We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +800 312616 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Preparing for a Six Sigma job interview? If yes, then it’s essential to familiarise yourself with the most common Six Sigma Interview Questions and answers. A comprehensive knowledge of these questions will serve as a helping hand in landing your dream job.
According to LinkedIn, there are more than 200,000+ Six Sigma job openings worldwide. With such a huge demand for Six Sigma professionals in the market, it can be challenging to be at the top of your game.
But you need not worry anymore. In this blog, you will learn the commonly asked 55+ Six Sigma interview questions that you must prepare to crack the interview on the first attempt .
Table of Contents
1) Six Sigma Interview Questions for Beginners
2) Six Sigma Interview Questions for Intermediaries
3) Six Sigma Interview Questions for Experts
4) Other commonly asked questions
5) Conclusion
Six Sigma Interview Questions for Beginners
Freshly graduated candidates often feel helpless while preparing for an interview due to a lack of guidance. But not anymore. It’s time to follow the right path. The following are some basic questions related to Six Sigma that can assist beginners during their preparation:
1) Explain the Pareto Principle.
The Pareto Principle, also called the 80/20 rule, states that approximately 80% of effects originate from 20% of causes. It highlights the uneven distribution of outcomes, where a small number of factors or inputs contribute to most of the results.
2) What are some different variations used in the Six Sigma process?
The different statistical measures used during the process are as follows:
a) Mean
b) Median
c) Range
d) Mode
3) Who is part of the implementation team?
The Six Sigma implementation team typically includes the following members:
a) Executive Sponsor: A high-level executive who provides support, resources, and guidance for the methodology’s initiative.
b) Champion: A leader who promotes and advocates the methodology within the organisation, ensuring alignment with strategic goals.
c) Master Black Belt: An expert in Six Sigma methodologies who provides training, coaching, and mentorship to Black Belts and Green Belts.
d) Black Belt: A trained professional responsible for leading projects and implementing process improvements.
e) Green Belt: A team member who supports projects under the guidance of a Black Belt, often leading smaller improvements.

4) What is meant by Six Sigma Level?
It is a technique used for assessing the consistency of an operation. Six Sigma Level quantifies the quality and capability of a process, indicating how well it performs when implemented within the methodology.
For example, if the accuracy of the process gets to a level where it has only 3.4 Defects Per Million Opportunities, it means that one must check with the DPMO score. Here's the list of a million opportunities for defects to happen:
a) 690,000
b) 308,537
c) 66,807
d) 6,210
e) 233
f) 3.4
5) How are Lean and Six Sigma different?
The following are some of the key differences between Lean and Six Sigma:
|
Lean |
Six Sigma |
|
Focuses on eliminating waste and increasing efficiency in processes. |
Focuses on reducing defects and improving process quality. |
|
Emphasises continuous improvement and value creation for the customer. |
Emphasises data-driven decision-making and process performance improvement. |
|
Targets process flow, cycle time reduction, and streamlined operations. |
Targets process variation reduction and statistical control of processes. |
|
Tools and techniques include Value Stream Mapping, 5S, and Kanban. |
Tools and techniques include Statistical analysis, DMAIC methodology, and Control Charts. |
6) What is Load Testing? How is it different from Performance Testing?
Load Testing is a kind of software testing methodolgy that assesses the behaviour of a system under specific load conditions. It involves simulating real-world usage scenarios by subjecting the system to a predefined level of concurrent users, transactions, or data volumes.
Load Testing is nothing but a subset of Performance Testing that specifically evaluates system behaviour under predefined load conditions. At the same time, Performance Testing includes a broader range of tests to assess the overall performance characteristics of the system.
7) Explain the Top-down approach.
The Top-down approach refers to a strategic method of implementing Six Sigma principles and methodologies within an organisation. It is usually adopted to align the business strategies and the customer needs.
8) Describe SIPOC.
SIPOC stands for Suppliers, Inputs, Processes, Outputs, and Customers. It is a high-level process mapping tool used in Six Sigma. SIPOC provides a concise overview of a process by identifying key components and their interactions.
