We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203 999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Are you wondering about what is IoT? It’s a vast network of devices—everything from gadgets to vehicles—connected to the internet, exchanging data to create more intelligent, automated systems.
This blog dives into the essence of IoT, breaking down how it works, its key technologies, and its transformative impact on industries and daily life. Whether you’re a tech lover or just curious, get ready to explore the exciting world where physical and digital realms come together seamlessly.
Table of Contents
1) What is IoT?
2) Why is IoT Important?
3) How Does IoT Work?
4) Challenges for IoT
5) What is Industrial IoT or Industry 4.0?
6) How has IoT Improved the World?
7) Future of IoT
8) Is Alexa an IoT Device?
9) Is my Phone an IoT Device?
10) Conclusion
What is IoT?
IoT, or the Internet of Things, links devices, sensors, and objects to collect and share data seamlessly, revolutionising smart homes, wearable healthcare, and modern agriculture, with a strong connection to IoT and M2M (Machine-to-Machine) communication. Though IoT feels modern, its roots date back to the 1970s with the invention of the barcode, which enabled efficient inventory tracking and laid the foundation for today’s connected world.
Over time, IoT applications expanded, from smart thermostats optimising home energy use to wearable fitness trackers transforming health monitoring. Without IoT, we’d lose interconnectivity, smart cities, automation, and data-driven innovations that enhance industries and daily life.
Why is IoT Important?
Businesses should care about IoT for a number of reasons. The main advantages of IoT are as follows:
a) Improved Efficiency: Organisations can leverage IoT Devices to automate and improve methods. For instance, IoT sensors are used to display equipment overall performance and accurate capacity issues before they devise downtime, thereby decreasing preservation costs and growing uptime.
b) Data-driven Decision-making: IoT gadgets produce vast volumes of records to guide enterprise choices and create new enterprise fashions. This is called information-pushed choice-making. Businesses can use this information to analyse and collect insights into market trends, consumer behaviour, and overall operational performance. This information facilitates the business enterprise make higher selections concerning approach, product improvement, and aid allocation.
c) Cost-savings: IoT can lower expenses and increase profitability for organisations by automating repetitive jobs and decreasing manual processes. In order to save energy expenses and increase sustainability, IoT Devices, for instance, can be used to optimise energy consumption and monitor usage.
d) Enhanced Customer Experience: Businesses may give their consumers more individualised and interesting experiences by leveraging IoT technology to collect data about customer behaviour.
Retailers may track client movements in-store and present tailored offers depending on their behaviour by utilising IoT Devices.
Unlock the Key to Success: Practice These IoT Interview Questions!
How Does IoT Work?
The internal mechanism of IoT is equally necessary and fascinating. Individuals keen on exploring and implementing their own systems will find great benefits in understanding IoT’s mechanics. The components of IoT work in tandem to make up an efficient ecosystem. So, now that you know What is IoT, explained below are the various stages involved in this ecosystem:
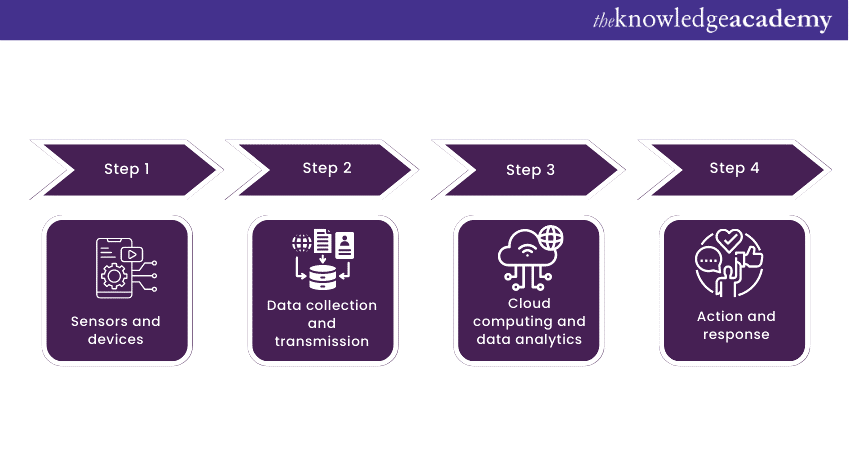
Sensors and Devices: Sensors and devices integrated into tangible items make up the initial phase of the Internet of Things. The temperature, humidity, and mobility are just a few of the environmental factors that these sensor-equipped smart devices can identify and measure. As the IoT ecosystem's eyes and ears, they collect information from the outside world.
Data Collection and Transmission: The subsequent level is data transmission, which happens while the sensors have amassed the essential data. Through several verbal exchange protocols, consisting of Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, this data is transmitted to a critical server or the cloud.
