We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +800 312616 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Which Enterprise Architecture to choose - ITIL vs COBIT vs TOGAF? Organisations often ask this question while choosing the best framework for IT management and Enterprise Architecture. While these three prominent frameworks aim to enhance IT operations, they differ in focus areas, methodologies, and intended outcomes.
Did you know that the Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) has been adopted by the world’s top-tier companies, including NASA, the UK National Health Service (NHS) and Disney, according to PeopleCert. On the other hand, Control Objectives for Information Technologies (COBIT) has been adopted by 170,000 large and small organisations worldwide, as reported by ISACA. Additionally, more than 870 member organisations worldwide use TOGAF, according to The Open Group. Considering the wide popularity of the three frameworks, it is essential to first familiarise oneself with them.
Read this blog to explore the differences between ITIL vs COBIT vs TOGAF. In this blog we discuss the scope and focus of the three frameworks, their stakeholders and target audiences, governance and compliance, and more.
Table of contents
1) What is ITIL – An overview
2) What is COBIT – An overview
3) What is TOGAF – An overview
4) What are the key differences between ITIL, COBIT and TOGAF?
5) Conclusion
What is ITIL – An overview
ITIL is a widely adopted framework for IT Service Management. It was developed by the UK government in the 1980s that provides a set of best practices and guidelines for managing IT services and aligning them with business goals.
The core objective of ITIL is to improve the quality and efficiency of IT service delivery by defining standardised processes and procedures. It offers a comprehensive framework of several key components, including service strategy, design, transition, operation, and continual service improvement.
This framework emphasises the importance of aligning IT services with business goals and establishing a customer-centric approach. It also promotes a Service Lifecycle approach, where services are planned, designed, implemented, and continually improved. Therefore, by following ITIL practices, organisations can achieve the following:
a) Enhanced service reliability
b) Reduced downtime
c) Improved efficiency to meet the needs of their customers
d) Effective communication and collaboration
e) Measure the performance of service performance

What is COBIT – An overview
Another popular framework that organisations use to govern and manage their IT processes effectively is COBIT. It was developed by Information Systems Audit and Control Association (ISACA) and provides a holistic approach to IT governance, risk management, and compliance.
At its core, COBIT aims to align IT activities with business goals, ensure efficient use of IT resources, and maintain high control over IT processes. It achieves this by defining a set of control objectives and management guidelines that span across various IT domains. This framework comprises five key principles that guide organisations in establishing a robust IT governance structure. These principles are as follows:
a) Meeting stakeholder needs
b) Covering the enterprise end-to-end
c) Applying a single integrated framework
d) Enabling a holistic approach
e) Separating governance from management
Further, COBIT emphasises the importance of establishing clear roles and responsibilities, defining policies and procedures, implementing effective controls, and continuously monitoring and evaluating IT processes. It also promotes using performance indicators and metrics to measure the effectiveness and efficiency of IT operations. Therefore, this framework is particularly relevant for organisations operating in regulated industries or those emphasising security and compliance.
What is TOGAF – An overview
TOGAF is a globally recognised standard for Enterprise Architecture. It provides a systematic approach to designing, planning, implementing, and governing Enterprise Architectures that align with business objectives.
While talking about TOGAF, the primary goal of the framework is to enable organisations to develop and maintain an Enterprise Architecture that supports business transformation and addresses complex challenges.
It offers a comprehensive framework comprising a set of principles, guidelines, and best practices for Enterprise Architecture development. TOGAF is divided into several architectural domains, including business architecture, data architecture, application architecture, and technology architecture. Each domain focuses on different aspects of the enterprise and provides a structured approach to address their unique requirements.
TOGAF emphasises the importance of stakeholder engagement, business alignment, and ongoing architecture governance as opposed to the other two frameworks. By adopting TOGAF, organisations can achieve several benefits, including the following:
a) Improved decision-making
b) Enhanced interoperability
c) Reduced complexity
d) Increased agility
e) Streamlined architecture development
f) Aligned technology investments with business strategies
Boost your career with TOGAF® Foundation and Practitioner Training. Master enterprise architecture and drive business transformation. Register now!
