We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on + 1-866 272 8822 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Embarking on a Cybersecurity career implies passing intensive interviews that would let you show your success in information security domains. However, the Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) is considered one of the highest-level certifications in the industry. While candidates aiming to pass the CISSP Interview Questions need to endure a rigorous preparation process, they would be presented with a great number of difficult questions.
Every question is painstakingly chosen to cover a wide range of areas, with topics ranging from fundamental principles to sophisticated Cybersecurity principles. This blog will lead its readers to the framework of the CISSP Interview Questions concisely.
Table of Contents
1) CISSP Interview Questions & answers
2) Basic-level CISSP Interview Questions
3) Intermediate-level CISSP Interview Questions
4) Advanced-level CISSP Interview Questions
5) Conclusion
CISSP Interview Questions & answers
Through CISSP Interviews, candidates commonly receive a vast selection of inquiries designed to assess their Cybersecurity knowledge, skills, and technology. Be it the network security fundamentals or the details of monitoring risk control, each question is aimed at checking the candidate's expertise level.
However, the correct choice of words and proper responses can demonstrate how the candidates are prepared. It shows whether an individual is ready to tackle current Cybersecurity problems and latest technologies.
Basic-level CISSP Interview Questions
Basic-level CISSP Interview Questions typically cover foundational concepts in Cybersecurity. Candidates may be asked about fundamental principles, terminology, and best practices. Let's explore some of those questions in detail:
1) What Is the Current Cost of Taking the CISSP Exam?
This question is designed to assess the seriousness and commitment to professional development. It determines whether the candidate has done enough research and planned for certification costs to manage their career-related expenses.
Sample Answer: The current cost of the CISSP exam is approximately £585. However, I recommend checking the official (ISC)² website for the most up-to-date fee, as prices may vary or change.
2) What Are the Best Study Guides Available for Preparing for the CISSP Exam?
The question assesses your level of engagement and research within industry standards, showing your dedication to passing the examination.
Sample Answer:
For CISSP exam preparation, I suggest the (ISC)² CISSP Official Study Guide for its extensive coverage, Shon Harris's CISSP All-in-One Exam prep material for detailed coverage and Eric Conrad's CISSP Practice Exams for its practice questions. Furthermore, the (ISC)² CISSP CBK is also recommended for understanding basic foundation and core concepts.
3) Where Can I Find Reliable CISSP Practice Exams to Help Me Prepare for the Actual Test?
The interviewer asks this question to see if you are prepared and familiar with the resources available to help you obtain reliable study materials. It also tests your ability to make the best use of available resources.
Sample Answer: I would look for reputable CISSP practice exams on reputable websites such as ISC2's official site or trusted study platforms like Cybrary or Udemy. In addition, I would look for practice exams suggested in CISSP study guides and forums such as Reddit or specialised security certification groups.
The interviewer checks whether you are prepared and well acquainted with the resources available to assist you obtain dependable
4) What Are the Steps and Requirements for Renewing a CISSP Certification?
The interviewer typically asks this question to assess your knowledge about the CISSP certification renewal process. It makes it easier to evaluate whether you are aware of the requirements needed to maintain the validity and recertification of the CISSP license.
Sample Answer: In order to stay updated of your CISSP Certification, you need to submit your renewal application before the certification expires. Moreover, you should stay on loop with any renewal process changes by checking the (ISC)² website in this regard.
5) Is Obtaining a CISSP Certification Worth the Investment in Time and Money?
The interviewer gauges your thoughts and views on CISSP certifications and their capacity for career advancement and prospective job opportunities. They want to assess whether your goal aligns with the CISSP certifications which would be rewarding to the effort and expense involved.
Sample Answer: I believe obtaining a CISSP certification is worth the investment because it significantly enhances career prospects and credibility in the cybersecurity field. Despite the time and cost, the advanced knowledge and recognition you gain can lead to better job opportunities and higher salaries.
6) What Are the Eligibility Requirements for Taking the CISSP Exam?
