We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +800 312616 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Have you ever wondered how we can control movements like walking or lifting objects, while our heart keeps beating without us thinking about it? The Difference Between Voluntary and Involuntary Muscles explains this fascinating contrast. Voluntary muscles help us perform actions on purpose, while Involuntary muscles take care of vital functions automatically. In this blog, we’ll dive into how these Muscles work and explore the key differences between them. Keep reading to learn how both muscle types play a key role in keeping our bodies active and healthy!
Table of Contents
1) What are Voluntary Muscles?
2) Understanding Involuntary Muscles
3) What is the Difference Between Voluntary and Involuntary Muscles?
a) Control
b) Location
c) Function
d) Nervous System Control
e) Fatigue Resistance
4) Conclusion
What are Voluntary Muscles?
Voluntary Muscles are muscles that we can control consciously. These muscles are attached to our bones and help us move parts of our body, like our arms and legs. When we decide to move, our brain sends signals to these muscles, making them contract. An example of Voluntary Muscles is the muscles in our arms that we use to lift objects. These muscles work when we want them to and stop when we don’t. They are also called Skeletal Muscles because they are attached to the skeleton.
Understanding Involuntary Muscles
Involuntary Muscles are muscles that we cannot control consciously. These muscles work automatically, without us having to think about it. They help with important body functions like breathing, digesting food, and pumping blood. Examples of Involuntary Muscles include the muscles in the heart and in the walls of the stomach. These muscles contract and relax on their own, without us needing to tell them to. They are also known as smooth muscles, except for the heart, which is made up of cardiac muscle.
What is the Difference Between Voluntary and Involuntary Muscles?
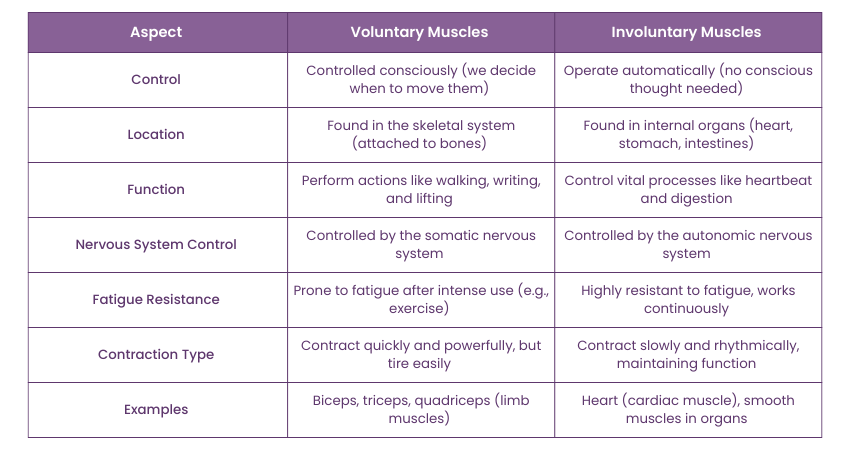
Now that you have learned what Voluntary and Involuntary Muscles are, it’s time to understand their differences. Here’s a detailed comparison of Voluntary vs Involuntary Muscles:
1) Control
Voluntary Muscles are under conscious control. We decide when and how to move them. For example, we choose to move our arms or legs when walking or lifting something. These muscles are directly influenced by the signals from the brain.
Involuntary Muscles, however, function automatically, without needing any conscious thought. They perform actions like regulating the heartbeat or breathing, which happen continuously without us thinking about them. This automatic control ensures vital processes keep running smoothly without our intervention.
2) Location
Voluntary Muscles are located in the skeletal system and are connected to the bones so that we can move our limbs. These muscles, similar to those that you find in the arms and the legs, are vital for actions like running or lifting objects.
On the other hand, Involuntary Muscles are fixed within internal organs such as the heart and stomach. These muscles do not have any outside work to perform, rather they have internal jobs to accomplish such as pumping blood, moving food in the digestive tract. Their location within the organs makes them do fundamental, constant functions that sustain our lives.