9) Name some tools used during the Six Sigma implementation.
Here are some commonly used tools during Six Sigma implementation:
a) DMAIC: Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve, and Control
b) Fishbone Diagram (or Cause-and-Effect Diagram)
c) Process Mapping
d) Control Charts
e) Pareto Chart
f) Statistical Process Control (SPC)
g) Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
h) Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
10) What is meant by DMAIC?
DMAIC stands for:
a) Define: Clearly define the problem, project goals, and customer requirements.
b) Measure: Collect data and measure the current performance of the process.
c) Analyse: Analyse the data to identify root causes and understand process variation.
d) Improve: Develop and implement solutions to address identified issues and improve the process.
e) Control: Establish control measures to sustain the improvements and continuously monitor the process.
Take your problem-solving skills to the next level with our DMAIC Training!
11) Name some of the crucial principles of Six Sigma.
The following are the principles of Six Sigma:
a) Focus on customer requirements
b) Utilising statistical analysis to identify problems
c) Improving the process by eliminating defects
d) Collaborating with stakeholders
e) Implementing flexible and responsive system
12) Explain COPQ in Six Sigma.
COPQ is the abbreviation for the 'Cost Caused by Producing Defects'; the following are the parameters upon which the cost depends:
a) Cost bore for lost opportunity
b) Cost for labour
c) Cost for rework
d) Cost for disposition
e) Cost bore for extra material
f) Cost bore for loss of sales/revenue
g) Cost for extra utilities
13) What is a Product Report?
A Product Report in Six Sigma is a document that provides detailed information regarding the product development process. This report includes information about the quality, reliability, performance, defects, or issues that were identified during development.
14) Name the different kinds of variations used in Six Sigma.
Here a list of variations used in Six Sigma.
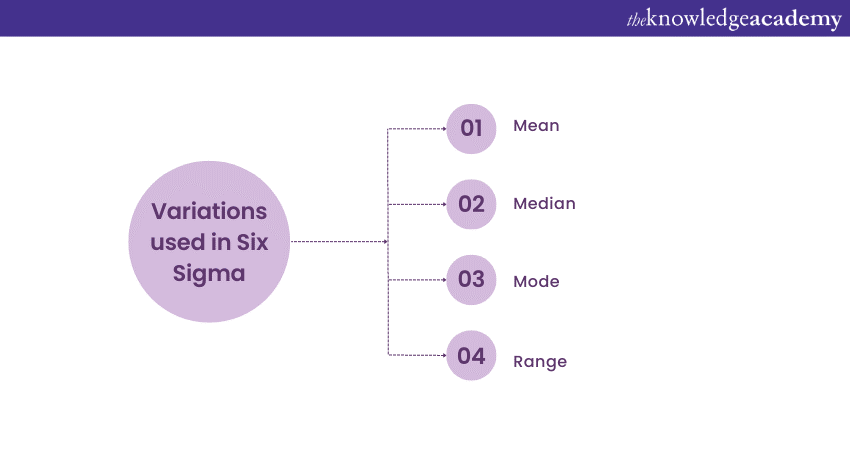
a) Mean: Averaging techniques are used to calculate and compare the variations.
b) Median: The variation is calculated and measured using a mid-point in a given data set.
c) Range: In data sets containing specific values, variations are calculated by the difference between the highest and lowest values divided by two. The lowest value is then added to the same.
d) Mode: Mode is the most occurred value in a data set.
15) Define the Load Testing Process
The Load Testing Process can be defined as a process to evaluate the behaviour and performance of the system under different load conditions using various performance metrics. These metrics are used to provide a detailed insight into how well the system is handling the load and identify any areas that require improvement.
16) Define Standard Deviation.
Standard Deviation can be defined as the degree of variation in a data set by measuring the variation in each value from the calculated mean.
17) What is the process of Sigma calculation?
