We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203 999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
- Retired : Designing and Implementing Enterprise-Scale Analytics Solutions Using Microsoft Azure and Microsoft Power BI DP500
- Microsoft Azure Administrator AZ104
- Data Engineering On Microsoft Azure DP-203 Certification
- Microsoft Azure Security Technologies AZ500
- Designing And Implementing Microsoft DevOps Solutions AZ400

If you’re eyeing a career in Cloud Computing, Azure certification is your golden ticket. The cloud market is not just thriving; it’s fiercely competitive. But don’t worry; with the right preparation, you can soar in this field. Dive into the world of Microsoft Azure with a set of interview questions tailored for Azure certifications. These Microsoft Azure Interview Questions are your secret weapon to ace that Azure interview.
Get ahead of the game by familiarising yourself with the top Microsoft Azure Interview Questions and answers. Whether you’re aiming to be an Azure Developer, an Azure Solution Architect, or an Azure System Admin, this guide has got you covered. So, let’s get started and turn you into an Azure whiz!
Table of Contents
1) Azure Interview Questions for freshers
2) Azure Interview Questions and Answers for intermediate candidates
3) MS Azure Interview Questions and Answers for experienced professionals
4) Conclusion
Azure Interview Questions for Freshers
The following are the basic Azure Interview Questions.
1) What do you know about Cloud Computing?
Cloud Computing delivers computing resources like storage, servers, databases, and software on-demand over the internet. It eliminates the need for physical infrastructure, offering scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency. Users access these resources through a web browser or application, paying only for what they use.
2) Explain about the Deploying Models in Cloud Computing.
This is a typical Azure Interview Question for the differentiation model. The three deployment models of cloud computing are as follows:
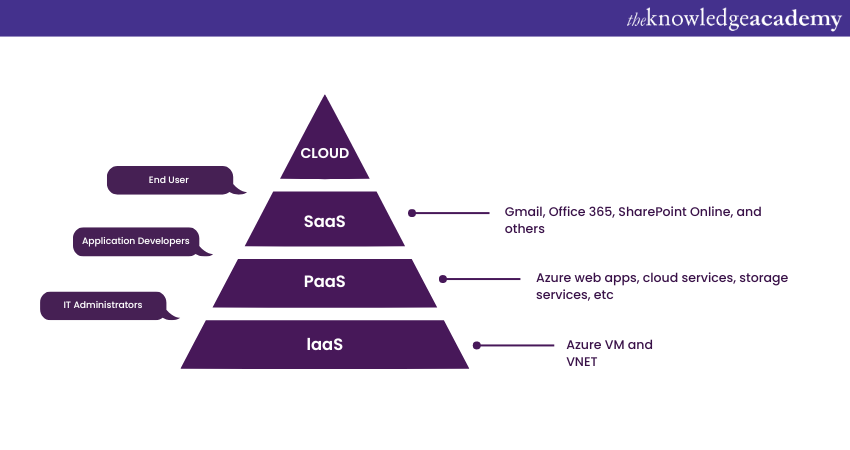
|
IaaS |
PaaS |
SaaS |
|
Infrastructure as a Service, or (IaaS), provides several infrastructure-level features, including OS and network connectivity. It operates on a pay-per-use basis. It serves as a host for apps. |
Platform as a Service, or (PaaS), consists of underlying infrastructure abstraction that speeds up application development by removing the hassle of hosting administration. |
Software as a Service or (SaaS) apps are used by a variety of IT specialists, business users, and private consumers. SaaS is all about finance via subscriptions or ads |
|
Examples of this kind of infrastructure are Azure Virtual Machines and VNET. |
Examples include Azure web apps, cloud services, storage services, etc. |
SaaS examples are Gmail, Office 365, SharePoint Online, and others. |
Want a career in cloud computing? Check out our Microsoft Azure Fundamentals AZ900 Course today!
3) What do you know about Azure Cloud?