What are the key differences between ITIL, COBIT and TOGAF?
TOGAF, ITIL, and COBIT are three frameworks used in the IT industry. Each framework serves different purposes and addresses specific aspects of IT management and Enterprise Architecture. Let’s compare these frameworks based on various factors:
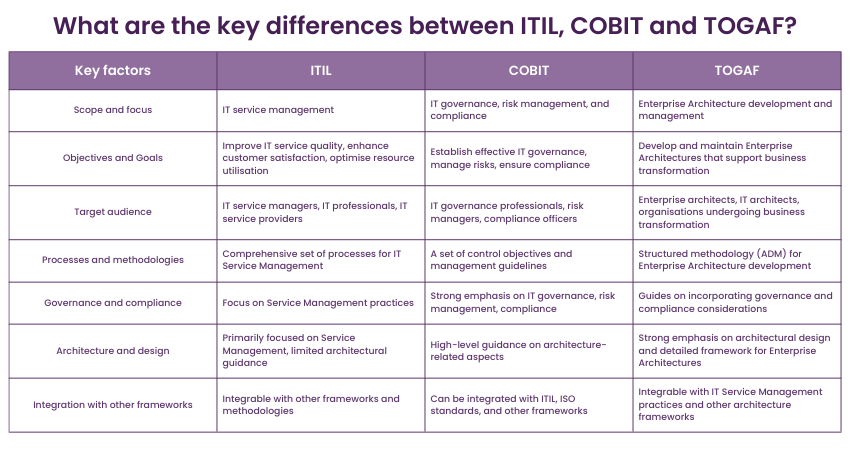
Scope and focus
The following points highlight the differences between COBIT, ITIL, and TOGAF from the perspective of scope and focus:
a) ITIL: It focuses on ITIL Service Management and aligning IT services with business objectives. It also provides best practices for delivering and managing IT services throughout their lifecycle.
b) COBIT: It focuses on IT governance, risk management, and compliance. It provides a framework to establish controls, align IT activities with business goals, and ensure effective management and oversight of IT processes.
c) TOGAF: The primary focus of the TOGAF framework is on Enterprise Architecture development and management. This is done by adopting a structured approach and guidelines that TOGAF provides for designing, planning, and governing Enterprise Architectures.
Objectives and goals
The following points highlight the differences between COBIT, ITIL, and TOGAF from the perspective of objectives and goals:
a) ITIL: It’s primary aim is improving IT service quality, enhancing customer satisfaction, and optimising resource utilisation.
b) COBIT: It’s aim is to ensure effective IT governance, risk management, and compliance. It focuses on establishing control objectives, managing risks, and aligning IT activities with organisational objectives.
c) TOGAF: At the same time, TOGAF aims to develop and maintain a well-defined Enterprise Architecture that supports business transformation. It focuses on creating a blueprint for aligning business processes, applications, data, and technology.
Learn how to implement the TOGAF framework for Enterprise Architecture. Register for our TOGAF® Foundation And Practitioner Training now!
Target audience and stakeholders
The following points highlight the differences between COBIT, ITIL, and TOGAF from the perspective of target audience and stakeholders:
a) ITIL: ITIL primarily targets IT Service Managers, IT Professionals, and organisations that provide IT services. It is relevant to both internal IT departments and external IT service providers.
b) COBIT: On the other hand, COBIT targets IT Governance Professionals, Risk Managers, and Compliance Officers. It suits organisations seeking to establish effective IT governance structures and ensure regulatory compliance.
c) TOGAF: The target audience for TOGAF is Enterprise Architects, IT Architects, and organisations involved in large-scale architecture initiatives. It is appropriate for organisations undergoing business transformation or seeking to improve their architectural practices.