The process of sigma calculation evaluates the variation in the process relative to customer requirements. The factors used to calculate include:
a) Total number of defects
b) Total number of units
c) Total number of defect opportunities
d) DPU
e) DPO
f) DPMO
g) Yield
18) Define 1.5 Sigma shift.
1.5 sigma shift is defined as the outcome of the process after multiple cycles of operations. In other words, the performance of the process will change to negative 1.5 sigma.
19) Define Regression in Six Sigma.
Regression analysis is a method used to calculate the relationship between a set of input variables with respect to an output variable. In the Six Sigma analysis phase, Regression analysis can be implemented to find out waste. It can be used to determine possible outcomes and measure if the results remain aligned with expected results when there is a change in a variable.
20) Define Defect and Defective in Six Sigma.
A Defect in Six Sigma is used to indicate non-compliance of a unit in the process with respect to the specified requirements. Defective in Six Sigma is defined as multiple unit failures or process failures. Defect and Defective are key terminologies in the Six Sigma process to identify problems that need to be fixed.
21) What is a Process Report?
Process Report is a part of the DMAIC process in Six Sigma. This report covers information regarding the performance of the process in each step in analytical form.
22) What are X-bar and R-charts?
X-bar and R-charts can be defined as quality control charts to monitor variation and the mean of the process. The X-bar provides information on changes in mean over time, while R-charts provide information on variations in the sub-groups over time.
23) What is Flowcharting and Brainstorming in Six Sigma?
Flowcharting in Six Sigma is the process of creating a diagram which contains information regarding the sequence of steps involved in an event, process or workflow. Brainstorming is a method used to generate creative and original ideas about the process, workflow, product, service or problems.
24) Define Lean Six Sigma.
Lean Six Sigma is defined as a performance methodology utilised in Six Sigma that involves removing elements that do not add value to the process, reducing variation in the process.
25) Define MSA in Six Sigma.
MSA is an abbreviation for Measurment System Analysis. MSA is used to determine the accuracy of the measurement systems. MSA evaluates the accuracy, precision and stability of a system.
26) What is the Nominal Group technique?
The Nominal Group technique is a methodology for making decisions within a group. This methodology is focused on the identification of problems by the majority, in contrast to the minority in a group.
27) What is Statistical Process Control (SPC)?
Statistical Process Control is a tool used in Six Sigma implementation. SPC is used in monitoring, controlling, and optimising the process to improve them on a periodic basis.
28) What is TRIZ?
TRIZ is an abbreviation for Theory of Inventive Problem Solving. This theory focuses on specific problems to identify any patterns which occur on a consistent basis across similar industries to find a possible solution. TRIZ is mostly utilised when commonly used Six Sigma tools prove insufficient to move the project in the desired direction.
Ready to enhance your managerial skills? Sign up for our Six Sigma Black Belt Training now!
Six Sigma Interview Questions for intermediaries
Are you willing to change your career path? Are you searching for newer prospects? If yes, then prepare for your next interview with Six Sigma Interview Questions and answers:
29) What is DPMO, and how to calculate it?
DPMO stands for Defects Per Million Opportunities. It is a metric used to measure the level of defects or errors in a process relative to the total number of opportunities for defects to occur. The formula for calculating DPMO is:
DPMO is DPMO = (Total Defects / Total Opportunities) x 1,000,000.
30) Explain the role of Champion in Six Sigma
Key aspects of the Champion's role include the following:
a) Providing strong leadership by actively promoting and supporting Six Sigma initiatives.
b) Ensuring that projects and goals are aligned with the organisation’s overall strategic objectives.
c) Allocating necessary resources, including budgets, personnel, and tools.
d) Facilitating training programs and providing guidance to project teams.
e) Tracking the project’s progress and monitoring its impact on Key Performance Indicators (KPIs).
f) Tracking the project's progress and monitoring its impact on Key Performance Indicators (KPIs).