Azure Cloud, created by Microsoft, is a comprehensive platform offering on-demand cloud services like storage, computing power, databases, and AI tools. Businesses can access these resources via the internet, scaling their needs up or down as required. This flexibility and pay-as-you-go approach make Azure Cloud cost-effective for various applications.
4) What are the Core Components of Microsoft Azure?
The core components of Microsoft Azure are as follows:
a) Compute
b) Storage
c) Database
d) Monitoring and management services
e) Content Delivery Network (CDN)
f) Azure networking
g) Web and mobile services
5) Differentiate between Azure Cloud and AWS?
The following are the differences between Azure Cloud and AWS:
|
Features |
Azure Cloud |
AWS |
|
Data analytics |
Azure Stream Analytics |
Amazon Kinesis |
|
Privacy and security |
Azure is secured by an AI-powered Cloud Defender service. |
AWS offers secure solutions by default, assuring enhanced privacy. |
|
Database service |
Hadoop, Spark, Storm, and HBase are all supported by the SQL Server database on Azure |
Six common database engines can be used with Amazon RDS, a database service. |
|
Backup |
Azure Backup |
Amazon Glacier |
|
Monitoring and Logging |
Azure ML studio, Azure Operational Insights |
Amazon CloudTrail, CloudWatch |
|
Pricing |
Azure is priced on a per-minute basis. |
AWS charges a per-hour fee. |
6) What are the Cloud Deployment Models in Azure?
The three cloud deployments in Azure are mentioned below-
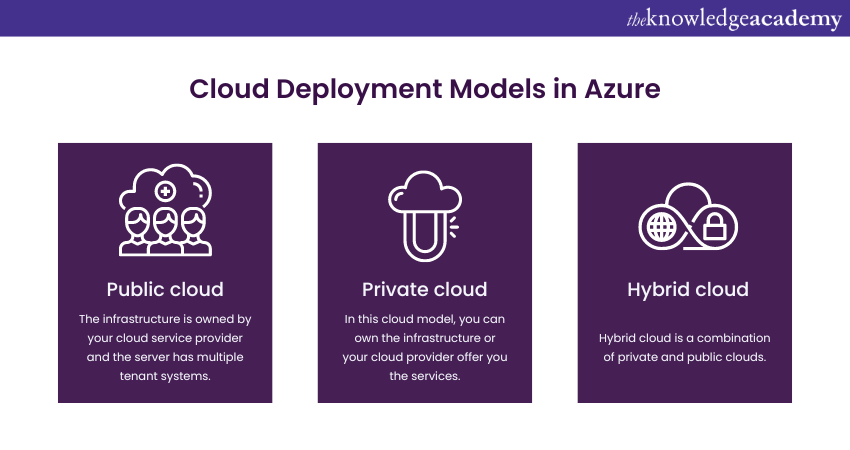
Public Cloud- The infrastructure is owned by a Cloud service provider and the server has multiple tenant systems.
Private Cloud- In this cloud model, you can own the infrastructure or your cloud provider offer you the services.
Example- Hosting your website on your servers or using a dedicated server from the Cloud provider to host your website.
Hybrid Cloud- Hybrid Cloud is a combination of private and public clouds. Example: You use your company's internal servers for confidential information and the public cloud hosts it on the website that is visible to the general public. This type of configuration is offered by a hybrid cloud.
7) Explain NSG.
A Network Security Group (NSG) consists of security rules that permit or prohibit inbound or outbound network traffic from certain Azure resource types. These security rules are termed Access Control List (ACL) rules. In this, each rule specifies the source, destination, port, and protocol. Network traffic between Azure services within an Azure virtual network is filtered using Azure network security.
8) Which Azure Service is used for Resource Management?