Cloud Computing and Data Analytics: The cloud serves as the repository for the gathered data, keeping it safe and enabling access for additional processing. The massive volumes of data produced by IoT Devices may be handled by cloud computing since it can provide the processing power and storage capacity needed.
Here, Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning—the two main data analytics techniques—come into action. They find patterns, trends, and useful information by deriving insightful conclusions from the data.
Action and Response: Following data analysis, the Internet of Things devices can act on the knowledge they have obtained. Examples of this include modifying temperature in a smart home, notifying healthcare systems, streamlining industrial processes, and so on.
Challenges for IoT
While IoT offers immense potential, several challenges must be addressed for widespread success. Here are some key hurdles:
a) Security Concerns: As the number of connected devices, particularly with the rise of IoT in Cyber Security, increases, so do the risks of cyberattacks. Ensuring secure communication, protecting data privacy, and implementing robust cybersecurity measures are essential to safeguard sensitive information and build trust.
b) Scalability: Managing the rapid growth of IoT Devices requires scalable infrastructure to handle vast amounts of data and maintain reliable connectivity across devices.
c) Data Management: The vast data generated by IoT Devices presents storage, processing, and analysis challenges. Effective data management strategies are crucial for deriving valuable insights and supporting informed decision-making.
d) Power and Energy Efficiency: Many IoT Devices rely on limited power sources, making energy optimisation vital to extend device lifespan, reduce costs, and minimise environmental impact.
e) Infrastructure and Connectivity: IoT depends on robust infrastructure and reliable connectivity, but areas with limited network coverage remain a challenge. Expanding network coverage and improving connectivity are key to wider IoT adoption.
Learn the best practices, and industry standards to maintain data privacy and protection, by signing up for the Security and Privacy in Internet of Things (IoT) Training now!
What is Industrial IoT or Industry 4.0?
Industrial IoT, or Industry 4.0, integrates IoT technologies and smart devices into industrial settings to enhance productivity, efficiency, and automation. It uses connectivity, data analytics, and automation to transform manufacturing processes into intelligent, interconnected systems.
Applications:
Predictive Maintenance:
a) IoT sensors monitor machine performance in real time.
b) Anomalies and potential failures are detected early, reducing unplanned downtime and optimising maintenance schedules.
Asset Tracking:
a) IoT-enabled sensors and tags track the location and condition of assets in real time.
b) Enhances inventory management, minimises loss/theft, and streamlines logistics operations.
Smart Factories:
a) Combines IoT Devices, robotics, and automation for seamless communication and collaboration.
b) Enables agile production, efficient supply chains, and custom manufacturing based on demand.
Data Analytics:
a) Collects and analyses data from multiple sources.
b) Provides insights for improving production efficiency, quality control, and supply chain optimisation.
Digital Twins:
a) Virtual replicas of physical assets or processes simulate, test, and optimise operations.
b) Reduces time-to-market and minimises production risks.
Acquire an understanding of digital twin technology drivers and enablers by signing up for the Digital Twin Course now!
How has IoT Improved the World?
IoT has emerged as a transformative force, bringing significant improvements to both businesses and consumers. Let's take a closer look at how IoT has revolutionised the world for these two key stakeholders, namely businesses and consumers:
Benefits for Businesses
IoT drives growth, efficiency, and innovation, benefiting businesses through real-time data and more intelligent operations. In manufacturing, it boosts productivity, reduces downtime, and enhances efficiency. IoT enables real-time tracking, accurate inventory, and smooth distribution in logistics by leveraging an advanced IoT Platform that integrates all data sources into one unified system.
Retailers use IoT for personalised marketing, smart shelves, and seamless checkouts, enhancing customer experiences. Additionally, IoT powers smart cities with efficient energy use, better traffic flow, and improved public safety.
Benefits for Consumers
IoT has ushered in a new era of convenience, connectivity, and personalised experiences, with consumers as key stakeholders in its market.
a) Smart Homes: Offer enhanced comfort, energy efficiency, and security with IoT Devices.
b) Automation: Simplifies daily tasks, from remote appliance control to voice-activated assistants.
c) Wearable Devices: Track fitness, sleep, and health, empowering individuals to manage well-being.
d) Healthcare: Enables remote patient monitoring, telemedicine, and timely interventions.
e) Connected Cars: Provide safety features, real-time traffic updates, and personalised driving experiences.
f) Entertainment: Transforms media consumption through smart TVs, streaming devices, and voice-activated speakers.
