We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +352 8002-6867 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Feeling overwhelmed by IT inefficiencies? Struggling with sluggish systems, redundant processes, and ballooning costs? Modern digital enterprises require a streamlined and efficient IT infrastructure to ensure business success. That's where Lean IT comes to the rescue! This results-oriented approach focuses on eliminating waste and maximising value within your IT operations. But What is Lean IT exactly, and how can it transform your business’ technological outlook?
This comprehensive blog will dive deep into the philosophy of What is Lean IT and explore its core principles and powerful tools. We'll discuss strategies to identify and eliminate IT waste, optimise resource allocation, and ultimately, achieve a more agile and cost-effective IT environment. Get ready to unlock the full potential of your IT department with the power of Lean IT!
Table of Contents
1) What is Lean IT?
2) Key Principles of Lean IT
3) Lean IT: Four Core elements
4) Implementing Lean IT: Steps and Strategies
5) 4 Real examples of Lean IT
6) Benefits and Challenges in Lean IT
7) Conclusion
What is Lean IT?
Lean IT epitomises the application of Lean principles within the Information Technology (IT) realm, aiming to augment efficiency and value. Lean IT concentrates on curtailing waste, refining processes, and enhancing service delivery to better fulfil customer requirements. By prioritising continuous improvement and collaboration, Lean IT endeavours to streamline IT operations, diminish costs, and heighten agility. Crucial elements encompass the eradication of superfluous steps, the enhancement of response times, and the cultivation of a culture rooted in perpetual learning and problem-solving. Lean IT also synergises seamlessly with other IT frameworks like ITIL and Agile, ensuring a comprehensive approach to IT management. The paramount objective is to forge a more responsive, efficient, and customer-centric IT environment.
Key Principles of Lean IT
Let’s look at some of the principles of Lean IT:
Value
Value forms the bedrock of Lean IT, interpreted from the customer's vantage point. It accentuates comprehending the customer's genuine needs and tailoring IT services to fulfil these requisites. By honing in on value, IT organisations ensure that every process and activity directly augments the customer experience. Identifying and amplifying value aids in prioritising endeavours that yield the most substantial benefits to the customer, thus bolstering satisfaction and loyalty.
Value Stream
The value stream encompasses the entire lifecycle of delivering a product or service, from conception to fruition. In Lean IT, mapping the value stream entails scrutinising each step within the process to discern value-adding activities and those that do not. This meticulous analysis aids in visualising the workflow and identifying inefficiencies. Understanding the value stream enables organisations to streamline processes, eliminate redundant steps, and ensure a seamless flow of value to the customer.
Flow
Flow within Lean IT pertains to cultivating an unbroken and smooth progression of tasks and activities throughout the value stream. It aspires to minimise delays, bottlenecks, and interruptions that can impede productivity. Ensuring a continuous flow enhances efficiency and accelerates the delivery of IT services. Techniques such as automating routine tasks and optimising resource allocation are employed to sustain a steady flow, resulting in faster and more dependable service delivery.
Pull
The pull principle mandates that work is initiated based on actual demand rather than forecasts. In Lean IT, this signifies that services and products are generated in response to customer needs, thereby avoiding overproduction and reducing waste. Implementing a pull system aids in aligning IT operations more closely with customer requirements, rendering the organisation more responsive and adaptable. It ensures resources are utilised efficiently and that services are delivered just in time to satisfy customer demands.
Unlock your potential with Certified Lean IT Training and take your career to new heights - join us now!
Perfection
Perfection epitomises the pursuit of continuous improvement within Lean IT. It involves an unwavering quest for superior methods to execute tasks and deliver services. By nurturing a culture of relentless refinement, organisations aim to eradicate waste, enhance processes, and attain elevated levels of quality and efficiency. Perfection represents an ongoing journey where incremental improvements are perpetually sought to create more value and elevate customer satisfaction. This principle promotes innovation and adaptability, driving long-term success.
