We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +971 8000311193 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Do you want to understand the forces that shape markets and the policies that impact your pockets? Welcome to the intriguing world of economics, but What is Economics? It's the study of the diverse choices that individuals, businesses, and nations make regarding the allocation of resources. Essentially, economics tracks the dance of supply and demand that drives our daily lives.
If you want a deeper insight into What is Economics, this blog is your ideal source of knowledge. So read on and simplify your understanding of economics and its diverse far-reaching implications.
Table of Contents
1) What is Economics?
2) The Basics of Microeconomics
3) The Basics of Macroeconomics
4) What do Economists do?
5) Key Economic Indicators Explained
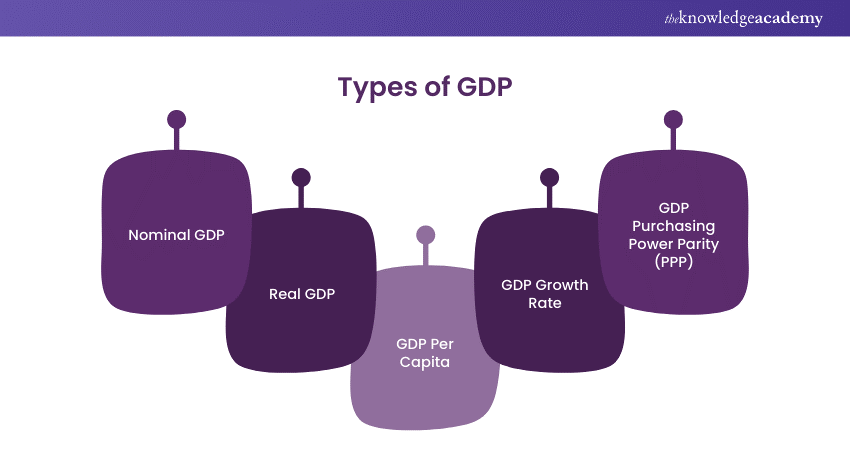
6) What is GDP, and Why is It Important in Economics?
7) What is the Role of Markets in Economics?
8) Conclusion
What is Economics?
Economics is a social science focused on the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The study of economics is primarily concerned with analysing the choices that businesses, individuals, governments, and nations make to allocate limited resources. This field impacts many other fields, including psychology, politics, gender, environment, business, and law.
The Basics of Microeconomics
Microeconomics involves studying the implications of individual human action and is the key to a person's financial health. It shows why and how different goods have different values. It addresses how businesses and individuals conduct and benefit from efficient production and exchange and how individuals can best coordinate with each other. Microeconomics offers a more comprehensive understanding of individuals, firms, and markets.
The Basics of Macroeconomics
Macroeconomics is a branch of economics that studies the behaviour of an overall economy, encompassing businesses, markets, consumers, and governments. It examines economy-wide phenomena such as price levels, inflation, economic growth rate, gross domestic product (GDP), national income, and changes in unemployment.
Some of the main questions addressed by macroeconomics include:
1) What causes unemployment?
2) What causes inflation?
3) What creates or stimulates economic growth?
Macroeconomics attempts to measure an economy's performance, understand what forces drive it, and project how performance can improve.
Want to learn how to collect and analyse historical data for greater financial information? Sign up for our detailed Financial Modelling and Forecasting Training now!
What do Economists do?
Economists play diverse roles, such as consultants, government advisors, professors, and private sector employees. Using empirical data or theoretical models, they evaluate programs, study human behaviour, and explain social phenomena. Their contributions inform everything from household decisions to public policy.
Their tasks include:
1) Forecasting market trends
2) Advising businesses, governments, and individuals
3) Recommending solutions to economic problems
4) Writing articles for academic journals and other media
Key Economic Indicators Explained
Economic indicators outline a country's economic performance. Published periodically by governmental agencies or private organisations, these economic indicators often considerably affect employment, stocks, and international markets. They may predict future economic conditions that drive markets and guide investment decisions. Let’s explore the key economic indicators.
1) Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
The Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the most comprehensive measure of a country's economic performance. It calculates the total market value of a country's finished goods and services in a given year. Many investors, analysts, and traders focus on the advance GDP report and the preliminary report, both issued before the final GDP figures. However, GDP is considered a lagging indicator, implying that it can confirm a trend but can't predict it.