31) Name some Quality Management tools
The following are some Quality Management tools commonly used in Six Sigma:
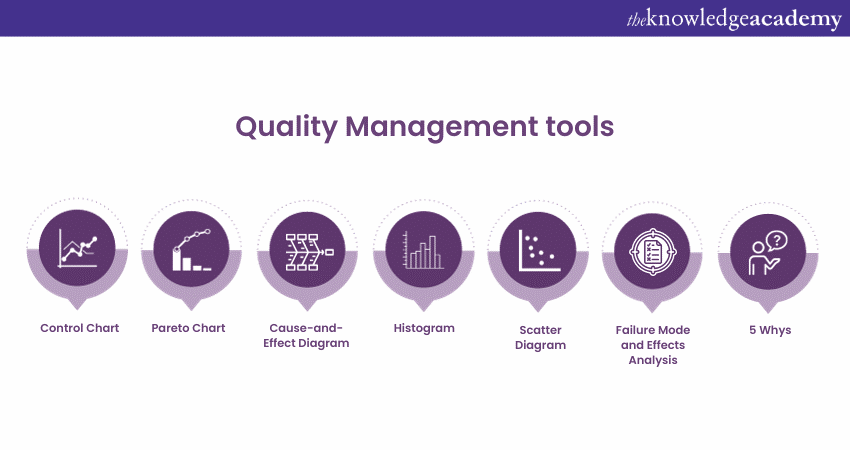
a) Control Charts: Monitor process performance and identify trends, variations, and abnormalities.
b) Pareto Chart: Prioritises problems or causes based on their frequency or impact, helping to focus improvement efforts.
c) Cause-and-Effect Diagram (Fishbone Diagram): Identifies and categorises potential causes of a problem.
d) Histogram: Helps understand the variation and in identifying potential issues in a process.
e) Scatter Diagram: Examines the relations between two variables, helping to identify potential correlations or patterns.
f) Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA): Identifies and mitigates potential failure modes and their effects on process performance.
g) 5 Whys: Identifies the root cause of a problem by repeatedly asking "why" to uncover underlying causes. The 5 Whys Root Cause Analysis is a simple yet effective problem-solving technique.
32) Briefly describe the three key elements of Six Sigma Process Improvement.
The three key elements of Six Sigma Process Improvement are:
a) Customers: Understanding and meeting customer needs and expectations is integral to Six Sigma. So, it’s important to define all possible metrics for the customers and ensure that they are dealt with.
b) Process: Emphasises on the improvement of processes to achieve better quality, efficiency, and effectiveness. It involves analysing and optimising the processes to reduce variations and defects, leading to improved outcomes.
c) Employees: Engaging and empowering employees is also crucial in the improvement efforts. It involves providing training, tools, and support to employees, enabling them to participate actively.
33) Explain the term FMEA.
FMEA refers to Failure Mode and Effects Analysis. It is a systematic methodology used in Six Sigma and Quality Management to identify and mitigate potential failures or defects in a process, product, or system.
34) What are the steps involved in Root Cause Analysis?
In Root Cause Analysis, the following steps are typically involved:
a) Identifying the problem or undesired outcome.
b) Gathering relevant data and information related to the problem.
c) Analysing the data to identify potential causes or factors contributing to the problem.
d) Using techniques to dig deeper into the underlying causes.
e) Evaluating and prioritising the identified causes based on their relevance and impact.
f) Determining the root cause(s) that, when addressed, will prevent the problem from recurring.
g) Developing and implementing corrective actions or solutions to address the root cause(s).
h) Monitoring and verifying the effectiveness of the implemented solutions.
i) Putting preventive measures to avoid similar problems in the future.
35) What is meant by DFSS?
DFSS refer to Design for Six Sigma. It is an approach within this methodology that focuses on designing and developing new products, processes, or services. It strongly emphasises meeting customer requirements and achieving high levels of quality from the outset.
36) Describe ARMI or RASI.
ARMI, which stands for Approver, Resource Person, Member, and Interested Party, is a role designation framework used in Six Sigma Project Management and decision-making processes. The framework helps establish clear roles and responsibilities, ensures stakeholder involvement, and facilitates effective decision-making and Project Management.