A) Azure Portal
B) Log Analytics
C) Application Insights
D) Azure Resource Manager
Answer: (D) Azure Resource Manager
Explanation- Azure Resource Manager, manages the infrastructures of various Azure services. The management layer in Azure is used to update and delete resources from Azure subscriptions. The related resources are organised in groups and deployed in JSON templates.
9) A Virtual Machine that runs on a Microsoft IIS Web Server that can accept and react to HTTP/HTTPS requests is called which role?
A) Client
B) Worker
C) Web
D) Server
Answer- (C) Web
Explanation: There are no roles like server or client roles. Hence, the correct ones should be web roles. Moreover, worker roles can only connect directly to clients or Azure storage.
Web Role in Azure Cloud is a service role that is customised and configured to support web apps developed using IIS-compatible programming languages and technologies. (IIS-Internet Information Services)
10) Which of the below-mentioned Web Apps can be Launched using Azure?
A) PHP
B) ASP.NET
C) WCF
D) All of the above
Answer- (D) All of the above
Explanation- Microsoft has made Java and Ruby Software Development Kit (SDKs) accessible. This allows the software built using these two programming languages to call the AppFabric service using the Azure service platform API.
Azure Interview Questions and Answers for Intermediate Candidates
The Microsoft Azure Interview Questions and answers for the intermediate level are as follows:
11) Describe Azure Redis Cache.
An open-source and in-memory Redis cache is also called as Azure Redis Cache.
Redis Cache supports web applications that retrieve data from the backend into caches and server web pages to improve application performance.
It offers a safe and secure way to cache your application's data in the Azure Cloud.
12) Explain the Various Storage Types in Azure.
Azure provides a range of storage options to meet various requirements:
a) Blob Storage: This is ideal for storing unstructured data like text, images, and videos. It supports block blobs, append blobs, and page blobs, making it versatile for different storage needs.
b) File Storage: Offering fully managed file shares that are accessible via the Server Message Block (SMB) protocol, this is perfect for legacy applications that need a traditional file system.
c) Queue Storage: This type facilitates reliable messaging between different parts of an application, allowing for asynchronous communication. It's a great choice for decoupling application components.
d) Table Storage: A NoSQL key-value store, Table Storage is designed for structured data. It provides high availability and scalability, making it suitable for large-scale applications.
e) Disk Storage: Managed disks for virtual machines come in various options, including Standard HDD, Standard SSD, and Premium SSD. These options ensure that you can choose the right balance of performance and durability for your specific workload.
13) What is Azure Storage Key?
The Azure storage key is used for authentication and validation of access. For authentication, there are two types of storage keys:
A) Primary Access Key
B) Secondary Access Key (to prevent application downtime)
Upskill yourself in Data fundamentals, with our Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals DP 900 course. Register now!
14) Describe Azure Service Fabric in detail.
Here are the functions of Azure Service Fabric:
1) Develops and manages distributed, scalable, and always-on applications
2) Simplifies application lifecycle management and the establishment of microservices
3) Scale and manages containers and microservices with consistency
4) The data-aware platform for stateful containers or microservices and low-latency, high-throughput workloads
5) Your choice of programming languages and models lets you run anything (supports Windows/Linux on Azure, on-premises, or other clouds)
6) Scales up to thousands of machines
15) Explain Azure SLA.
The Azure Service Level Agreement (SLA) is a contract that ensures access to Cloud service. SLA access is provided for at least 99.95% of the time when two or more roles of each instance are deployed on Azure. When a role instance's process is inactive 99.9% of the time, detection and corrective action will be initiated.
16) Differentiate between Available sets and Azure Scale Sets
Availability Sets and Azure Scale Sets serve different purposes in Azure.Availability Sets ensure high availability for VMs by distributing them across multiple fault domains and update domains, protecting against hardware failures and maintenance events. They enhance reliability within a data centre.
Azure Scale Sets enable automatic scaling of VM instances, providing high availability and elasticity for applications. They let you manage, configure, and update many VMs as a single unit, automatically adjusting the number of instances based on demand.