The interviewer asks this question to analyse your understanding of the essential criteria needed to sit for the CISSP exam. They want to ensure you know the qualifications, experience, and prerequisites necessary to be eligible for the certification.
Sample Answer: As a student, I understand that to be eligible for the CISSP exam, you need at least five years of work experience in information security, with at least three years in one or more of the CISSP domains. Conversely, you can still become an Associate of (ISC)2 if you don't meet these requirements.
7) What Are the Steps Involved in Becoming CISSP Certified?
The interviewer asks this to assess your awareness of the certification process. They want to know if you're aware of the steps involved in becoming a CISSP-certified professional, from studying for the exam to passing it and meeting the required experience.
Sample Answer: To become CISSP certified, I would first study the CISSP domains and use various resources like study guides and practice exams. Then, I'd register for and pass the CISSP exam. Lastly, I’d need to provide proof of my work experience and agree to the (ISC)² Code of Ethics to get certified.
8) Over Which Port Does the Ping Utility Operate?
This question seeks to know about the candidate's technical knowledge regarding networking protocols and utilities.
Sample answer: The instrument Ping does not work over a port number and utilises the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP). Rather, it makes the ICMP echo request message and continues to be inactive for the ICMP echo reply message to compute the round-trip time.
9) Define Malware.
This question is purposed to assess the candidate's knowledge on the topic of Cybersecurity threats and terminology. It aims at evaluating the candidate’s skills in identifying and distinguishing between the multiple classes of malicious software.
Sample answer: Malware designates a software, intended to be destructive to the target computer, server, client, or network. It mostly encompasses viruses, worms, Trojans, ransomware, spyware, and adware.
10) Explain the Concept of Patch Management.
This question examines the candidate's understanding of the Cybersecurity practice and their processes. It intends to assess if the applicant appreciates the essence of keeping up to date with the security of software systems through patch management.
Sample answer: Patch management constitutes the activity of searching for, acquiring and testing the patches/updates then applying them to software systems with the aim of addressing vulnerabilities, bugs or security issues. It targets the software and limiting the software's vulnerability to the hacker’s attack by pinpointing the attack zone.
11) Which Access Control Mechanism Allows Multiple Users From a Group to Access a Resource?
This question evaluates the candidate's awareness of access control mechanisms usage and applying them in network security practice. It tries to evaluate the candidates' level of understanding about using role-based access control (RBAC) and its benefits in managing permissions.
Sample answer: RBAC control system grants several members of a group to obtain a common resource. It puts the rights and duties of different user roles and users as per their duties and jobs.
12) Can You Elaborate on Access Control Services?
The main goal of this question is to assess the candidate’s knowledge about Cybersecurity hazards, which include phishing attack mechanism. Moreover, it measures whether the candidate can explain how cybercriminals can obtain sensitive information through the use of various tactics.
Sample answer: Phishing schemes are mostly carried out when a website, an email or a message which seem to come from a legitimate source are used. Through this, attackers lure the users to reveal their passwords, login credentials, or financial data by pretending as a trustworthy source.
Establish your expertise in information security - join our CISSP Certification now!
Intermediate-level CISSP Interview Questions
Intermediate-level CISSP Interview Questions delve deeper into specific areas of Cybersecurity. These questions may explore topics like encryption algorithms, incident response procedures, security assessments, and security architecture design principles. Let's discuss some of those questions in the following points:
13) What Is the Average Salary for Professionals Holding a CISSP Certification?
The interviewer asks such questions to understand if you know the value of this certification in the job market. It also checks your awareness of industry standards and salary expectations related to your qualifications.
Sample Answer: The average salary for professionals holding a CISSP certification in the UK typically ranges from £70,000 to £90,000 per annum, depending on experience, location, and inflated rates. In London, it can go even higher due to demand in the cybersecurity sector.
14) How Does the CISM Certification Compare to the CISSP Certification in Terms of Career Opportunities and Industry Recognition?
