We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203 999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

If you are intrigued by Sherlock Holmes, you’ll likely find Digital Forensics fascinating. Think of it as the modern, digital version of classic detective work. Digital Forensics gained prominence in the 1980s, a time when computers were still a mystery to many.
In this blog, you will learn about What is Digital Forensics, its importance, applications, techniques, and more. So, wasting no time, let's begin our mysterious and career-empowering journey!
Table of Contents
1) Understand What is Digital Forensics?
2) Importance of Digital Forensics
3) Key Branches of Digital Forensics
4) Steps in the Digital Forensics Process
5) Applications of Digital Forensics
6) Common Digital Forensics Techniques
7) Benefits of Digital Forensics
8) Drawbacks of Digital Forensics
9) Conclusion
Understand What is Digital Forensics?
Digital Forensics is the field of forensic science that specialises in detecting and eliminating cyber-attacks, online frauds and malicious activities through evidence-gathering processes like those used by classic detectives (like Sherlock Holmes).
However, it's important to note that Digital Forensics is often confused with computer forensics, and many people use them interchangeably. To differentiate, computer forensics is the Digital Forensics branch, which focuses only on gathering evidence through computation devices, including computers, tablets, and smartphone phones. Digital Forensics focuses broadly on all digital devices for evidence-gathering, including network systems, servers, cloud storage, and IoT devices.
Importance of Digital Forensics
Digital Forensics is of vast importance, especially given the steep rise of digital technology in the recent decade. Below are some of its essential importance.
a) Cybercrime and Data Breaches: It provides critical evidence in legal cases which include digital elements, such as unauthorised access, online fraud, or cyberstalking. Experts utilised their techniques to recover and analyse digital evidence from hard drives, emails, and cloud storage.
b) Incident Response: Organisations utilise Digital Forensics to cope up incident response to identify, respond to, and mitigate cyberattacks. It helps understand how attacks happened, what vulnerabilities were exploited, and what data was used in the malpractice, to close security gaps and preventing future incidents.
c) Data Integrity: Digital Forensics ensures that organisations adhere strictly with data security and privacy regulations. Some of the techniques used for auditing and verifying are the proper handling of sensitive information and addressing breaches in a quick time to avoid legal penalties and reputational damage.
d) Research & Development: With the rise of technology, new challenges and opportunities in forensic analysis have developed. Experts implement latest techniques and tools to stay ahead of cybercriminals, enhance forensic processes, and adapt to the changing digital ecosystem.
e) Cyber Security Awareness: Digital Forensics is important in investigations and case studies, where professionals highlight risks and vulnerabilities in digital systems. This knowledge informs the public, businesses, and policymakers about the significance of Cyber Security measures and best practices for safeguarding sensitive information from cyber threats.
Key Branches of Digital Forensics
Given the vast applications of Digital Forensics, the field is divided into five key branches. Although there are six, the sixth one — computer forensics has already been explained in the preceding sections. The other branches are described in detail below:
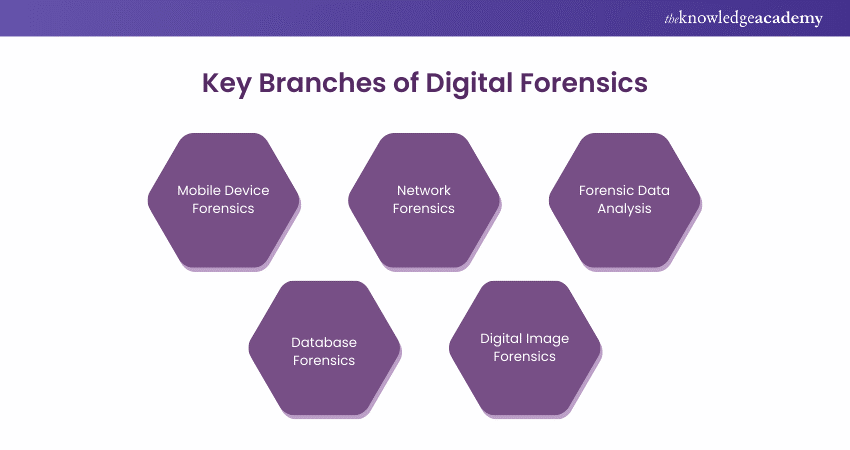
1) Mobile Device Forensics
Unlike computer forensics, mobile device forensics deals with recovering and analysing data along with the evidence from smartphones. This includes deleted messages, call logs, photos, and other relevant information to solve cases.