37) What level of understanding do you have regarding Statistical tools?
Statistical tools are a crucial part of Six Sigma. These tools are designed to help an organisation diagnose the details of various aspects of the process. Performance, defects, problems, and variations are a few key areas in which these tools are helpful. Statistical tools are capable of handling large data sets to provide accurate results, making data processing more convenient and improving the efficiency of the overall process.
38) What are the benefits of using Lean Six Sigma?
The following are the benefits of Lean Six Sigma:
a) This methodology removes defects in the process.
b) It assists in managing large teams.
c) Utilising Lean Six Sigma ensures efficient business process.
d) It assists in prioritising tasks.
e) It provides transparency in the project.
f) It improves project visibility at the team level.
g) It improves teams’ productivity.
h) It helps in saving time.
39) Explain in detail, what is meant by DMAIC Six Sigma methodology?
DMAIC is short for Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve, and Control. DMAIC is a methodology utilised for improving upon the existing process within a system. This methodology is aimed at identifying any scope for process improvement on a regular interval. The goal of applying this methodology is to achieve maximum process efficiency. Implementing DMAIC takes place in five phases, in which the entire process is evaluated on various parameters to optimise the process flow resulting in improved outcomes.
40) Explain what an Affinity Diagram is.
An Affinity Diagram is a visual tool used during problem-solving and brainstorming sessions. The tool is primarily used to organise and categorise ideas or data into logical groups based on their relationships or similarities. It provides the following capabilities:
a) Idea organisation
b) Grouping by themes
c) Visual representation
d) Facilitates collaboration
e) Identifying patterns and insights
f) Decision-making support
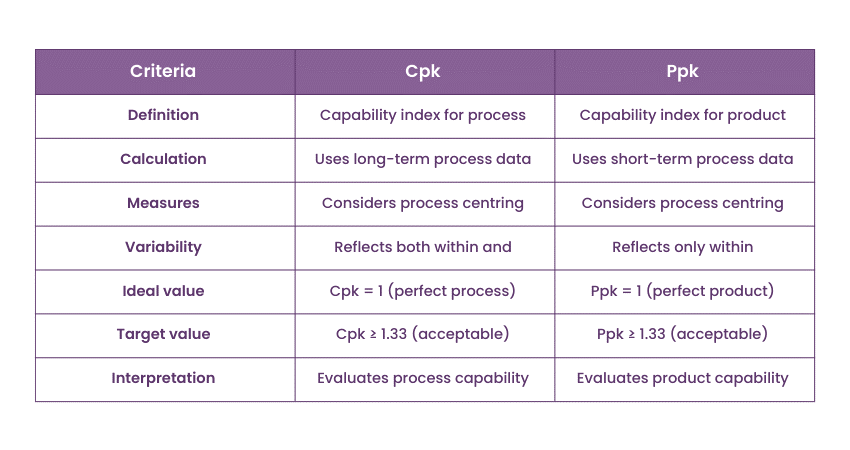
41) Differentiate between Cpk and Ppk
Consider the following table summarising the differences between Cpk and Ppk:
Don't miss this opportunity to learn about Six Sigma methodologies Six Sigma Master Black Belt Course.
Six Sigma Interview Questions for Experts
Given below are Six Sigma Interview Questions for Experts:
42) What is the role of Master Black Belt in Six Sigma implementation?
The Master Black Belt (MBB) plays the following roles in Six Sigma implementation:
a) Driving Six Sigma initiatives at an organisational level by developing strategies.
b) Establishing goals and ensuring alignment with the overall business objectives.
c) Coaching and training Black Belts and Green Belts by equipping them with the necessary skills and knowledge to effectively execute projects.
d) Selecting and prioritising Six Sigma projects based on their potential impact on business performance and customer satisfaction.
e) Ensuring the quality and integrity of projects by reviewing methodologies, data analysis, and project outcomes.
f) Acting as Change Agents, promoting a culture of continuous improvement and driving the adoption of Six Sigma methodologies throughout the organisation.
