We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +352 8002-6867 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Are you having trouble keeping your expenses in check? Have you wanted to cut costs for a very long time? There is something that can help you with this - Budget. So, what is a Budget? A Budget is the perfect answer to all your questions.
A Budget is a resource management plan that details a given period's projected income and expenses. It can be of different types. A Budget plays several roles in people’s lives; it helps private individuals, companies, and governments meet financial commitments by directing resources optimally.
A Budget is a plan for managing, controlling and monitoring money in aspects of income and expenditure, which in turn assists in the enhancement of a good standard of living and debt-free mode as well as an excellent financial framework for tackling the following financial needs. This yields explicit financial performance scenarios, making it easy to make sound decisions and promoting accountability.
Table of Contents
1) What is a Budget?
2) Why create a Budget?
3) The significance of Budgeting
4) Types of Budget
5) Step-by-step process to create a Budget
6) Conclusion
What is a Budget?
Budget can be defined as a planned financial statement that shows expected receipt sources and anticipated receipt uses over a particular period. It assists people, companies, and states by providing them with methods of spending money, identifying which expenses are most important, and determining how plans can be fulfilled.
A Budget thus helps control income and expenditure, improve spending practices, spend within our means, and possibly save for rainy days. It is beneficial in giving details about the state of the company’s finances, thereby assisting management in making informed decisions.
Why create a Budget?
Developing a Budget to aid financial management and achieve short-term and long-term objectives is always good practice. Budgets are vital tools that enable individuals and organisations to forecast and control the flow of their money so that they can spend it wisely.
The first and perhaps the most crucial purpose of preparing a Budget is to gain insight into one's financial status. It gives an overall snapshot of one's income and expenses, with tips on how to spend less in specific categories. This awareness is essential for developing a positive attitude toward financial management and the process of setting proper goals and aims.
A Budget also encourages creating a fund for rainy days since it allows you to prepare for such eventualities. The financial buffer can help make one secure and financially stable in the event of an illness or loss of a job.
Besides, the process of Budgeting enhances discipline and accountability. It ensures thrift and wise expenditures, with an emphasis on basic needs over wants. In the case of businesses, Budgets serve as the best tools for planning, controlling resources, and assessing performance to support sustainable growth and profitability.
Acquire new skills crucial for workplace efficiency and effectiveness with our Personal Development Courses – join now!
The significance of Budgeting
Here are some points that will help you understand the significance of Budgeting:
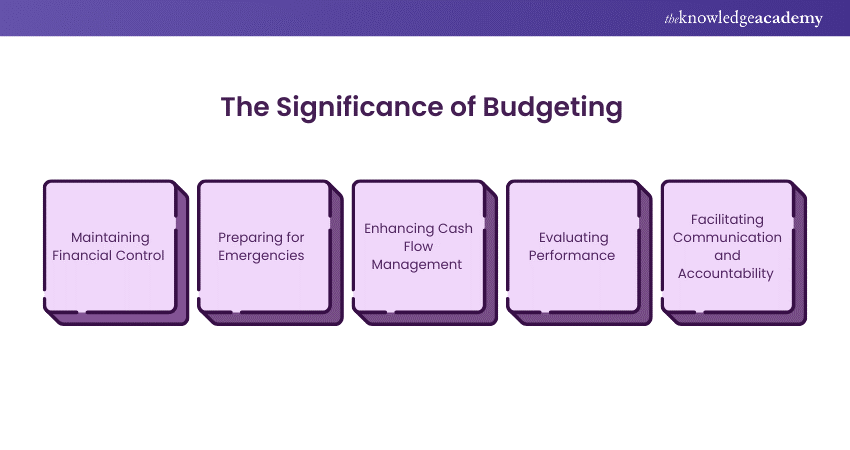
1) Maintaining Financial Control
Budgeting helps you control your income and expenditures since you can see your balance in detail. By limiting the amount of money spent and monitoring the expenses made, a Budget prevents you from going over the Budgeted amount and directing money to priority areas to avoid incurring debts, hence achieving financial control.
2) Preparing for Emergencies
Emergency funds are also important in any well-laid-down Budget to cover diseases, accidents, and job losses. Creating and maintaining an emergency fund, part of an appropriate monthly Budget, allows individuals and organisations to be financially prepared for unforeseen expenses and remain financially stable.
3) Enhancing Cash Flow Management
Budgeting helps manage cash flows by projecting and controlling the timing of resources and obligations. It also assists in determining the surplus or deficiency of cash flow and planning the finances well in advance. This makes it easy to prepare and manage expenditure and income patterns to support an operation's functioning.