17) What is Azure Traffic Manager? Explain its benefits in Azure.
Azure traffic manager also known as the traffic load balancer assist the users by providing high availability and responsiveness by evenly spreading traffic across all Azure regions worldwide. The following are some of its benefits:
1) There are various automatic failover options available
2) It reduces the application downtime
3) It makes it possible to split up user traffic among several different locations
4) It allows users to identify the country from which people are connecting
18) Can you give a brief description of Azure Blob Storage and their type?
Azure Blob Storage is a versatile cloud service from Microsoft, perfect for storing vast amounts of unstructured data, whether it be text or binary files. It boasts remarkable scalability, durability, and accessibility, making it an excellent choice for data lakes, backups, and media files.
There are three types of blobs available in Azure Blob Storage, each tailored to different needs:
a) Block Blobs: These are designed for efficiently storing text and binary data. They excel at handling large file uploads, making them a go-to for general-purpose storage.
b) Append Blobs: These are perfect for logging operations. You can keep adding data to the end of these blobs, which makes them ideal for scenarios where you need a continuous log of information.
c) Page Blobs: These are optimised for random read and write operations and are typically used for virtual hard disk storage in Azure virtual machines. They provide the performance necessary for disk-intensive applications.
19) Define Azure Virtual Machine Scale Sets.
Azure Virtual Machine Scale Sets, often called VMSS, is a feature that Microsoft Azure provides for efficient and scalable VM management. This service is particularly valuable in scenarios where you need to run multiple identical VMs to handle high traffic, ensure fault tolerance, or manage workloads that require auto-scaling.
20) How are you benefitted by integrating Azure with the Hybrid Cloud?
The Azure Hybrid Cloud increases productivity by supporting Azure and Azure Stack by creating and deploying Cloud-based on-premises applications. By integrating hybrid Cloud with Azure, you can leverage its benefits in the following ways:
1) Azure services are integrated with DevOps practices and technologies for better efficiency.
2) Regular updates in Azure services and other Azure applications are more beneficial to users.
3) It supports deployment across locations, on-premises, in the Cloud, etc.
4) This hybrid integration speeds up the application development process.
MS Azure Interview Questions and Answers for experienced professionals
The Microsoft Azure Interview Questions for professionals are as follows:
21) Define Roles in Azure and their uses.
In simple words, Roles are just servers. These servers are controlled Platform as a Service (PaaS) Virtual Machines with load balancing that cooperate to accomplish a common goal. They are used to manage and delegate access to Azure resources and services. Roles are crucial for enforcing security and access control within Azure, ensuring that only authorised individuals or processes can interact with resources. This helps protect data and maintain compliance with security policies and regulations.
22) Differentiate between Azure Service Bus Queues and Azure Storage Queues.
The following are the differences between Azure Service Bus Queues and Azure Storage Queuesin tabular format.
|
Feature |
Azure Service Bus Queues |
Azure Storage Queues |
|
Purpose |
Enterprise messaging with advanced features |
Simple, scalable message queuing |
|
Message size |
Up to 256 KB (Standard), 1 MB (Premium) |
Up to 64 KB |
|
Maximum queue size |
80 GB |
Up to 500 TB |
|
Maximum queue size |
Yes, guaranteed with sessions |
No guaranteed FIFO |
|
Duplicate detection |
Supported |
Not supported |
|
Transaction support |
Supports transactions |
No transaction support |
|
Dead-lettering |
Supported |
Supported |
|
Advanced features |
Topics, subscriptions, sessions, transactions |
Basic features |
|
Protocol |
AMQP, HTTPS |
REST API |
|
Use case |
Complex workflows, enterprise integration |
Simple, large-scale applications |
23) How to create a VM using Azure CLI?
To create a Virtual Machine (VM) using Azure CLI, follow these steps:
1) Open a command prompt or terminal.