This question tests your comprehension of the distinctions between the CISM and CISSP certifications, particularly their effects on career pathways and industry recognition. They want to know if you can compare the two certifications and understand their significance in the cybersecurity field.
Sample Answer: Both CISM and CISSP certifications are highly respected, but CISM focuses more on management and governance, while CISSP is a broader certification that covers various cybersecurity domains. In addition, CISSP offers more global recognition, while CISM is valued for leadership roles in information security management.
15) How Does the CISSP Certification Differ From the Security+ Certification in Terms of Requirements and Career Benefits?
The interviewer asks this to see if you understand the key differences between CISSP and Security+ certifications, particularly regarding prerequisites and how each impacts career growth. Additionally, it helps assess your knowledge of cybersecurity certification paths.
Sample Answer: CISSP is more advanced and requires several years of experience, while Security+ is entry-level and has no strict experience requirement. In addition, CISSP offers higher career growth and global recognition, while Security+ is excellent for starting a cybersecurity career and building foundational skills.
16) What Are the Main Differences Between the Ceh (Certified Ethical Hacker) and CISSP Certifications?
The interviewer asks this question to explore your understanding of the distinctions between CEH and CISSP, particularly with regard to focus areas, abilities, and potential careers. It also helps you determine whether you can distinguish between a certification that focuses on ethical hacking and cybersecurity management.
Sample Answer: CEH focuses more on ethical hacking and penetration testing and teaches you offensive security skills, while CISSP covers a broader range of cybersecurity topics, including management and governance. Moreover, CEH is ideal for hands-on roles, while CISSP is more suited for leadership and strategic positions.
17) How Does the SSCP Certification Compare to the CISSP Certification in Terms of Scope and Difficulty?
The interviewer asks this question to understand your knowledge of the differences between SSCP and CISSP certifications. They want to know how well you understand the scope and difficulty of each certification, as this can indicate your level of expertise and readiness for cybersecurity roles.
Sample Answer: SSCP is more focused on fundamental cybersecurity skills and is usually regarded as simpler, making it appropriate for entry-level positions. CISSP, on the other hand, covers a broader and deeper range of topics, necessitating more experience and knowledge, and is frequently regarded as more complex and targeted at higher-level positions.
18) What Role Does an Information Systems Security Manager Play, and How Does the CISSP Certification Help in This Career Path?
The interviewer asks this to see if you understand the key responsibilities of an Information Systems Security Manager and how the CISSP certification can support and enhance your career in this role. They want to see how well you understand the job and the importance of accreditation in preparing for it.
Sample Answer: An Information Systems Security Manager is responsible for protecting an organisation's data and IT infrastructure, as well as ensuring compliance with security policies and risk management. Alternatively, the CISSP certification benefits by providing advanced knowledge and skills in these areas, making it easier to deal with complex security challenges and advance in this career path.
19) What Are the Top Information Security Certifications Available Today, and Where Does the CISSP Rank Among Them?
The interviewer asks this to assess your understanding of the current information security certification landscape and to determine where you see the CISSP fitting in. They want to see if you can identify the best certifications and assess the CISSP's standing among them.
Sample Answer: Some of the top information security certifications today include CISSP, CISM, and CompTIA Security+. The CISSP is highly regarded and frequently regarded as one of the top certifications due to its broad coverage of security domains and industry recognition for advanced expertise.
20) How Are Phishing Attacks Executed?
This question concentrates on getting the candidate's understanding of phishing attacks, and the strategies used in their execution.
Sample answer: Phishing is commonly done through websites, fake emails, or messages. It aims to persuade people to give out confidential details, including logins, usernames, or banking details, by pretending to be involved in an authority matter.
21) What Steps Would You Take to Secure a New Server?
This question evaluates a candidate's ability to outline the necessary steps that enhance the security of a newly deployed server.