2) Retail Sales
The retail sales report (generated during the middle of each month) measures the total receipts of all merchandise sold in stores. Sampling retailers across the country serve as the proxy of consumer spending levels. Consumer spending represents more than two-thirds of the GDP, proving useful for gauging the economy's general direction
3) Industrial Production
The industrial production report is released monthly by the Federal Reserve and reports changes in the production of mines, factories, and utilities. The capacity utilisation rate, which is included in this report, estimates the portion of productive capacity being used rather than standing idle in the economy. If its level is below 80%, the likelihood of a recession may increase.
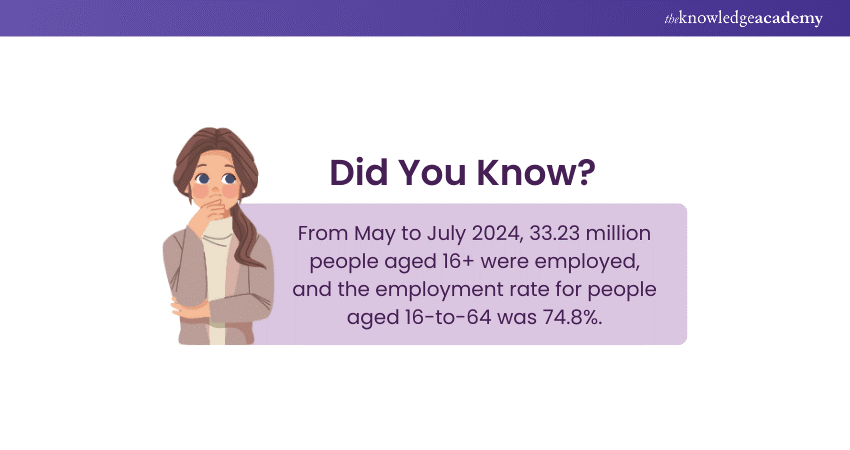
4) Employment Data
The UK Data Service holds a full range of labour market and employment data from key government surveys. A sharp increase in employment is indicative of prosperous economic growth, and contractions may be imminent if a significant decrease occurs. However, these are generalisations, and it is important to consider the economy's current position.
5) Consumer Price Index (CPI)
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is the benchmark for measuring inflation as it determines the level of retail price changes, and the costs consumers pay. The CPI compares the monthly price changes and year after year. The release of this report may increase volatility in fixed income, equity, and forex markets. Greater-than-expected price increases are a sign of inflation, which'll likely cause the underlying currency to depreciate.
What is GDP, and Why is It Important in Economics?
GDP, or Gross Domestic Product, represents the total value of all goods and services produced within a country over a specific period. It is crucial as it reflects the economy’s size, growth trends, and overall health, guiding policymakers and investors in economic planning.
What is the Role of Markets in Economics?
Markets are essential in economics as they enable the buying and selling of goods and services. They allocate resources efficiently, determine prices through supply and demand, and encourage competition and innovation. Markets drive economic activity and connect consumers with producers effectively.
Learn to manage investments and maximise returns effectively with our Finance Courses!
Conclusion
In conclusion, economics goes beyond mere numbers and graphs. It's essentially the story of individual and business choices that shape our world. By understanding What is Economics, you gain valuable insights into the forces that dictate the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services on individual and national level. The diverse aspects of economics outlined in this blog will equip you with the knowledge to analyse global trends.
Learn how to project indirect costs pertaining to warehousing, transportation and taxes in our comprehensive Costing and Pricing Training – Register now!
Frequently Asked Questions

With a background in economics, you can pursue roles like Financial Analyst, Economic Consultant, Data Analyst, Policy Advisor, Market Researcher, Investment Banker, or academic. Opportunities also exist in global organisations like the IMF, World Bank, and governmental agencies.

Inflation impacts the economy by reducing purchasing power, making goods and services costlier. Moderate inflation can drive economic growth, but excessive inflation leads to uncertainty, erodes savings, and increases living costs, affecting both consumers and businesses negatively.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Management Courses, including the Economics for Managers Course and the Costing and Pricing Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into How to Build a Financial Model.
Our Accounting and Finance Blogs cover a range of topics related to economics, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your economics knowledgebase, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Accounting and Finance Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Economics for Managers Course
Economics for Managers Course
Fri 10th Jan 2025
Fri 14th Mar 2025
Fri 9th May 2025
Fri 11th Jul 2025
Fri 12th Sep 2025
Fri 14th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