Lean IT: Four Core Elements
Here are some of the core Lean IT elements:
1) Behaviours and Mindsets
Behaviours and mindsets constitute the bedrock of Lean IT, concentrating on nurturing a culture of continuous improvement and customer-centricity. This entails motivating employees to adopt a proactive stance towards problem-solving, welcoming change, and persistently seeking methods to refine processes. A Lean mindset fosters collaboration, innovation, and an unwavering commitment to delivering value. Leaders are pivotal in exemplifying these behaviours, setting the organisational ethos.
2) Management Systems
Management systems in Lean IT provide the scaffolding for astute decision-making and process governance. These systems ensure objectives are clearly articulated, progress is diligently monitored, and performance is perpetually enhanced. Key components include performance metrics, feedback loops, and regular evaluations. Effective management systems synchronise IT operations with business objectives, ensuring resource optimisation and sustainable improvements.
3) Operating Procedures and Practices
Operating procedures and practices encompass the standardised methods and techniques deployed to execute IT processes. Lean IT underscores the significance of standardisation in eliminating variability and ensuring uniformity in service delivery. This includes adopting best practices, documenting processes, and utilising tools such as value stream mapping and root cause analysis. Standardised procedures aid in reducing errors, augmenting efficiency, and providing a lucid roadmap for process enhancement.
4) Capabilities and Organisation
Capabilities and organisation pertain to the skills, competencies, and structure requisite for supporting Lean IT initiatives. Cultivating the appropriate capabilities involves training and developing staff to imbue them with Lean principles and methodologies. The organisational structure should endorse collaboration, adaptability, and effective communication. By aligning capabilities with organisational objectives, Lean IT ensures the workforce is proficient in driving and sustaining continuous improvement endeavours.
Streamline Your IT Operations – Download the Lean IT PDF Today!
Implementing Lean IT: Steps and Strategies
Implementing Lean IT necessitates a structured methodology to guarantee successful adoption and sustained enhancement.
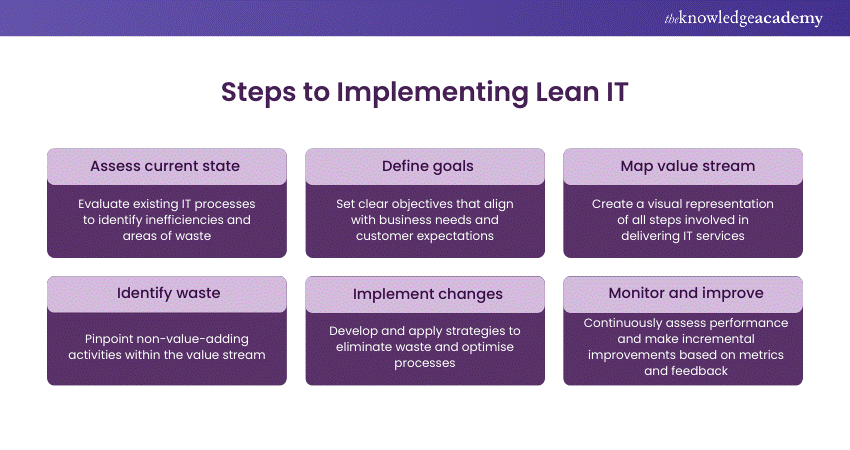
The initial step involves assessing the current state of IT operations, evaluating existing processes, identifying inefficiencies, and recognising areas of waste. Subsequently, defining goals is imperative, with objectives that align with business needs and customer expectations clearly articulated.
Once goals are delineated, mapping the value stream becomes essential. This entails creating a comprehensive visual representation of all steps involved in delivering IT services and facilitating the identification of value-adding and non-value-adding activities. Following this, pinpointing waste within the value stream allows for identifying areas requiring improvement.
The next step is implementing changes. Formulate and apply strategies to eliminate waste and optimise processes, which may encompass adopting new technologies, reengineering workflows, and training staff. Continuous improvement is ensured through vigilant monitoring and refinement, regularly assessing the performance of IT operations and using metrics and feedback to guide ongoing enhancements.
Effective communication and engagement across the organisation are crucial to overcoming resistance to change and fostering a culture of continuous improvement. Leadership commitment and involvement at all levels ensure that Lean IT principles are embedded within the organisational ethos, leading to sustainable success and improved IT service delivery.
