We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +352 8002-6867 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Microsoft Power Apps has become a game-changer in app development, enabling businesses to create custom solutions effortlessly. Many organisations have encountered an innovation challenge: the rising costs associated with Power Apps. In this blog, you will learn about Microsoft Power Apps Costs and factors that have led to a cost increase.
Let us explore why these costs have increased and how your organisation can navigate the expense maze while harnessing the power of this remarkable platform.
Table of Contents
1) Brief overview of Microsoft Power Apps and its significance
2) Understanding Microsoft Power Apps
3) Factors contributing to cost increases
4) Licensing changes
5) Increased demand
6) Managing Microsoft Power Apps Costs
7) Conclusion
Brief overview of Microsoft Power Apps and its significance
Microsoft Power Apps is a groundbreaking platform developed by Microsoft that empowers organisations to create custom applications with remarkable ease and efficiency. It has garnered immense significance in modern business by offering a low-code or no-code solution, bridging the gap between traditional application development and business users. Even individuals with limited coding expertise can design and deploy applications tailored to their needs.
The significance of Microsoft Power Apps lies in its ability to democratise app development within organisations. It enables business units, departments, and employees to take charge of their app requirements, reducing dependence on IT departments and accelerating the delivery of solutions. This agility is crucial in today's rapidly changing business environment, where the ability to respond swiftly to new challenges or opportunities is paramount.
Power Apps seamlessly integrates with other Microsoft tools and services like SharePoint, Power BI, and Microsoft 365, enhancing its adaptability and utility across various domains. Microsoft Power Apps is a transformative force enabling organisations to innovate, optimise, and stay competitive in a digital age, from automating manual processes to creating data-driven dashboards.
Whether you are a beginner or an experienced user, our expert-led Microsoft Power Apps For End Users 55265AC will equip you with the skills and knowledge you need to create powerful custom applications.
Understanding Microsoft Power Apps
Understanding Microsoft Power Apps is pivotal for organisations to harness its capabilities effectively. This versatile platform empowers technical and non-technical users to create custom applications with remarkable ease. At its core, Power Apps offers a low-code/no-code approach to app development, making it accessible to a broad spectrum of users.
Critical facets of understanding Microsoft Power Apps include:
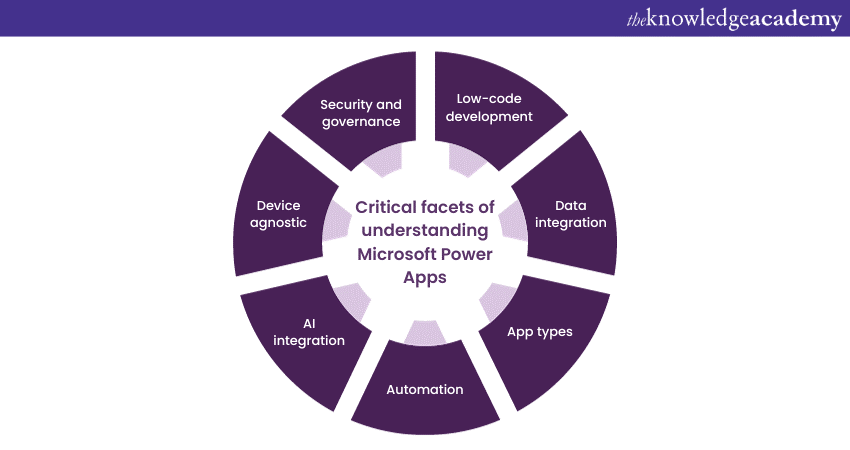
1) Low-code development: Power Apps offers a visual, drag-and-drop interface that simplifies the app development. Users can build apps by connecting pre-built components and defining business logic without delving into complex coding.
2) Data integration: It seamlessly integrates with various data sources, including Microsoft 365, SharePoint, and external databases, permitting users to access and exploit data from multiple systems within their apps.
3) App types: Power Apps supports canvas apps, which provide complete design flexibility, and model-driven apps that are data-centric and adhere to a standardised layout. Users can select the style that is most useful and suits their needs.
4) Automation: The platform incorporates Power Automate (formerly Flow), enabling users to automate workflows and streamline business processes.
5) AI integration: Power Apps can leverage AI and machine learning capabilities, such as AI Builder, to add intelligence to applications, making them more predictive and responsive.
6) Device agnostic: Power Apps ensures that created applications are responsive and can be used across various devices, from desktops to mobile devices, without requiring extensive adjustments.
7) Security and governance: It provides robust security features and governance controls, ensuring that sensitive data remains protected and compliant with organisational policies.
Discover a world of opportunities with our Microsoft Dynamics 365 Training courses.
