We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +352 8002-6867 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) is an approach that helps business firms to grow. Organisations, particularly in the manufacturing sector, count on delivering products to their target audience. That can happen only with a steady flow of raw materials and necessary supplies. That’s why managing relationships with vendors and suppliers is crucial to the smooth running of the enterprise.
Read this blog to know about “What is Supplier Relationship Management?” You will learn the process of SRM, its benefits, challenges and more.
Table of Contents
1) What is Supplier Relationship Management (SRM)?
2) How Supplier Relationship Management works?
3) The Supplier Relationship Management process
4) Benefits of Supplier Relationship Management (SRM)
5) Challenges in Supplier Relationship Management
6) Conclusion
What is Supplier Relationship Management (SRM)?
SRM involves handling interactions with vendors supplying goods, materials, or services to a company. This entails assessing these relationships and strategising to enhance them for improved business efficiency. By analysing the vendor list, companies can identify key suppliers crucial for business continuity and performance. Through these assessments, managers can foster better working relationships with important vendors, ensuring smooth operations and optimal performance.
Many professionals use Supplier Relationship Management to manage supply chains. They communicate frequently with vendors due to managing procurement, project management and operations. That’s why SRM is often referred to as supply chain management. It is also close to what is commonly called vendor management and procurement processes.
However, there are many differences between SRM and the other related fields. The major aim of vendor management is the costs and service agreements between vendors and organisations. Meanwhile, the goal of procurement is to purchase themselves. In that, they deal with ordering, contracting, invoicing, and paying off those procurements.
How Supplier Relationship Management works?
Every organisation has unique approaches. However, given below are a few common steps involved in the SRM process:
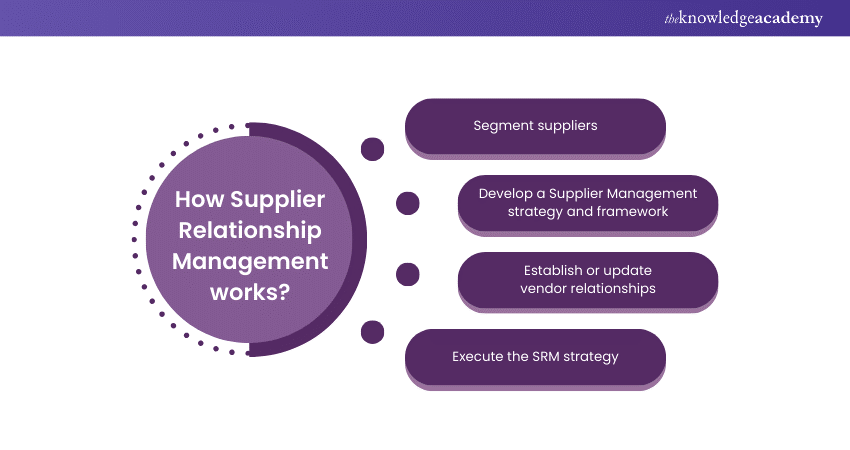
1) Segment suppliers
This is the first and fundamental step in the SRM process. In this step, business firms identify all its suppliers and categorises them by their significance to the business. This ensures the suppliers key to the success of a business get proper attention.
2) Develop a Supplier Management strategy and framework
Here, the organisation designs a strategic plan for how Supplier Relationship Management will work with each Supplier or category of suppliers. While all suppliers play a significant role in success, organisations should start with the category of suppliers deemed most critical. Aligning business strategy processes and assigning stakeholders according to business goals requires a strategic approach and supporting framework that addresses governance and performance management.
3) Establish or update vendor relationships
This step involves communicating Supplier Relationship Management plans, strategies and initiatives with key suppliers. It can help advance relationships and provide valuable insights into what will ensure mutual success.
4) Execute the SRM strategy
The executives who are responsible for SRM must ensure that the strategy is implemented and that they or designated managers take on daily oversight. They should devise ways to monitor progress and identify potential points of failure in the SRM strategy or its execution.
Manage your workflow resources with our Workforce Resource Planning Training - Sign up right now!
The Supplier Relationship Management process
Every organisation has unique approaches. However, given below are a few common steps involved in the SRM process.
1) Segmentation of the supply base
Supplier segmentation involves categorising suppliers to enhance relationships and gain insights. For instance, grouping suppliers by provided items reveals risks of scarcity or oversupply, impacting savings and efficiency. Using frameworks like the Kraljic matrix further refines segmentation based on item importance and risk. This aids negotiations, especially during disruptions, ensuring effective resource allocation.
Supplier relationship managers employ diverse segmentation methods to add value to businesses, adapting as needed. Experimentation and innovation in segmentation methods are encouraged to optimise supplier management practices and adapt to evolving supply chain challenges.
2) Development of a supplier strategy
This step combines envisioning ideal supplier scenarios and strategising necessary actions to align current arrangements with these ideals. Let's consider a scenario: Supplier A offers quality but expensive products; Supplier B lacks cooperation, and Supplier C lacks reliability for critical components. Ideal solutions include negotiating lower prices with A, improving communication with B, and diversifying vendors for redundancy with C. Execution involves obtaining competitive offers for A, fostering better relations with B, and gradually transitioning some business from C to another reliable supplier to mitigate risk. Planning and proactive communication are essential for seamless implementation and minimal disruption.