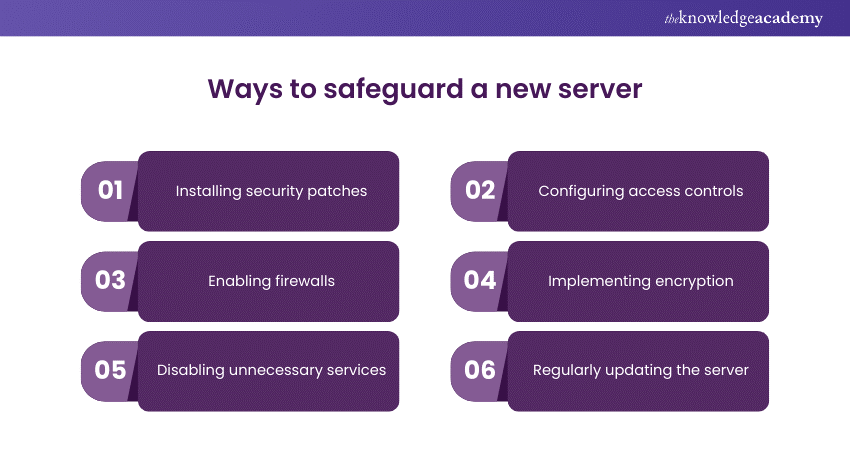
Sample answer: Securing a new server involves various steps such as installing security patches, configuring access controls, enabling firewalls, implementing encryption, disabling unnecessary services, and regularly monitoring and updating the server for security vulnerabilities.
22) Explain the Phases of Network Attacks.
This question seeks to evaluate the candidate's knowledge of the lifecycle of network attacks and their different stages. It assesses the candidate's ability to describe the various phases involved in launching and executing a network-based cyber-attack.
Sample answer: Network attacks typically unfold in several phases, including reconnaissance, scanning, exploitation, and exfiltration. During reconnaissance, attackers gather information about the target network. Scanning involves identifying vulnerabilities and weaknesses. Exploitation entails launching attacks to compromise systems. Exfiltration is the unauthorised extraction of data from the target network.
23) What Are the Distinctions Between BCP and DR?
This question evaluates the candidate's knowledge of Business Continuity Planning (BCP) and Disaster Recovery (DR) concepts. It assesses the candidate's knowledge of the differences between these two practices and how they ensure organisational resilience.
Sample answer: Business Continuity Planning (BCP) concentrates on maintaining important business functions during and after a disaster. Disaster Recovery (DR) focuses on restoring IT infrastructure and operations following a disruptive event, emphasising system recovery and resumption of services.
24) What are the key differences between IPv4 and IPv6 in terms of security features?
The interviewer asks this to assess your understanding of how IPv4 and IPv6 differ in security features. They want to see if you know the advancements and improvements in security that IPv6 offers over IPv4 and how these differences impact network security.
Sample Answer: IPv6 improves security over IPv4 by integrating IPsec support directly into the protocol, providing better encryption and authentication options. Additionally, IPv6’s design reduces the need for network address translation (NAT), which can simplify security configurations and enhance end-to-end security.
25) Which Type of Attack Utilises “Salesmanship” and Conversations?
This question aims to assess the candidate's understanding of social engineering attacks and their tactics. It seeks to evaluate the candidate's ability to identify and describe the type of attack that relies on manipulation techniques and interpersonal skills to deceive individuals.
Sample answer: Social engineering attacks utilise "salesmanship" and conversations to manipulate individuals into divulging confidential information or performing actions that compromise security. Examples include phishing, pretexting, baiting, and tailgating.
26) What Tools Exist for Asymmetric Key Authentication?
This question evaluates the candidate's knowledge of cryptographic authentication methods, specifically asymmetric key authentication. It aims to assess the candidate's familiarity with tools and technologies used for implementing asymmetric key authentication in secure communication systems.

Sample answer: Various tools exist for asymmetric key authentication, including Open Secure Sockets Layer (OpenSSL), GNU Privacy Guard (GnuPG), Secure Shell (SSH), and Microsoft BitLocker, offering robust encryption and authentication capabilities.
Safeguard your organisation's digital assets by joining our Chief Information Security Officer Training - book your spot now!