Factors contributing to cost increases
The rising costs of Microsoft Power Apps can be attributed to several evolved interconnected factors. Organisations must understand these factors to manage their budgeting and resource allocation for Power Apps development and usage. Here, we delve into each of these contributing factors:
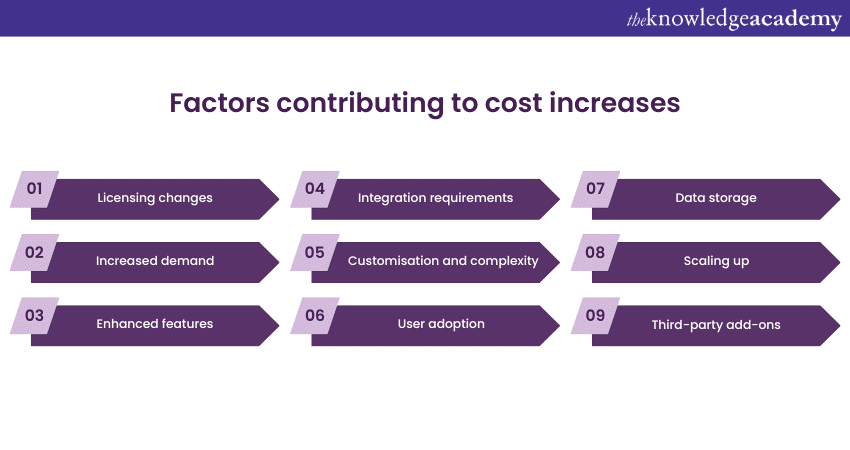
a) Licensing changes: Microsoft has introduced changes to its licensing models for Power Apps. These changes include shifting from a per-app pricing model to a per-user model, which may increase costs for organisations with users who only occasionally access the apps. Introducing premium connectors and data storage limits can also lead to additional expenses.
b) Increased demand: As more organisations recognise the value of Power Apps in digital transformation initiatives, the need for Power Apps has surged. With higher demand, Microsoft can justify premium pricing, knowing that many businesses rely on this platform for critical processes.
c) Enhanced features: Microsoft continuously enhances Power Apps with new features, capabilities, and integrations with other services. While these improvements offer added value, they may also come at an increased cost, especially if organisations adopt premium features.
d) Integration requirements: Power Apps is often used with other Microsoft services like Power BI, SharePoint, and Microsoft 365. Integrating these services can enhance functionality but may also incur additional licensing and infrastructure costs.
e) Customisation and complexity: Organisations often require highly customised and complex apps, which may necessitate more advanced licensing options and development efforts. Customisations can lead to increased costs in terms of development time and resources.
f) User adoption: The success of Power Apps depends on user adoption. Organisations may incur additional costs in movement and aid to ensure that employees can effectively use the applications.
g) Data storage: Storing data within Power Apps can incur costs, particularly if an organisation exceeds the allotted storage limits. Organisations with large volumes of data may need to pay for additional storage, contributing to overall expenses.
h) Scaling up: As organisations grow or expand their usage of Power Apps, costs can increase exponentially. This includes licensing additional users and scaling the infrastructure to accommodate a more extensive user base and complex applications.
i) Third-party add-ons: Many organisations use third-party add-ons and connectors to extend Power Apps' functionality. These add-ons often come with their costs, which can add up to the overall expense.
Licensing changes
Licensing changes have significantly contributed to the increased costs of Microsoft Power Apps. Microsoft has evolved its licensing models to align with the changing business needs and user demands landscape. These changes have notably impacted how organisations budget for and pay for their Power Apps usage. Here is a closer look at the licensing changes:
1) Shift from per-app to per-user licensing: Historically, Power Apps was often licensed per-app, where organisations paid for individual apps separately. However, Microsoft has transitioned to a per-user licensing model, where users can use as many apps as they need, resulting in a more user-centric approach. While this can be cost-effective for heavy users, it can increase costs for organisations with occasional or light app users.
2) Premium connectors and features: Microsoft has introduced premium and advanced features that require additional licensing fees. These premium offerings provide enhanced functionality and integrations but come at an extra cost, potentially impacting an organisation's budget.
3) Data storage limits: Power Apps limits data storage capacity based on licensing tiers. Organisations that exceed their allocated storage limits may need additional storage capacity, incurring other expenses.
5) Power Apps plans: Microsoft offers various Power Apps plans, such as Power Apps Per App, Power Apps Per User, and Power Apps Per Device. Organisations must carefully consider their requirements and select the appropriate plan, as the choice of method can significantly affect costs.
6) License enforcement: Microsoft has increased its focus on enforcing licensing compliance. Organisations are encouraged to ensure they have the licenses for their users and applications to avoid penalties.
Unlock the potential of the Microsoft Power Platform App Maker PL100 certification training and supercharge your organisation's capabilities.