Processes and methodologies
The following points highlight the differences between COBIT, ITIL, and TOGAF from the perspective of process and methodologies:
a) ITIL: It provides a comprehensive set of processes and methodologies for managing IT services, including service strategy, development, transition, operation, and continual service improvement.
b) COBIT: COBIT provides a set of control objectives and management guidelines for IT governance, risk management, and compliance.
c) TOGAF: TOGAF offers a structured methodology for developing and managing Enterprise Architecture, known as the Architecture Development Method (ADM). It includes various phases, guidelines, and artefacts to facilitate architectural development.
Governance and compliance
The following points highlight the differences between COBIT, ITIL, and TOGAF from the perspective of governance and compliance:
a) ITIL: This framework guides IT service governance; however, its primary focus is on Service Management practices rather than governance frameworks or regulatory compliance.
b) COBIT: COBIT strongly emphasises IT governance, risk management, and compliance compared to the other two frameworks. It provides a framework for establishing controls, managing risks, and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations and standards.
c) TOGAF: While it does not explicitly address governance and compliance, TOGAF guides incorporating governance and compliance considerations within the Enterprise Architecture development process.
Architecture and design
The following points highlight the differences between COBIT, ITIL, and TOGAF from the perspective of architecture and design:
a) ITIL: ITIL does not focus extensively on architectural design. Its primary focus is managing IT services and ensuring their alignment with business needs.
b) COBIT: Conversely, COBIT provides high-level guidance on architecture-related aspects, such as defining architecture principles and ensuring alignment with business goals. However, it is not as comprehensive as TOGAF regarding architectural design.
c) TOGAF: TOGAF strongly emphasises architectural design and provides a detailed framework for developing and managing Enterprise Architecture. It covers multiple architectural domains and guides designing and aligning architectural components.
Integration with other frameworks
The following points highlight the differences between COBIT, ITIL, and TOGAF from the perspective of integration with other frameworks:
a) ITIL: ITIL is integrable with other frameworks and methodologies, such as Agile, DevOps, and Six Sigma, to enhance IT service management practices.
b) COBIT: COBIT can be integrated with ITIL, ISO standards, and other frameworks. It leverages its synergies to establish a robust governance and control environment.
c) TOGAF: TOGAF can be integrated with IT Service Management practices and other architecture frameworks. This enables organisations to align their architectural initiatives with other IT management disciplines.
Enhance your IT service management skills with ITIL® 4 Specialist: Business Relationship Management. Join now to drive value!
Conclusion
ITIL vs COBIT vs TOGAF, this tussle goes on and on as each framework has its unique objectives, target audience, and methodologies. Understanding the key differences between these frameworks is crucial for organisations to choose the most suitable approach to meet their specific IT management and architectural needs
Enhance your IT career with ITIL® 4 Specialist: IT Asset Management training in the UK. Boost efficiency and compliance today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming IT Service Management Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 TOGAF® Foundation and Practitioner Training
TOGAF® Foundation and Practitioner Training
Mon 13th Jan 2025
Mon 20th Jan 2025
Mon 27th Jan 2025
Mon 10th Feb 2025
Mon 17th Feb 2025
Mon 24th Feb 2025
Mon 10th Mar 2025
Mon 17th Mar 2025
Mon 24th Mar 2025
Mon 31st Mar 2025
Mon 14th Apr 2025
Tue 22nd Apr 2025
Mon 28th Apr 2025
Tue 6th May 2025
Mon 19th May 2025
Tue 27th May 2025
Mon 9th Jun 2025
Mon 16th Jun 2025
Mon 23rd Jun 2025
Mon 30th Jun 2025
Mon 14th Jul 2025
Mon 21st Jul 2025
Mon 28th Jul 2025
Mon 11th Aug 2025
Mon 18th Aug 2025
Tue 26th Aug 2025
Mon 8th Sep 2025
Mon 15th Sep 2025
Mon 22nd Sep 2025
Mon 29th Sep 2025
Mon 6th Oct 2025
Mon 13th Oct 2025
Mon 20th Oct 2025
Mon 27th Oct 2025
Mon 10th Nov 2025
Mon 17th Nov 2025
Mon 24th Nov 2025
Mon 8th Dec 2025
Mon 15th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