Advanced-level CISSP Interview Questions
Advanced-level CISSP Interview Questions delve into the intricacies of Cybersecurity, requiring candidates to demonstrate in-depth understanding and expertise. These questions can include advanced cryptography techniques, emerging threats, and the intricacies of incident response. To better understand such queries, let's go through the following points:
27) Elaborate on the CIA Triad.
This question aims to assess the candidate's understanding of fundamental concepts in Cybersecurity, specifically the CIA triad, which stands for Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. It seeks to evaluate the candidate's ability to explain the significance of each component and their interrelation in maintaining information security.
Sample answer: The CIA triad is a foundational concept in Cybersecurity that encompasses three essential principles: Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. Confidentiality ensures that data is accessible only to authorised individuals or entities, protecting it from unauthorised access or disclosure. Integrity ensures that data remains accurate, consistent, and unaltered throughout its lifecycle, safeguarding it from unauthorised modification or tampering.
28) What Are Your Post-CISSP Certification Objectives?
This question seeks to understand the candidate's career aspirations and goals following the completion of the CISSP certification. It aims to assess the candidate's motivation and commitment to professional development in the field of Cybersecurity.
Sample answer: “My post-CISSP certification’s objectives include further advancing my expertise in Cybersecurity through continuous learning and training. I aim to specialise in specific areas, such as cloud security or ethical hacking, as well as pursue additional certifications to broaden my skill set and enhance my career prospects. Additionally, I aspire to contribute to the Cybersecurity community through knowledge sharing, mentorship, and participation in industry events and forums.”
29) What Is the Rationale Behind the Presence of Various Fire Extinguisher Types on the Premises?
This question evaluates the candidate's understanding of fire safety measures and the purpose of different types of fire extinguishers. It aims to assess the candidate's knowledge of fire prevention and response strategies in various environments.
Sample answer: The presence of various fire extinguisher types on the premises is essential to effectively combat different classes of fires, such as Class A, Class B, and Class C fires. Each type of fire extinguisher is designed to extinguish specific types of fires involving different materials, such as wood, flammable liquids, or electrical equipment. By having a variety of fire extinguisher types available, organisations can ensure that they are prepared to respond to a range of fire hazards.
30) Define the Roles Involved in Data Classification.
This question aims to assess the candidate's understanding of data classification principles, and the roles involved in the data classification process. It seeks to evaluate the candidate's knowledge of the responsibilities of key stakeholders in managing and safeguarding sensitive information.
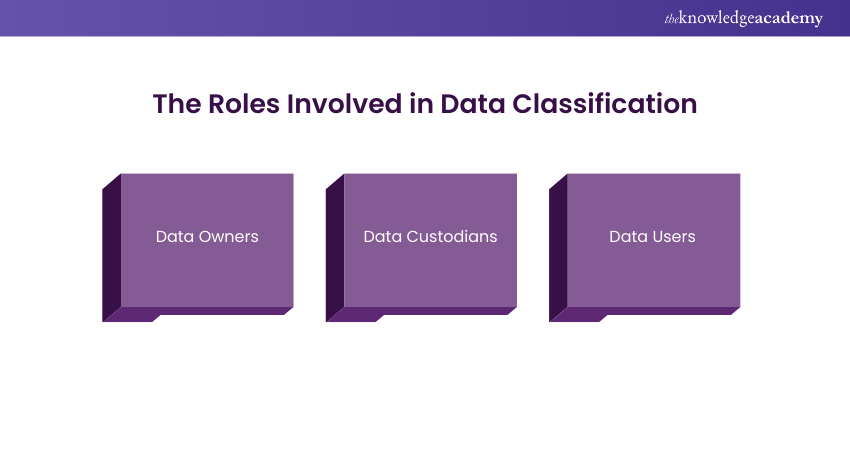
Sample answer: Data classification involves categorising data based as per its sensitivity, criticality, and regulatory requirements to determine appropriate protection measures. The roles involved in data classification include data owners, data custodians, and data users. Data owners are responsible for determining the classification of data and defining access rights based on its value and usage within the organisation. Data custodians are responsible for implementing security controls and managing data storage in accordance with classification requirements. Data users are individuals who access and utilise data within the organisation, adhering to access permissions and security policies established by data owners and custodians.
