses, including Nanotechnology Training, Reverse Engineering Training, and Internet of Things IoT Systems and Applications Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Reverse Engineering.
Our Advanced Technology Blogs cover a range of topics related to Nanotechnology, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Advanced Technology skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Advanced Technology Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Nano Technology Training
Nano Technology Training
Fri 29th Nov 2024
Fri 24th Jan 2025
Fri 21st Mar 2025
Fri 2nd May 2025
Fri 27th Jun 2025
Fri 29th Aug 2025
Fri 3rd Oct 2025
Fri 5th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