43) What do you understand by Data Collection Plan?
A Data Collection Plan is a structured approach that outlines the methods, procedures, and tools to be used for gathering data during a project or study. The following are the key elements of the Data Collection Plan:
a) Objective
b) Data Types and sources
c) Sampling strategy
d) Data collection methods
e) Data quality assurance
f) Data collection schedule
44) How can you develop SIPOC Process Map?
Developing a Suppliers, Inputs, Processes, Outputs, Customers (SIPOC) Process Map involves the following steps:
a) Identify the process
b) List the outputs
c) Identify the customers
d) Identify the inputs
e) List the process steps
f) Identify the suppliers
g) Create the SIPOC Map
h) Validate and refine
45) How do organisations estimate the cost of Six Sigma implementation?
Organisations estimate the cost of Six Sigma implementation through various approaches, which can include:
a) Allocating internal resources: The cost is calculated by considering the time and effort dedicated by internal employees who work full-time on Six Sigma projects.
b) Task-based costing: A more informal approach involves categorising tasks, including data collection, measurements, and interactions with stakeholders. Further, compensating individuals based on the tasks they perform.
c) Consulting fees: If external consultants are involved in the implementation, their fees are considered part of the cost estimation.
d) Return on Investment (ROI): Some organisations consider the potential cost savings or revenue gains resulting from projects a part of the cost estimation. The implementation cost is weighed against the expected financial benefits.
46) What is a Kano Model?
The Kano Model is a technique used for product development and customer satisfaction analysis. It categorises customer preferences into the following categories:
a) Basic
b) Performance
c) Excitement
d) Indifferent
e) Reverse
47) When should you use Kaizen events?
Kaizen Events should be used when there is a need for rapid improvement in a specific process or area. They effectively address immediate problems, implement quick changes, and foster continuous improvement within a short timeframe.
48) Describe the Fishbone or Ishikawa Diagram.
The Fishbone or Ishikawa Diagram is an effective tool for visualising and analysing the causes of a problem or effect. It helps teams to identify and address the underlying factors contributing to the issue, leading to targeted solutions and continuous improvement. It is also known as a Cause-and-Effect Diagram.
49) What are Control Charts? What are the rules for using them?
Control Charts are statistical tools used to monitor and control processes over time. They provide a visual representation of process variation and help identify when a process is out of control. Following are the rules to use them:
a) Plot data points over time.
b) Establish control limits.
c) Monitor for data points falling outside the control limits.
d) Apply control rules or tests to detect patterns or unusual variations.
e) Take corrective action when the process is out of control.
50) In a process operating at a five Sigma Level, how many numbers of opportunities fall outside the specified limits set by the customer?
a) 66807
b) 233
c) 3.4
d) 6210
The answer is Option B. The Sigma 4 standard represents the average level of precision that indicates the maximum number of defects per million in a process. So, at a five Sigma level, there are approximately 233 errors per million.
51) What myths have you heard about the Six Sigma process?
Some popular misconceptions about the Six Sigma process are:
a) The methodology focuses solely on reducing defects.
b) It is limited to production and project deployment .
c) Six Sigma is merely a training program without real-world application.
d) Engineering operations are not suitable for implementing this methodology.
Boost your career with our comprehensive Six Sigma Certification Training.
Other commonly asked questions
Interviewers always ask some common questions to all the candidates, whether a fresher or an experienced individual. These questions essentially test your soft skills and basic knowledge about the industry. So, let’s have a look at some of the commonly asked Six Sigma Interview Questions and answers:
52) Please give your introduction.
The introduction is the first step to making a good impression on the interviewer. Here are a few tips to give your introduction:
a) Firstly, give your personal information, such as your name, place of birth and interests.
b) Proceed with your educational qualifications (In reverse-chronological order).
c) Further, talk about your previous job while mentioning your achievements.
d) Be confident.