Elevate your skills and expand your opportunities with our CISSP-ISSAP Training - register today!
31) What Specific Considerations Are Pertinent to Cloud Computing?
This question evaluates the candidate's knowledge of Cloud Security's best strategies to mitigate risks in cloud-based deployments.
Sample answer: Several specific considerations are pertinent to Cloud Computing, including data security and privacy, compliance with regulations and standards, data residency and sovereignty, etc. Such aspects require implementing robust security measures like encryption, access controls, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits.
32) Expound Upon Five Principles of Secure Design.
This query allows the interviewer to understand the candidate's knowledge on Cybersecurity design principles. It further ascertains the candidate's familiarity with basic concepts and good practices when dealing with security aspects of application design and implementation.
Sample answer: The main five principles of secure design are the least privilege principle, defense in depth, fail-safe defaults, separation of duties, and simplicity. Their tasks comprise the following:
a) Least privilege- Ensures that users have enough access to perform their duties
b) Defence-in-depth- Defence-in-depth means installing several layers of security controls in order to adequately defend against the possible threats.
c) Fail-safe defaults- Enable systems to revert to a stable and secure condition by mitigating the effects of security breaches and system failures.
d) Separation of duties- Splits roles between individuals or groups to cut down on risks involved in conflicts of interest and abuse as well as fraud.
e) Simplicity- Allows to clarify the system design and improve the possibility of identification and addressing security vulnerabilities.
18) How Many Types of Firewalls Exist, and What Sets Them Apart?
This question evaluates the candidate's knowledge of network security principles and firewall technologies. It also assesses their understanding of different firewall types and their respective features.
Sample answer: There are several types of firewalls, including packet-filtering firewalls, stateful inspection firewalls, application-level gateways, and next-generation firewalls. Each type of firewall has unique features and capabilities that distinguish it from others.
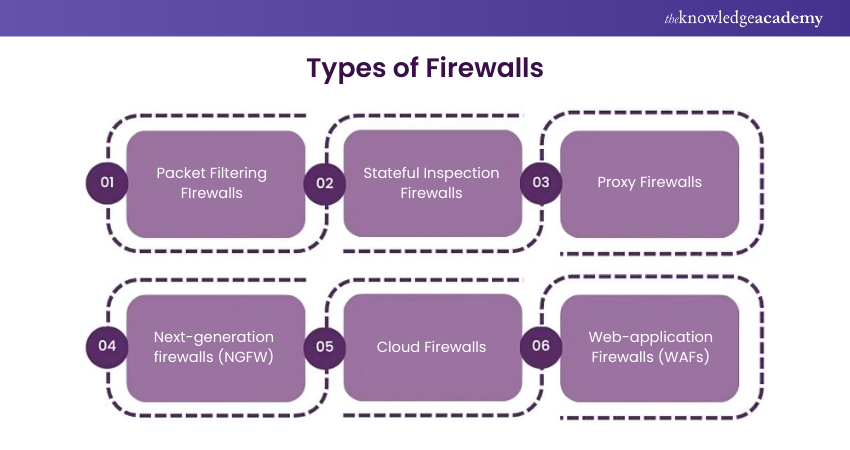
Packet-filtering firewalls inspect network packets and filter traffic as per certain predefined rules and criteria like IP addresses, ports, and protocols. Stateful inspection firewalls maintain state information about active connections and apply more advanced filtering based on the context of network traffic. Application-level gateways, also known as proxy firewalls, inspect application-layer protocols and provide granular control over network traffic. Next-generation firewalls integrate advanced threat detection and intrusion prevention capabilities, such as deep packet inspection, application awareness, and threat intelligence, to provide enhanced security against modern cyber threats.