2) Use the following command to create a VM:
az vm create --resource-group YourResourceGroup --name YourVMName --image YourImage --admin-username YourUsername --admin-password YourPassword
3) Replace the placeholders with your own values:
a) YourResourceGroup: Name of the Azure resource group.
b) YourVMName: Name for your VM.
c) YourImage: Azure VM image (e.g., "UbuntuLTS" or "Win2019Datacenter").
d) Your username: Admin username for the VM.
e) YourPassword: Admin password for the VM.
This command creates a VM in the specified resource group using the provided image, username, and password. You can customise it further by adding options like VM size, virtual network configuration, and more.
24) Explain how applications handle connection failure in Azure.
Applications handle connection failure in Azure by implementing retry policies, using exponential backoff strategies, and configuring transient fault handling. They also utilise Azure's built-in features like automatic failover, load balancing, and geo-redundancy to ensure high availability and resilience against connectivity issues.
Build a career in Artificial intelligence & Machine Learning with our Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning Course. Register today!
25) Describe Azure AD and its uses.
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) is a cloud-based identity and access management service from Microsoft. It helps organisations manage user identities and control access to applications and resources securely.
Azure AD supports single sign-on (SSO), enabling users to access multiple applications with one set of credentials. It provides Multi-factor Authentication (MFA) for enhanced security and integrates with on-premises Active Directory, facilitating hybrid identity management.
Azure AD is essential for managing user access to Office 365, Azure services, and thousands of other SaaS applications, ensuring secure and efficient user authentication and authorisation across cloud and on-premises environments.
Learn to administer Azure from scratch with our Microsoft Azure Administrator AZ104 Course. Sign-in now!
26) What is a Dead Letter Queue?
A Dead Letter Queue (DLQ) is a messaging queue used to store undeliverable messages that cannot be processed successfully. It helps identify issues by capturing failed messages for later analysis, ensuring that problematic messages do not disrupt the main message flow.
28) What is a break-fix in MS Azure?
The technical problem in MS Azure is referred to as a “break-fix issue”. It is a technical word used in the industry to describe "work associated in supporting a technology when it fails in the normal course of its function, requiring intervention by a support organisation to be restored to functioning order."
29) What happens when there are numerous failed authentication requests in Azure ID Authentication for a user or application?
The Azure account will be locked in this case. It will be based on the protocol analysis of the entered password and IP address from which the login request was made.
30) Explain the requirements of creating VMs and how to maintain secured traffic.
Creating Virtual Machines (VMs) requires selecting the appropriate VM size, operating system, and storage options based on workload needs. You must also configure networking, including assigning IP addresses and setting up virtual networks. To maintain secure traffic, implement Network Security Groups (NSGs) to control inbound and outbound traffic, use Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) or Azure ExpressRoute for secure connections, and enable Azure Firewall for advanced threat protection.
Additionally, encryption should be applied to data at rest and in transit, regularly update and patch VMs, and enforce Multi-factor Authentication (MFA) and Role-based Access Control (RBAC) for user access.
31) Which web applications can be hosted on Azure among the given options?
a) ASP.NET
b) PHP
c) WCF
d) All of the above
The answer is all of the above. Microsoft has developed SDKs for Java and Ruby and allowed applications written in that language to interact with the Azure Service API and the AppFabric Service.
32) Do data disks find support within Scale Sets?