Take the first step towards becoming a Lean IT expert today – join our Lean IT Certification.
4 Real Examples of Lean IT
Here are some real examples of Lean IT:
Insurance company
An insurance company implemented Lean IT to streamline its claims processing. By mapping the value stream, they identified redundant steps and automated routine tasks, significantly reducing processing time. This led to faster claim settlements, improved customer satisfaction, and lower operational costs.
Production company
A production company applied Lean IT to its IT support operations. They standardised troubleshooting procedures and utilised data analytics to identify common issues. This approach reduced downtime, increased productivity, and enhanced the overall efficiency of their IT support services.
Bank
A bank adopted Lean IT principles to improve its online banking services. By eliminating bottlenecks in the development process and implementing continuous integration and deployment (CI/CD), they accelerated the release of new features and enhancements. This resulted in a more responsive and user-friendly online banking platform.
Consultancy
A consultancy firm utilised Lean IT to optimise its project management processes. They introduced standardised project templates and automated reporting tools, reducing administrative overhead and improving project delivery times. This enabled consultants to focus more on value-added activities and client engagement.
Advance your career with our ITIL® 4 Leader in Digital and IT Strategy Certification – register today!
Benefits and Challenges in Lean IT
Embracing Lean IT practices can yield numerous benefits. However, organisations may also face certain challenges. Let’s look at both of them:
Benefits of Lean IT
a) Improved Efficiency: By eliminating waste and optimising processes, Lean IT enhances operational efficiency, leading to faster service delivery and better resource utilisation.
b) Cost Reduction: Lean IT helps reduce costs by minimising unnecessary expenditures and improving productivity, resulting in significant savings for the organisation.
c) Enhanced Quality: Focusing on value and customer needs, Lean IT improves the quality of IT services and products, leading to higher customer satisfaction.
d) Greater Agility: Lean IT enables organisations to respond quickly to market changes and customer demands, enhancing their flexibility and competitiveness.
e) Employee Empowerment: Lean IT fosters a culture of continuous improvement and collaboration, encouraging employees to contribute ideas and take ownership of process enhancements.
Challenges in Lean IT Implementation
a) Resistance to Change: Employees may resist changes to established processes, requiring effective communication and involvement to overcome reluctance.
b) Cultural Shift: Adopting Lean IT necessitates a cultural shift towards continuous improvement and customer-centricity, which can be difficult without strong leadership.
c) Resource Constraints: Implementing Lean IT may demand investments in new technologies and training, posing challenges for organisations with limited resources.
d) Sustaining Improvements: Maintaining the momentum of Lean IT initiatives requires ongoing monitoring and reinforcement, which can be challenging to sustain over the long term.
Ready to implement Lean Six Sigma? Download the Lean Six Sigma Project Examples PDF and get practical examples to guide your next improvement project.
Conclusion
Now, being empowered with the knowledge of What is Lean IT, you're ready to tackle IT inefficiencies head-on! Eliminate waste, streamline processes, and optimise your IT resources. Embrace Lean IT – the key to a more agile, cost-effective, and successful technology foundation!
Unlock your potential in IT Service Management with our comprehensive ITIL® 4 Foundation Certification Course - join us now!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Lean capacity?

Lean capacity refers to the optimal use of resources in a process to meet customer demand without excess or waste. It ensures efficient operations by balancing workload, reducing bottlenecks, and maintaining flexibility for fluctuations in demand.
What are the five rules of Lean?

The five rules of Lean are:
a) Identify value
b) Map the value stream
c) Create flow
d) Establish pull
e) Seek perfection
These principles aim to optimise processes by eliminating waste, ensuring smooth workflows, responding to demand, and continuously improving.
What are the other resources and offers provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is the Knowledge Pass, and how does it work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are related courses and blogs provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Lean IT Courses, including the Certified Lean IT Training, and more. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into the IT Assest Management.
Our IT Service Management Blogs cover a range of topics related to Lean IT, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your IT Service Management skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Business Improvement Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Certified Lean IT Training
Certified Lean IT Training
Thu 22nd May 2025
Thu 18th Sep 2025
Thu 20th Nov 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