3) Collaboration with suppliers
Supply chain managers may neglect the crucial role of collaboration in SRM. Usually, the focus stays on transactional aspects, ignoring the value of nurturing collaborative relationships with suppliers. Collaboration can take two forms: informal human connections and formal partnerships between organisations. Informal collaboration arises through Supplier Relationship Management, enabling mutual understanding beyond transactions.
Suppliers may provide insights on upcoming changes while customers share their needs. Some relationships evolve into formal collaborations, even involving customers in product development. Examples abound, such as Visa and Citigroup partnering with Costco for co-branded credit cards. Such collaborations drive innovation, as seen in the transportation sector's partnerships. Moreover, big companies nurturing small startups foster future suppliers' growth and alignment with customer needs.
4) Implementation of the strategy
Supplier Relationship Managers who excel in the initial steps will find the next ones easier. Effective planning facilitates smooth execution, so sticking to the developed strategy is crucial. Although deviations may occur, strong collaborative relationships with suppliers enable adjustments as needed. Additionally, supplier segmentation aids in prioritising tasks during unforeseen situations. By leveraging these tools, managers can navigate challenges effectively, ensuring continued success in supplier management.
5) Enhancement of supplier quality
Improving supplier quality involves two main approaches. Firstly, companies can optimise what items suppliers provide and when they deliver them. By segmenting suppliers and assessing their strengths and weaknesses, organisations can adjust order timing to enhance quality and delivery speed. Secondly, direct collaboration with suppliers can lead to quality improvements.
Simply communicating needs and preferences can prompt suppliers to make beneficial changes. For instance, requesting specific product enhancements tailored to your requirements can result in significant improvements. Effective communication ensures suppliers understand your needs and capabilities, facilitating mutually beneficial improvements in quality and service.
Manage your workflow resources with our Workforce Resource Planning Training - Sign up right now!
Benefits of Supplier Relationship Management (SRM)
Increasing efficiency is crucial for businesses, especially in manufacturing with external vendors supplying materials. Supply Relationship Management (SRM) helps run a smoother operation, leading to better profits. It ensures streamlined processes, optimal resource use, and lower costs. Plus, SRM fosters good communication with suppliers, improving product quality and delivery times. Overall, investing in SRM means a more efficient and profitable business.
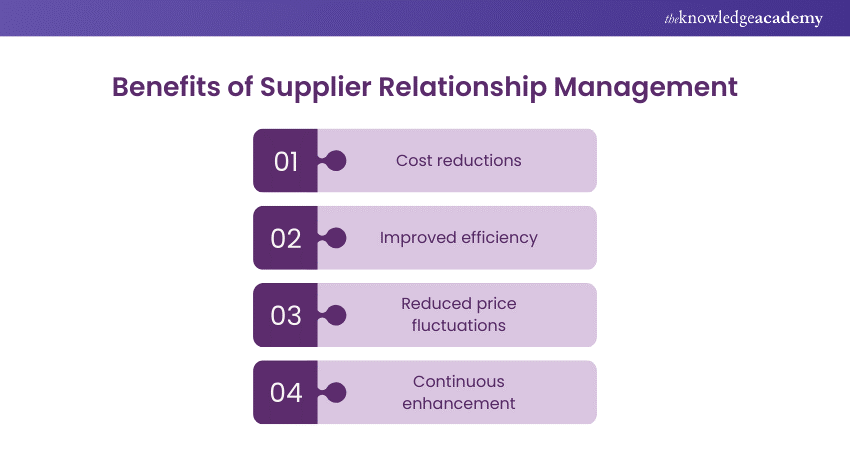
1) Cost reductions
Building relationships with vendors is about saving money and ensuring smooth operations. Supplier Management and Relationship (SMR) strategies focus on long-term cost savings through mutually beneficial partnerships. These relationships help cut setup costs and address issues like availability, delays, and material quality, ultimately benefiting customers. Prioritising collaboration with vendors leads to efficient supply chains and happier customers.
2) Improved efficiency
Maintaining relationships with suppliers prevents communication gaps and potential problems. Trust-building with vendors fosters improved working conditions, ensuring a smoother supply chain flow. This translates to fewer disruptions, and in case of issues, strong supplier connections expedite resolutions.
3) Reduced price fluctuations
Commodity prices can fluctuate, causing concerns for customers if product costs rise. With Supplier Relationship Management (SRM), manufacturers can often secure fixed prices for materials, ensuring stability even amid market fluctuations. Many vendors are open to offering fixed pricing in exchange for long-term contracts from manufacturers. This arrangement provides predictability in costs, offering reassurance to both manufacturers and customers.
4) Continuous enhancement
Creating a win-win bond between manufacturers and suppliers fosters trust and encourages feedback and idea sharing. This communication enhances efficiency, streamlines processes, and improves customer service. Using project management software to integrate ordering and inventory control further facilitates these advantages.