2) Network Forensics
Network forensics deals with the analysis of clues, data, and evidence from computer networks. It helps to track down cyber-attacks easily by looking at the network traffic and logs.
3) Forensic Data Analysis
Forensic Data Analysis is a broader term that includes studying data evidence from diverse digital sources, such as File Systems, Logs, Cloud Storage, etc.
4) Database Forensics
Data Forensics deals with analysing data and evidence from vast online records and database management systems (DMS). It includes deleting records, understanding data changes, why they have been made, and whether there is any tempering with the primary database.
5) Digital Image Forensics
Digital Image Forensics is examining digital images on platforms like social media to prevent alternations and detect fraudulent images. It can be useful in cases involving fake or misleading visuals.
Kickstart your professional Cyber Security journey with Certified Cyber Security Professional Training – join now!
Steps in the Digital Forensics Process
There are four steps in the Digital Forensics process. These steps are described as follows:
1) Data Collection
This is the first step of Digital Forensics, where the expert investigators gather all the valuable digital evidence. This includes data from computers, phones, servers, or other digital devices. The main goal of this step is to ensure that all relevant data is preserved without alteration.
2) Examination
In this step, the collected data is intricately analysed to understand its contents. Investigators examine the files, identify the hidden or deleted information, and then utilise specialised tools to come to conclusion. The main aim of this step is to find evidence relevant to the case.
3) Analysis
After that, the examined data is analysed deeply through pattern identifications and various specialised techniques. The Digital Forensics expert tries to understand the correlation between evidence and the incident.
4) Reporting
This is the final step, in which these experts prepare reports to show their findings to stakeholders and lawmakers. These visuals examine everything related to their work in the case, like how they analysed the data and what conclusions were drawn.
Applications of Digital Forensics
The key applications of digital forensics are described in the subsequent sections.
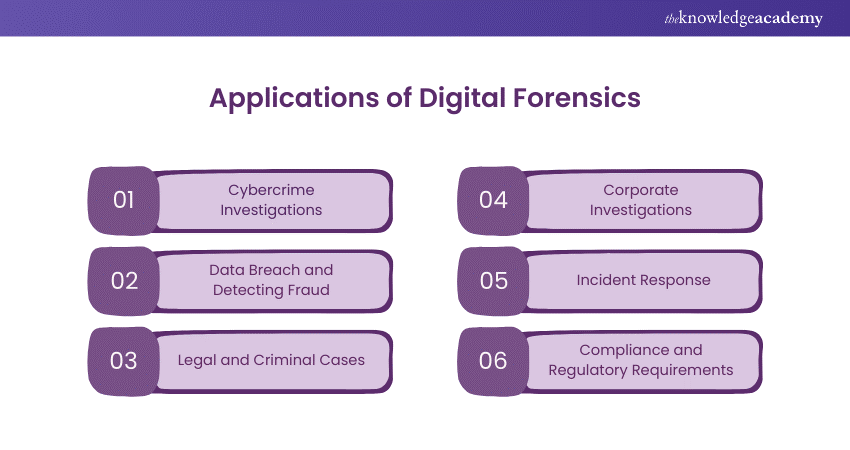
1) Cybercrime Investigations
a) Purpose: Investigate cybercrimes like hacking, phishing, and ransomware.
b) Process: Analyse compromised systems, logs, network traffic, and malicious software.
c) Outcome: Trace attack origins, understand methods, and identify perpetrators for prosecution.