3) Function
Voluntary Muscles help us perform purposeful actions like writing, jumping, or smiling, all of which are initiated by our conscious decision to move. These muscles are crucial for tasks that require physical effort or coordination.
In contrast, Involuntary Muscles manage functions that happen automatically, such as controlling heartbeats, breathing, and digestion. These processes are essential for survival and occur without our conscious involvement. Involuntary muscles allow the body to maintain these vital functions continuously, ensuring that things like the circulatory and digestive systems work properly.
Learn meditation techniques to manage stress with our Meditation Course – Join today!
4) Nervous System Control
Voluntary Muscles are controlled by the somatic nervous system, which allows for conscious movement and coordination. The signals from the brain tell the muscles when to contract or relax for planned activities.
In contrast, Involuntary Muscles are controlled by the autonomic nervous system, which operates outside of our awareness. This system regulates the functions of internal organs, ensuring actions like heartbeat and digestion occur without needing us to think about them. The autonomic nervous system helps keep the body’s automatic functions running smoothly, even when we're not consciously aware of them.
5) Fatigue Resistance
Voluntary Muscles, due to their rapid contraction, are more prone to fatigue after intense use. For example, muscles in the arms or legs can tire quickly during prolonged physical activity or heavy lifting. After strenuous exercise, Voluntary Muscles need time to recover and repair.
On the other hand, Involuntary Muscles, particularly the cardiac muscle in the heart, are highly resistant to fatigue. They work tirelessly, contracting and relaxing rhythmically without tiring, allowing the heart to pump blood continuously. This endurance is vital for sustaining essential life functions without interruption.
6) Contraction Type
Voluntary Muscles contract quickly and powerfully, allowing us to perform rapid and intense movements like sprinting or lifting heavy weights. However, this quick contraction means they can tire easily and need rest after intense use.
In contrast, Involuntary Muscles, such as those in the heart or digestive system, contract more slowly and rhythmically. This allows them to maintain long-term functions without exhausting the body. For example, the heart contracts rhythmically throughout our lifetime to pump blood. These muscles can maintain consistent performance without wearing out, unlike Voluntary Muscles.
7) Examples
Examples of Voluntary Muscles include the biceps, quadriceps, and triceps, which allow us to perform everyday activities like lifting, walking, and writing. These muscles are responsible for movements that require conscious thought and control.
On the other hand, Involuntary Muscles include the heart (cardiac muscle), the muscles in the digestive tract (smooth muscles), and the muscles in the blood vessels. These muscles perform automatic processes, like pumping blood, pushing food through the stomach, and regulating blood flow, all without conscious effort.
Discover the power to shape a vibrant life with our Active and Healthy Lifestyles Training – transform your well-being today!
Conclusion
Understanding the Difference Between Voluntary and Involuntary Muscles helps us see how our body works. It's like teamwork between the movements we control and the ones that happen automatically. Exploring these muscles shows how our actions and automatic processes work together to keep us moving and healthy.
Start sculpting your path to a healthier you with our Nutrition And Fitness Training – sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions

Voluntary movements include walking, writing, speaking, waving, and playing an instrument, controlled consciously by the brain. Involuntary movements, on the other hand, occur without conscious thought and include heartbeats, digestion, reflexes like blinking, breathing, and pupil dilation.

The smallest and weakest muscle in the body is the stapedius muscle. It is located in the ear. It helps control vibrations in the ear and is much smaller than most other muscles.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Healthy Lifestyles Training, including the Life Coach Training, Active and Healthy Lifestyles Training, and Nutrition Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Occupational Psychologist.
Our Health & Safety Blogs cover a range of topics related to Voluntary and Involuntary Muscles, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Health and Safety knowledge, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Health & Safety Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Life Coach Training
Life Coach Training
Fri 14th Feb 2025
Fri 11th Apr 2025
Fri 13th Jun 2025
Fri 15th Aug 2025
Fri 10th Oct 2025
Fri 12th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