4) Evaluating Performance
Budgeting is a tool for comparing financial performance. It involves estimating actual income and expenses against projected standards that aid individuals and organisations in recognising their strengths and weaknesses. Budgeting enables people to make the right financial decisions, increase effectiveness, and meet financial objectives.
5) Facilitating Communication and Accountability
A Budget provides accountability and encourages communication between households and other organisations. It fosters accountability because everyone is aware of the financial goals and the roles they have been assigned to undertake. Budgeting is also valuable for organisations since it makes all departments responsible for their overall financial health, hence the need to use resources efficiently.
Types of Budgets
There are different types of Budgets which you can look into if you are starting to Budget for the first time. These are as follows:
1) Master Budget
The Master Budget is a thorough financial planning technique that consolidates an organisation's Budget. It includes projections for sales, production, expenses, and other economic activities, providing an overall financial plan for the entire organisation. It is a central planning tool that guides strategic decision-making and performance evaluation.
2) Fixed Budget
A Fixed Budget remains unchanged regardless of variations in business activity levels. It is based on assumptions made at the start of the Budgeting period and does not adjust for changes in sales or production volumes. This type of Budget is helpful for organisations with stable and predictable operations.
3) Financial Budget
The Financial Budget focuses on an organisation’s goals, detailing expected revenues, expenses, and capital needs. It includes projections for the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement, ensuring that the organisation’s financial resources are managed effectively to meet strategic objectives.
4) Cash Budget
A Cash Budget estimates the inflows and outflows of cash over a specific period. It helps organisations manage their cash flow, ensuring sufficient liquidity to meet obligations. Organisations can plan for shortfalls and surpluses by projecting cash needs, facilitating better financial planning.
5) Sales Budget
The Sales Budget forecasts expected sales revenues for a specific period. It is based on market analysis, historical sales data, and sales targets. This Budget is crucial for planning production, inventory management, marketing strategies, and aligning sales goals with overall business objectives.
6) Capital Expenditure Budget
The Capital Expenditure Budget outlines planned investments in long-term assets such as machinery, equipment, and buildings. It details the costs and timing of these investments, ensuring that the organisation allocates resources effectively for capital projects that support growth and operational efficiency.
7) Operating Budget
An Operating Budget estimates the revenues and expenses related to a business's daily operations. It includes projections for sales, cost of goods sold, and operating expenses. This Budget helps organisations plan their operational activities and manage their financial performance.
8) Flexible Budget
A Flexible Budget adjusts according to changes in business activity levels. It provides a more accurate financial plan, varying with actual sales or production volumes. This type of Budget is helpful for organisations with fluctuating operations, allowing for better responsiveness to changes in the business environment.
9) Zero-based Budget
A Zero-based Budget requires each expense to be justified for each new period, starting from zero. Unlike traditional Budgeting methods that adjust previous Budgets, zero-based Budgeting requires thoroughly evaluating all costs, ensuring that resources are allocated based on current requirements and priorities.
10) Incremental Budget
An Incremental Budget is based on the previous period's Budget, with adjustments made for expected changes. This type of Budget assumes that existing operations will continue and only new expenses or changes are considered. It is simple to implement but may overlook opportunities for cost savings or efficiency improvements.
11) Government Budget
A Government Budget outlines a government's expected revenues and costs over a specific period, usually a fiscal year. It includes allocations for various public services and programs, reflecting the government's priorities and economic policies. It serves as a tool for fiscal management and policy implementation.
12) Production Budget
The Production Budget calculates the total number of units produced to meet sales goals and inventory requirements. It helps in planning production activities, ensuring sufficient resources to meet demand. This Budget is essential for managing manufacturing operations and maintaining optimal inventory levels.
13) Project Budget
A Project Budget details the estimated costs associated with a specific project. It includes projections for all expenses related to the project, such as labour, materials, and overheads. This Budget helps plan and control project costs and make sure the project is completed within the allocated Budget.
Understand how you can prepare for an interview with our Interview Skills Training – register now!