Yes, data disks are fully supported within Scale Sets. These Sets can specify a shared data disk configuration that is universally applied to all Virtual Machines within the set. Other data storage options include the following:
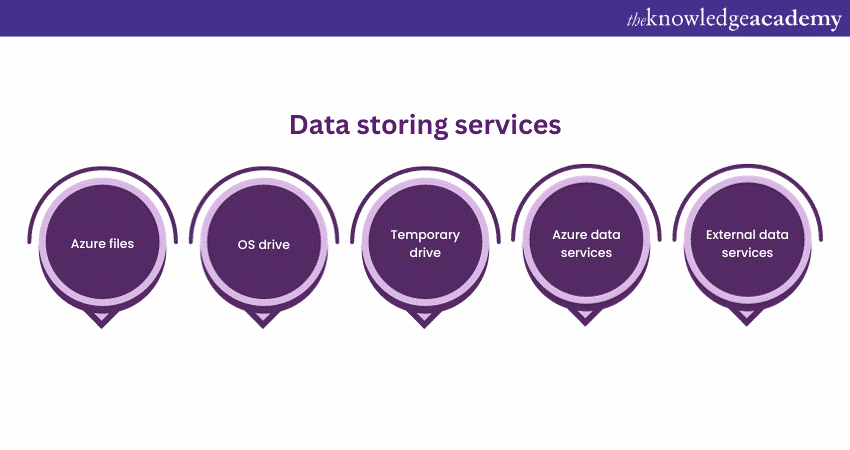
a) Azure files (SMB shared drives)
b) OS drive
c) Temporary drive (local storage, not backed by Azure storage)
d) Azure data services (e.g., Azure tables, Azure blobs)
e) External data services (e.g., remote databases)
33) What does the term 'Availability Set' refer to?
An Availability Set is a strategic assembly of Virtual Machines (VMs) designed to convey to Azure the architectural layout of your application for redundancy and continual availability. It is better to create two or more VMs within an availability set to ensure high availability and meet the 99.95% Azure SLA (Service Level Agreement). The Azure SLA covers unplanned maintenance events when you rely on a single VM in conjunction with Azure Premium Storage.
34) What do you mean by 'Fault Domains'?
Fault domains represent a logical categorisation of underlying hardware resources that share the same power source and network switch. You can think of them as being similar to racks in an on-premises data centre.
When you deploy Virtual Machines (VMs) within an Availability Set, Azure's system intelligently allocates these VMs across various fault domains. This allocation strategy serves to reduce the consequences of potential physical hardware failure, network disruption, or power outages.
35) What is the concept of 'Update Domains'?
An Update Domain refers to a logical cluster of the hardware that can go through maintenance or reboot concurrently. When you establish VMs within an Availability Set, Azure's infrastructure distributes these VMs across multiple update domains. The distribution guarantees that, during Azure's routine maintenance activities, at least one instance of your application remains operational. It is important to note that the rebooting order of update domains during planned maintenance may not be sequential, but only one update domain is rebooted at a time.
Become an Azure DevOps Engineer with our Designing and implementing Microsoft DevOps Solutions AZ400 Course now!
36) What is the function of Network Security Groups (NSGs)?
Network Security Groups (NSGs) are sets of Access Control List (ACL) rules that determine the permission or denial of network traffic for subnets, Network Interface cards (NICs), or a combination of both. NSGs can be linked to subnets, or they can be directly associated with individual NICs connected to a subnet. When an NSGSA is connected to a subnet, the ACL rules are implemented for all the VMs within the subnet. Furthermore, you can regulate traffic to a specific NIC by directly associating an NSG with that NIC.
37) Is there compatibility between Scale Sets and Azure AVAILABILITY SETS?
Yes, Scale Sets are inherently equipped with availability features, five fault domains and five update domains. Scale Sets exceeding 100 VMs extend across multiple placement groups and effectively resemble multiple availability sets..
It is entirely possible for a set of VMs in an Availability Set to coexist within the same virtual network as a Scale Set of VMs. A typical configuration involves placing control node VMs (typically requiring distinct configurations) in an availability set while housing data nodes within the Scale Set.
38) What is the purpose of Azure Active Directory?
Azure Active Directory serves as an identity and access management system designed to ease access control for your employees regarding specific products and services within your network.
It includes services such as Salesforce.com and Twitter, among others. Azure AD offers built-in support for a range of applications featured in its gallery and allows straight-forwardsimple integration.
39) What does Virtual Network (VNet) entail?