Note: if you are a fresher, mention your achievements during college.
53) What is Six Sigma?
It is one of the simplest yet tricky questions that an interviewer may ask you. Be mindful while giving the answer. Answer this question in the following manner:
1) Define the methodology.
2) Next, talk about its benefits.
3) Finally, describe how you have used the methodology during Project Management.
54) How can Sigma Implementation benefit your organisation?
Implementing Six Sigma can bring numerous benefits to organisations, including:
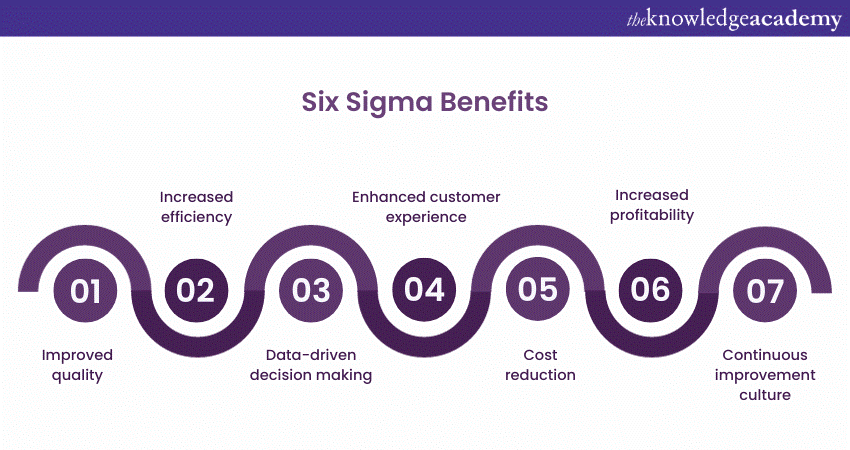
By harnessing the power of Six Sigma, organisations can achieve significant improvements in their processes, performance, and overall business outcomes.
55) Who was the inventor of Six Sigma?
The inventor of Six Sigma, Motorola, a multinational telecommunications company, popularised and formalised Six Sigma as a systematic approach to quality management in the 1980s.
56) What basic skills should a Six Sigma Professional have?
A Six Sigma Professional should possess the following basic skills:
a) Data analysis
b) Problem-solving ability
c) Process mapping and measurement skills
d) Project Management skills
e) Strong communication
f) Change Management skills
Conclusion
By mastering Six Sigma Interview Questions and answers, you can position yourself as a competent and valuable candidate for Six Sigma roles. Just stay focused and let your passion for continuous improvement shine through.
Ready to take your Six Sigma skills to the next level? Register for our Six Sigma Green Belt Course.
Upcoming Business Improvement Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Six Sigma Green Belt
Six Sigma Green Belt
Mon 31st Mar 2025
Mon 7th Apr 2025
Mon 14th Apr 2025
Tue 22nd Apr 2025
Mon 28th Apr 2025
Tue 6th May 2025
Mon 12th May 2025
Mon 19th May 2025
Tue 27th May 2025
Mon 2nd Jun 2025
Mon 9th Jun 2025
Mon 16th Jun 2025
Mon 23rd Jun 2025
Mon 30th Jun 2025
Mon 7th Jul 2025
Mon 14th Jul 2025
Mon 21st Jul 2025
Mon 28th Jul 2025
Mon 4th Aug 2025
Mon 11th Aug 2025
Mon 18th Aug 2025
Tue 26th Aug 2025
Mon 1st Sep 2025
Mon 8th Sep 2025
Mon 15th Sep 2025
Mon 22nd Sep 2025
Mon 29th Sep 2025
Mon 6th Oct 2025
Mon 13th Oct 2025
Mon 20th Oct 2025
Mon 27th Oct 2025
Mon 3rd Nov 2025
Mon 10th Nov 2025
Mon 17th Nov 2025
Mon 24th Nov 2025
Mon 1st Dec 2025
Mon 8th Dec 2025
Mon 15th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