Step-by-Step Process to Create a Budget
Here is a detailed step-by-step process on how you can create a Budget:
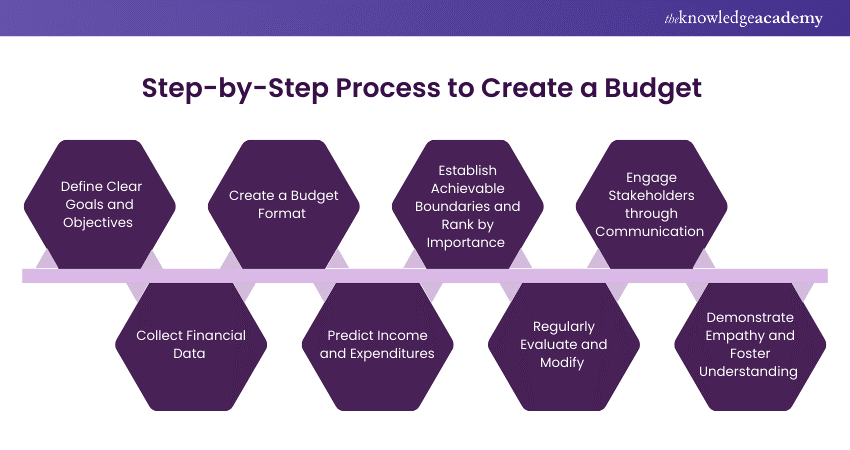
1) Define Clear Goals and Objectives
Start by identifying specific financial goals and objectives you aim to achieve with your Budget. These can include saving for a significant purchase, reducing debt, or ensuring sufficient funds for operational expenses. Clear goals provide direction and purpose, guiding the Budgeting process and ensuring all efforts align with achieving these objectives.
2) Collect Financial Data
Gather all relevant Financial Data, including income statements, expense reports, bank statements, and other financial records. This data provides a comprehensive view of your current financial situation, helping you understand where your money comes from and how it is spent. Accurate data collection is crucial for creating a realistic and practical Budget.
3) Create a Budget Format
Choose a format for your Budget that suits your needs, whether it's a spreadsheet, Budgeting software, or a simple written document. The format should be easy to understand and use, allowing you to clearly outline income sources, categorise expenses, and track financial activity. A well-structured format helps to organise financial information effectively.
4) Predict Income and Expenditures
Estimate your expected Income and Expenditures for the Budgeting period. Base these predictions on historical data, market trends, and any known changes. Accurately forecasting income and expenses helps create a realistic Budget that reflects your financial capabilities and limitations, ensuring you can meet your financial goals.
5) Establish Achievable Boundaries and Rank by Importance
Set clear spending limits and prioritise expenses based on their importance. Distinguish between essential and non-essential expenditures, ensuring that critical needs are met first. Establishing achievable boundaries helps maintain financial discipline and prevents overspending while prioritising expenses ensures funds are allocated to the most vital areas.
6) Regularly Evaluate and Modify
Continuously monitor your Budget’s performance and compare actual financial activity against your projections. Regular evaluation helps identify discrepancies and areas for improvement. Adjust your Budget to reflect all the changes in income, expenses, or economic goals. This flexibility ensures that your Budget remains effective and relevant over time.
7) Engage Stakeholders through Communication
Through clear and open communication, all relevant stakeholders are involved in the budgeting process. This includes discussing financial goals, sharing progress, and seeking input on budget adjustments. Engaging stakeholders fosters collaboration and ensures that everyone is aligned with the financial objectives, promoting a sense of shared responsibility and commitment.
8) Demonstrate Empathy and Foster Understanding
Recognise the impact of financial decisions on all involved parties and show empathy in your approach. Foster an environment of understanding by listening to concerns and addressing them thoughtfully. Demonstrating empathy helps build trust and cooperation, ensuring the Budgeting process is inclusive and considerate of everyone’s needs and perspectives.
Learn how you can create a Budget with our Introduction to Managing Budgets Course- join now!
Conclusion
Understanding What is Budget will help you reduce your expenses and plan for your future financial goals. By following these steps and involving stakeholders, you can create an effective Budget that supports your financial objectives, promotes fiscal discipline, and ensures financial stability and success.
Learn how to adapt to changes in working routine or environment with our Stress Management Course!
Frequently Asked Questions

A short-term Budget is a financial plan that covers a brief period, usually up to a year, to manage income and expenses efficiently, ensuring financial stability and goal achievement within a limited timeframe.

Budget notes are detailed explanations and justifications for each item in a budget, providing context, rationale, and additional information to ensure clarity and transparency in financial planning and decision-making.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Personal Development Courses , including the Introduction to Managing Budgets, Time Management Training, Attention Management Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into How to Create a Marketing Budget.
Our Business Skills Blogs cover a range of topics related to Budgeting, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Budgeting skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Introduction to Managing Budgets
Introduction to Managing Budgets
Fri 14th Feb 2025
Fri 11th Apr 2025
Fri 13th Jun 2025
Fri 8th Aug 2025
Fri 10th Oct 2025
Fri 12th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