VNet is essentially a virtual manifestation of your network within the Cloud environment. It establishes logical segregation and ensures that the instances you deploy in the cloud remain isolated from the remainder of your resources.
40) What sets Subscription Administrator and Directory Roles apart?
Upon Azure signup, individuals are automatically assigned the Subscription Administrator role. A Subscription Administrator can utilise either a Microsoft account or a work or school account from the associated Directory to manage services through the Azure portal. This Role authorises service management within the Azure subscription. Additional users can be added to co-admins for those requiring access with the same subscription.
Azure AD, on the other hand, consists of a distinct array of administrative roles responsible for overseeing directory and identity-related functions. These Administrators can access a spectrum of features within the Azure portal or the Azure classical portal. The specific admin role dictates their responsibilities, such as user creation, role assignment, password resets, license management, and domain administration.
41)What do you mean by Redis Databases?
Redis databases serve as a means of logically partitioning data within a single Redis instance. These databases share the cache memory, and the actual memory consumption of each Database is contingent upon the keys and values stored within it. For example, suppose you have a C6 cache with 53 GB of memory. In that case, you have the flexibility to allocate the entire 53 GB to one database or distribute it among multiple databases as per your requirements.
42) What are the different power states of VM?
The following are the different power states of VM:
|
Power State
|
Description
|
|
Starting
|
This signifies the starting point of the Virtual Machine's startup. |
|
Running
|
Denotes the operational status of the Virtual Machine. |
|
Stopping
|
Indicates the process of bringing the Virtual Machine to a halt.
|
|
Stopped
|
Illustrates that the Virtual Machine is no longer in operation. |
|
Deallocating
|
Refers to the procedure of deallocating resources from the Virtual Machine.
|
|
Deallocated
|
Represents the state where the Virtual Machine is removed from the hypervisor but remains accessible in the control plane. Virtual Machines in the deallocated state do not accumulate computer charges. |
43) What do you mean by Azure Search?
Azure Search is a Cloud-based search-as-a-service that offloads the complexities of server and infrastructure management to Microsoft. This results in a readily available service that you can populate with your data, allowing you to introduce search functionality into your web or mobile applications seamlessly. With Azure Search, you can improve your applications with a powerful search experience using a simple REST API or .NET SDK, all while avoiding the need to handle search infrastructure or acquire specialised expertise in the field of search technology.
44) What distinguishes Azure's special regions?
Azure's special regions are distinct from standard regions due to their unique compliance and service offerings. These include regions like Azure Government, which provides a dedicated cloud for US government agencies with stringent compliance and security requirements, and Azure China, operated by 21Vianet, adhering to Chinese regulations. Other special regions support specific data residency needs and offer services to cater to particular industries or sectors.
These regions ensure that organisations with unique compliance, regulatory, or operational requirements can utilise Azure services while meeting their specific mandates and maintaining data sovereignty and high security.
45) What are the primary components of the Windows Azure platform?
The primary components of the Windows Azure platform include:
a) Azure Compute: Provides Virtual Machines , container services, and App Services for hosting and running applications.
b) Azure Storage: Offers scalable storage solutions like Blob Storage, Queue Storage, Table Storage, and Disk Storage for data management.
c) Azure Networking: Comprises Virtual Networks, Azure Load Balancer, VPN Gateway, and Azure DNS to manage network infrastructure and secure connections.
d) Azure Databases: Includes SQL Database, Cosmos DB, and Database for MySQL, PostgreSQL, and MariaDB for relational and NoSQL database needs.
e) Azure Identity: Utilises Azure Active Directory (AD) for identity management and access control.
f) Azure Management and Security: Encompasses tools like Azure Monitor, Security Center, and Azure Policy for monitoring, security, and compliance.
The Windows Azure platform comprises three core segments: Compute, Storage, and Fabric.
a) Windows Azure compute:
Windows Azure offers a coding platform managed by its hosting environment, delivering computational capabilities through components. It supports three main role types:
1) Web roles, ideal for web application programming and backed by IIS7.