34) How Do Organisations Classify Data, and Who Is Responsible for This Process? Why Is It Necessary?
This question is geared to seek the candidate's knowledge of data classification rules and their significance in the context of information security management.
Sample answer: Categorising data entails organising the data into various classes including public data, internal data, confidential data and restricted data, which are related to the value and sensitivity of the organisation. Moreover, data owners usually do this job by deciding data classifications and setting access rights based on the value of data and its usage by the organisation. The practice of data custodianship requires managers to implement security measures and manage data storage in compliance with exposure levels.
35) Define Security Models and Provide an Explanation for One Model.
This question assesses the candidate’s knowledge of security models in the Cybersecurity. It is meant to appraise the candidate on distinct methods of constructing and devising security policies and controls.
Sample answer: Security models define rules and structures for enforcing access controls and keeping confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information. An example of a security model is the Bell-LaPadula model, which operates on Mandatory Access Controls (MAC). It determines entry rights of entities to access objects according to their security level clearances. Alongside this, it safeguards the flow to avoid data leakage from top to bottom, which in turn protects confidentiality and information safety.
36) Describe the OSI Model.
This question concerns the candidate's knowledge of network protocols model and the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) and their role in providing a flow of communication between the network devices.
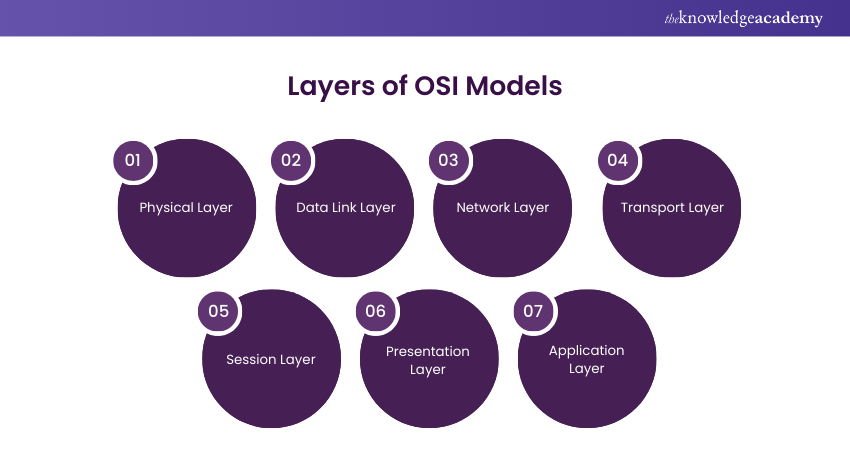
Sample answer: The OSI model is a conceptual framework that allows the standard publication of telecommunications functions or computing systems into seven layers of abstraction. Its main different layers include physical, data link, transport, network, application, session, and presentation. Their functionalities are as follows:
a) Physical layer- Looks after the transmission of raw data over physical media
b) Data link layer- Establishes and maintains links between devices on the same network
c) Network layer- Looks after the routing of data packets across numerous networks
d) Transport layer- Ensures reliable transmission of data between devices
e) Session layer- Manages communication sessions between applications
f) Presentation layer- Handles data formatting and translation
g) Application layer- Provides interfaces for applications to access network services
37) Explain TCSEC and ITSEC.
It is a knowledge test question that evaluates a candidate's understanding of Cybersecurity standards and evaluation criteria. It determines the candidate's comprehension of Trusted Computer System Evaluation Criteria (TCSEC) and Information Technology Security Evaluation Criteria (ITSEC) and their roles in identifying the security features of computer systems.
Sample answer: TCSEC, also known as the Orange Book, is a standard used by the US Department of Defense to evaluate the security capabilities of computer systems. It defines criteria for classifying and rating the security features of computer systems based on levels of trustworthiness, ranging from D (minimal protection) to A (verified protection). ITSEC is a European standard used to evaluate the security capabilities of information technology systems. It defines criteria for assessing the security functionality and assurance of IT products and systems, including requirements for security features, documentation, and testing. Both TCSEC and ITSEC provide guidelines and assurance levels for evaluating the security posture of computer systems and ensuring that they meet specified security requirements.