Increased demand
The surging demand for Microsoft Power Apps has been a driving force behind the increasing costs associated with the platform. Several factors contribute to this heightened demand:
1) Digital transformation initiatives: Many organisations use digital transformation efforts to modernise their processes and systems. Power Apps has emerged as a crucial tool in this journey, enabling businesses to rapidly develop and deploy custom applications tailored to their evolving needs.
2) Pandemic-induced remote work: The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of remote work and digital solutions. Power Apps played a pivotal role in helping organisations adapt to this new work paradigm by facilitating remote collaboration, automation of tasks, and data accessibility.
3) Business user empowerment: Power Apps' low-code/no-code capabilities empower business users and subject-matter experts to create applications without extensive reliance on IT departments. This democratisation of app development has led to a surge in demand from various business units.
4) Appetite for streamlined processes: Organisations are increasingly seeking ways to simplify operations, enhance productivity, and reduce manual processes. Power Apps offers a quick and efficient means to achieve these goals, driving demand for its adoption.
5) Growing ecosystem: Microsoft's expansive ecosystem, including Power BI, SharePoint, and Microsoft 365, has spurred demand for Power Apps as organisations seek integrated solutions that seamlessly work together.
Managing Microsoft Power Apps Costs
Managing Microsoft Power Apps Costs is essential for organisations leveraging this platform efficiently without overspending. Here are strategies and best practices to keep expenses in check:
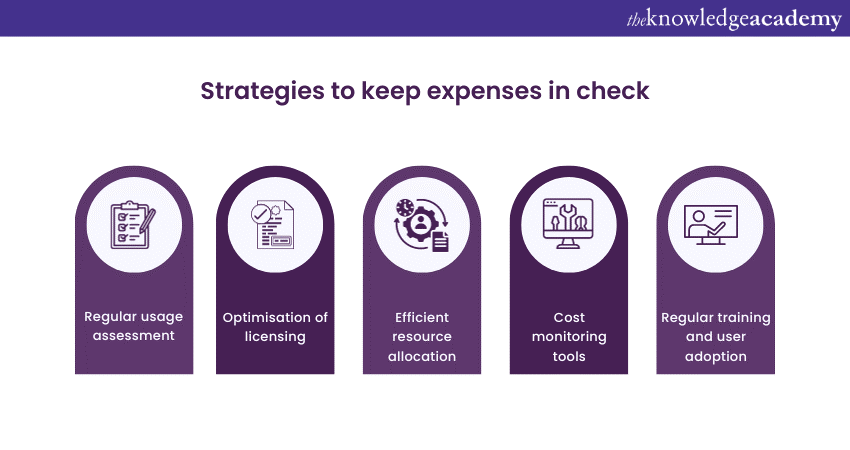
1) Regular usage assessment: Continuously evaluate your Power Apps usage. Identify which apps are actively used, by whom, and for what purposes. Decommission or consolidate apps that are no longer needed to reduce licensing costs.
2) Optimisation of licensing: Choose the most cost-effective licensing model based on user needs. For users who only occasionally use Power Apps, consider lower-tier licenses. Conversely, invest in appropriate permissions for heavy users requiring premium features to avoid overage charges.
3) Efficient resource allocation: Allocate resources judiciously. Assign licenses and resources based on roles and responsibilities within your organisation. Avoid over-licensing users who do not require all features and under-licensing those who need more capabilities.
4) Cost monitoring tools: Utilise cost monitoring and reporting tools to track Power Apps expenses. Microsoft provides cost management capabilities in its Power Platform admin centre, enabling you to gain insights into usage and costs.
5) Regular training and user adoption: Invest in training programs to enhance user proficiency. When users are skilled and confident in utilising Power Apps, they are less likely to create unnecessary, inefficient, or redundant apps, reducing costs associated with app development and maintenance.

Conclusion
In technology and innovation, Microsoft Power Apps have been empowering organisations seeking digital transformation. As the journey to harness its capabilities unfolds, the topic of Microsoft Power Apps' cost must be addressed.
In this blog, we have explored the intricacies behind the rising expenses associated with Power Apps, from licensing changes to enhanced features and increased demand. While these factors present challenges, they also underscore the platform's indispensability.
As organisations strive to navigate the expense maze, one thing remains clear: By understanding the dynamics of Microsoft Power Apps Cost and implementing strategic cost management practices, businesses can continue to harness the power of this remarkable platform, driving efficiency, innovation, and success in the digital era.
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Microsoft Technical Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Microsoft Power Apps for End Users 55265AC
Microsoft Power Apps for End Users 55265AC
Thu 19th Dec 2024
Thu 9th Jan 2025
Thu 6th Mar 2025
Thu 8th May 2025
Thu 3rd Jul 2025
Thu 4th Sep 2025
Thu 6th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