2) Worker roles, designed for background processing tasks in conjunction with web roles.
3) Virtual machine (VM) roles are used for the seamless migration of Windows Server applications to Windows Azure.
b) Windows Azure storage:
Windows Azure Storage encompasses four distinct storage services:
1) Queues are used help in communication between web roles and worker roles.
2) Tables are used for the storage of structured data.
3) BLOBs (Binary Large Objects) are used for storing content, files, or large datasets.
4) Windows Azure Drives (VHD) allows the mounting of page BLOBs and enabling uploading and downloading via BLOBs.
c) Windows Azure AppFabric:
Windows Azure AppFabric provides five essential services:
1) Service bus
2) Access
3) Caching
4) Integration
5) Composite
46) What exactly is Microsoft Azure Storage Explorer?
Microsoft Azure Storage Explorer serves as a versatile tool for connecting with and overseeing your Azure storage service accounts and resources spanning various subscriptions. This tool is compatible with Azure Storage, Azure Cosmos DB, and Data Lake Storage. It allows you to perform tasks like resource creation, deletion, viewing, and updates.
One remarkable feature of Storage Explorer is its ability to function independently of Cloud connectivity or the need for local emulators. This characteristic not only improves productivity and efficiency but also helps in reducing operational costs. Furthermore, it's supported by the strong security measures synonymous with Azure's industry-leading standards.
47) Define Azure Monitor.
Azure Monitor is a pivotal service within the Azure ecosystem, designed to offer comprehensive performance and availability monitoring for a wide spectrum of applications and services. This functionality extends beyond Azure itself, making it compatible with applications and services across various cloud environments and on-premises setups. Azure Monitor is designed to aggregate data from diverse sources into a unified data platform. This allows thorough analysis to detect both trends and irregularities in your system's performance.
48) Explain SQL Azure Database.
SQL Azure Database represents a cloud-based solution that allows you to establish a connection to cloud services to store your databases. It leverages Microsoft Azure as an optimal platform, embracing the Platform as a Service (PaaS) model that improves the hosting of multiple databases within the same account.
Microsoft Azure SQL, similar to SQL Server, has core features such as high availability, scalability, and robust security.
One distinguishing characteristic of Microsoft Azure SQL Database is its automatic backup mechanism. It routinely creates backups for each active database, replicates them geographically and ensures a one-hour Recovery Point Objective (RPO) for geo-restore capabilities.
49) What's the Storage Capacity for Virtual Machines?
The Storage Capacity for each Data Disk in a Virtual Machine can go up to 1 TB. The allowable number of Data Disks you can attach depends on the size of the Virtual Machine.
Azure-managed Disks are the preferred storage solution for persistent data in Azure Virtual Machines as they allow you to use multiple managed Disks with each Virtual Machine. Managed Disks come in two variants, offering durable storage options: Premium and Standard Managed Disks.
50) Explain Role Instance in Azure.
A Role Instance is essentially a Virtual Machine where your application code operates based on the active role configurations. In Cloud services, you have the flexibility to define multiple instances of a role as specified in the cloud service configuration files.
Conclusion
Microsoft Azure Interview Questions and Answers are vital tools in the hiring process. They help employers identify qualified candidates, allow job seekers to demonstrate their skills, and ensure that the right candidate is selected for Azure-related roles.
Unleash the boundless potential of the Cloud, sculpting your skills and knowledge into a masterpiece of digital innovation with our Microsoft Azure Certification!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Microsoft Technical Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Microsoft Azure Fundamentals AZ-900 Certification
Microsoft Azure Fundamentals AZ-900 Certification
Fri 31st Jan 2025
Fri 7th Mar 2025
Fri 2nd May 2025
Fri 4th Jul 2025
Fri 5th Sep 2025
Fri 28th Nov 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