Future of IoT
The future of IoT is full of potential, with several key areas set for significant advancements:
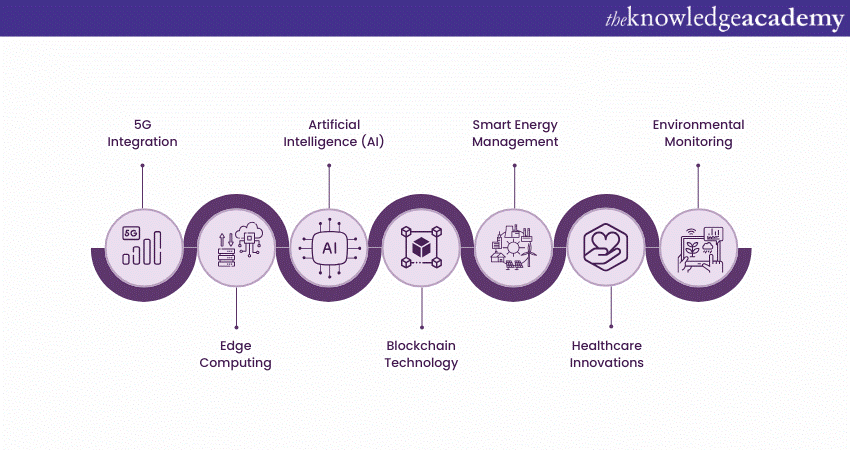
a) 5G Integration: 5G Networks will provide faster, more reliable connectivity, enabling seamless communication between IoT Devices. 5G Appliaction will unlock new possibilities in autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and immersive virtual reality.
b) Edge Computing: By processing data closer to its source, edge computing reduces latency, cuts data transfer costs, and improves efficiency, allowing real-time analysis and faster decision-making.
c) Artificial Intelligence (AI): IoT and AI will enhance automation and decision-making by analysing data, identifying patterns, and predicting outcomes, impacting sectors like smart homes, healthcare, and manufacturing.
d) Blockchain Technology: Blockchain offers secure, decentralised data storage and transactions, improving IoT security, data integrity, and trustless interactions. It will have applications in supply chains, identity verification, and secure data sharing.
e) Smart Energy Management: IoT will revolutionise energy management with smart grids and devices that optimise energy consumption, distribution, and pricing, promoting sustainability and reducing waste.
f) Healthcare Innovations: IoT will transform healthcare by enhancing real-time health monitoring, IoT in Healthcare, telemedicine, and AI-powered virtual assistants, improving patient care and accessibility.
g) Environmental Monitoring: IoT sensors will track air quality, water usage, and waste management, helping monitor and conserve natural resources and promote sustainable practices.
Enhance your understanding of 5G, mobile clouds and cognitive radio technology, by signing up for the 5G Wireless Training now!
Is Alexa an IoT Device?
Yes, Alexa is an IoT Device. It connects to the internet and communicates with other smart devices in your home, allowing you to control lighting, temperature, and entertainment via voice commands. Understanding the role of IoT devices in the context of 5G networks is often a key area in 5G Interview Questions and Answers.
Is my Phone an IoT Device?
While smartphones can interact with IoT Devices, they are not considered IoT Devices. They act as controllers for IoT networks, connecting to and managing other IoT-enabled devices through apps and services.
Conclusion
In conclusion, what is IoT? It’s the driving force behind the connected world we live in today. From shaping smarter homes and industries to revolutionizing cities, IoT seamlessly links devices, systems, and data. Beyond just technology, it’s a transformative revolution—enhancing convenience, efficiency, and innovation. The impact of IoT in marketing is also profound, enabling data-driven strategies, personalized customer experiences, and smarter automation. Ultimately, IoT is redefining everyday moments, turning them into seamless, automated experiences that push the boundaries of what’s possible.
Acquire knowledge about the latest cutting-edge innovations, by signing up for the Advanced Technologies Courses now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Does IoT Integration Require Specialised Skills Within an Organisation?

Yes, IoT integration demands specialised skills like programming, data analytics, cybersecurity, and networking within an organisation. Moreover, such skills can effectively manage devices, data flow, security, and interoperability for seamless integration and operation.
What Skills are in Demand for IoT Careers?

Skills in demand for IoT careers include proficiency in programming languages like Python, understanding of data analytics and machine learning. You should also have expertise in cybersecurity, knowledge of networking protocols, and ability to work with Internet of Things platforms.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Advanced Technologies Courses, including the 5G Wireless Training, Introduction to Virtualisation Technologies Training, and Building Chatbots with Alexa Skills and Amazon Lex Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into IoT Architecture.
Our Advanced Technology Blogs cover a range of topics related to IoT, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Technical skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Data, Analytics & AI Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Internet of Things IoT Systems and Applications Training
Internet of Things IoT Systems and Applications Training
Thu 22nd May 2025
Thu 17th Jul 2025
Thu 18th Sep 2025
Thu 20th Nov 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