Challenges in Supplier Relationship Management
SRM brings significant benefits to organisations, but it also comes with challenges. These challenges demand constant attention to both quantitative and qualitative aspects while avoiding common pitfalls. Here are four major categories of Supplier Relationship Management challenges:
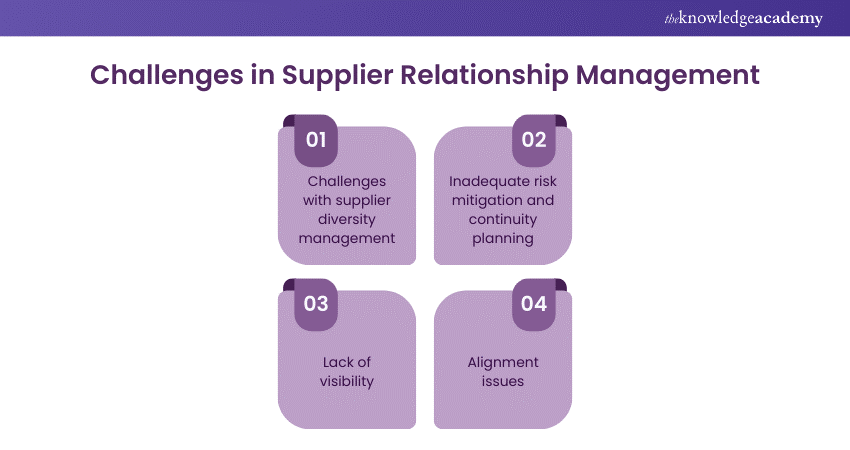
1) Challenges with supplier diversity management
Supplier diversity addresses two distinct challenges: mitigating supply chain risk and increasing purchasing from minority-owned businesses. Balancing diversification with deep supplier relationships is crucial. While diversification reduces risk, consolidating purchases with one Supplier may yield volume discounts but poses a single point of failure. Conversely, managing numerous suppliers offers redundancy but challenges relationship-building. The optimal balance varies by business needs.
The second aspect focuses on sourcing from historically underrepresented or underserved groups, such as minorities, women, veterans, and LGBTQ+ individuals. Beyond social impact, supplier diversity programs benefit businesses by enhancing brand reputation, fostering competitiveness, and expanding networks. However, many minority-owned businesses lack the financial capacity to handle large contracts, necessitating supply chain finance solutions for successful partnerships.
Maintain cost efficiency with our Costing And Pricing Training - Register now!
2) Inadequate risk mitigation and continuity planning
Recent rises in supply chain disruptions and business turnover have made maintaining business continuity more challenging. Supplier Relationship Managers face evolving risks associated with these disruptions. Some helpful techniques include:
1) Trace supply chains further upstream to anticipate issues
2) Diversify supply chains to mitigate outages and shortages
3) Proactively communicate upcoming needs to suppliers with more advance notice than before
These methods can help mitigate the impact of disruptions and enhance business continuity.
3) Lack of visibility
Visibility in supplier relationships doesn't occur naturally but requires intentional development through effective Supplier Relationship Management. Even with strong visibility, understanding a supplier organisation remains limited compared to internal insights. Overcoming visibility challenges involves both technical and interpersonal strategies. This includes implementing supply chain visibility tools and maintaining regular communication with supplier contacts. By combining technological aids with personal engagement, businesses can enhance transparency and better navigate supplier relationships.
4) Alignment issues
Despite Supplier Relationship Management's emphasis on positive supplier collaborations and deep relationships, it's crucial to recognise that your interests won't always perfectly align with those of your suppliers. Price negotiations are a common source of misalignment, as each party seeks a favourable deal. Additionally, suppliers may aim to enter your market or innovate to compete with you, while your own R&D efforts may aim to replace suppliers. Sometimes, organisations simply struggle to synchronise their goals. Achieving alignment requires extra effort from the SRM team, especially when incentives for collaboration are lacking.
Conclusion
Supplier Relationship Management is more than just negotiating contracts. It's about trust, collaboration, commitment, transparent communication, and compliance with the SRM process. Investing in technologies like Customer Relationship Managers (CRMs) is crucial for a strategic SRM strategy. These elements help build strong relationships between buyers and sellers, driving mutual success.
Learn how to deliver services on time with our Productivity And Time Management Training- Sign up today!
Frequently Asked Questions

Organisations can implement SRM effectively by establishing clear communication, setting mutual goals, conducting regular performance evaluations, fostering collaboration, and leveraging technology for streamlined processes and data-driven insights.

Suppliers are vital as they provide goods or services essential for business operations. They impact quality, cost, and overall success. Maintaining strong relationships ensures reliability, innovation, and competitive advantage.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Business Skills, including 8D Problem-Solving Training, Financial Management and Behaviour Management Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Top 15 Principles of Customer Service.
Our Business Skills Blogs cover a range of topics related to Leadership, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Project Management skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Business Sustainability Course
Business Sustainability Course
Fri 13th Dec 2024
Fri 7th Feb 2025
Fri 4th Apr 2025
Fri 6th Jun 2025
Fri 8th Aug 2025
Fri 3rd Oct 2025
Fri 5th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