38) Define DoS and DDoS Attacks.
This question evaluates the candidate's understanding of denial-of-service (DoS) and distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. It aims to assess the candidate's knowledge of multiple types of cyber-attacks and their impact on network availability and performance.
Sample answer: A denial-of-service (DoS) attack is a cyber-attack which targets the network resources of a system by flooding it with a massive amount of traffic which overloads and thus denies the use of the original system. During DoS assault attacks, the attacker increases the intensity of Internet traffic or command redirecting through one attacker to a certain system. On the other hand, a Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attack is more advanced and involves various computers (botnets) organising and launching the simultaneous attack. It targets a single entity, which in turn results in more volume and better containment of the attack.
39) Discuss DevOps Security.
This question aims to assess the candidate's understanding of DevOps security practices and principles. It seeks to evaluate the candidate's knowledge of ensuring the security of software development and deployment processes.
Sample answer: DevOps security focuses on integrating security practices and principles into DevOps workflows to ensure that software development and deployment processes prioritise security. It involves incorporating security testing, automation, and compliance checks into DevOps pipelines to identify and remediate vulnerabilities throughout the software development lifecycle. DevOps security aims to foster a collaborative culture among development, operations, and security teams to address and minimise risks in software delivery. By integrating security into DevOps practices, organisations can accelerate time-to-market, improve software quality, and enhance overall security posture.
40) Define Banner Grabbing and OS Fingerprinting
This question aims to assess the candidate's understanding of reconnaissance techniques used by attackers to gather information about target systems. It seeks to evaluate the candidate's knowledge of banner grabbing and OS fingerprinting and their significance in Cybersecurity.
Sample answer: Banner grabbing and OS fingerprinting are reconnaissance techniques used by attackers to gather information about target systems. Banner grabbing involves retrieving information from application banners or service responses to identify system software and version numbers. Attackers can use banner grabbing to identify potential vulnerabilities or misconfigurations in target systems and tailor their attack strategies accordingly. OS fingerprinting involves analysing network packets or responses to figure out the operating system running on the target host.
41) What Recent Changes Have Been Made to the CISSP Exam Format or Content?
The interviewer typically asks such questions to assess your understanding of current CISSP exam updates and changes. They want to see if you stay up to date on the certification's evolution and understand how these changes may affect preparation and the exam.
Sample Answer: The recent change to the CISSP Exam is its updated content, which reflects its commitment to cybersecurity's latest trends and emphasis on cloud security and privacy. In addition, the exam format now includes a blend of multiple-choice and advanced questions to assess your practical knowledge and problem-solving skills.
42) What Are the Differences Between the Roles of a Chief Security Officer (CSO) and a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO), and How Can a CISSP Certification Benefit Each Role?
The interviewer asks this to assess your understanding of the differences between the CSO and CISO roles and how the CISSP certification supports them. They want to see if you can differentiate the responsibilities and explain the value that the certification brings to each position.
Sample Answer: The Chief Security Officer (CSO) usually handles every aspect of organisational security, including physical and information security, while the Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) focuses specifically on protecting information systems. Furthermore, the CISSP certification benefits both roles by providing advanced cybersecurity knowledge, but it is especially valuable for CISOs due to its emphasis on information security management and strategies.
Conclusion
In this blog, we have covered the Top 42+ CISSP Interview Questions and sample answers to help you prepare effectively for your next CISSP Interview. By understanding these questions and concepts, you can demonstrate your knowledge and expertise in Cybersecurity and increase your chances of success in the interview process.
Gain the expertise to protect vital data and systems - join our Information Systems Security Management Training now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 CISSP Certification
CISSP Certification
Mon 6th Jan 2025
Mon 17th Mar 2025
Mon 26th May 2025
Mon 14th Jul 2025
Mon 22nd Sep 2025
Mon 24th Nov 2025
Mon 8th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