2) Data Breach and Detecting Fraud
a) Purpose: Detect and investigate data breaches.
b) Process: Examine affected systems to determine breach methods and exposed data.
c) Outcome: Identify vulnerabilities, assess damage, and strengthen security measures.
3) Legal and Criminal Cases
a) Purpose: Support investigations and court proceedings with digital evidence.
b) Process: Recover deleted files, analyse emails, and examine digital transactions.
c) Outcome: Build cases, prove or disprove claims, and provide insights into criminal activities.
4) Corporate Investigations
a) Purpose: Investigate internal issues like employee misconduct and data tampering.
b) Process: Analyse company systems and devices for evidence of wrongdoing.
c) Outcome: Protect assets, uphold policies, and maintain a secure working environment.
5) Incident Response
a) Purpose: Handle security incidents and breaches.
b) Process: Quickly gather and analyse data to understand and contain threats.
c) Outcome: Manage incidents effectively and prevent further damage.
6) Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
a) Purpose: Support compliance with regulations and standards (for example, GDPR and HIPAA).
b) Process: Verify compliance, conduct audits, and ensure the proper handling of data.
c) Outcome: Meet legal and regulatory requirements.
Stay ahead of cyber threats- sign up for our Cyber Security Awareness Course!
Common Digital Forensics Techniques
There are various techniques in Digital Forensics that are widely used in modern applications. These techniques are described below:
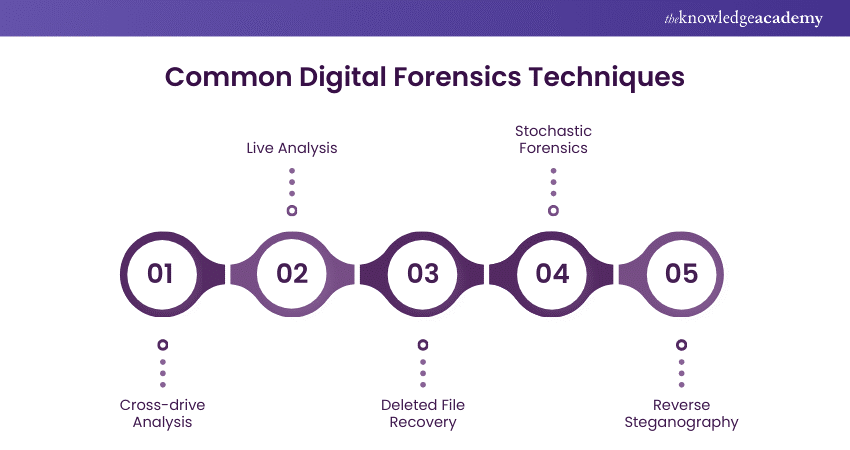
1) Cross-Drive Analysis
Cross-drive analysis involves comparing data from multiple storage devices to find connections or patterns. For example, if investigators have several hard drives from different computers, they look for similar files, metadata, or traces across these drives. This helps understand whether the same user or malicious activity exists on different devices.
2) Live Analysis
Live analysis means examining a computer or device while it is still running. Instead of waiting for the device to be shut down or rebooted, forensic experts analyse it in real-time to capture the current activities, such as open files, running processes, and network connections. This method helps understand what is currently happening on the device.
3) Deleted File Recovery
Deleted file recovery specialises in retrieving previously deleted files but not overwritten ones. When files are deleted, they often remain on the storage device until new data replaces them. Forensic tools can scan the device to recover these deleted files, which might contain valuable evidence.
4) Stochastic Forensics
Stochastic forensics uses statistical methods to analyse and understand digital evidence. Instead of looking at specific data points, this technique uses probabilities and patterns to uncover hidden information or detect anomalies. It helps make sense of large data volumes by identifying likely scenarios or behaviours.
5) Reverse Steganography
Reverse steganography involves uncovering hidden information that has been embedded within other files, like images or audio. For example, someone might hide a secret message inside a picture. Forensic experts use techniques to detect and extract this hidden information, revealing what was concealed.
Benefits of Digital Forensics
The crucial benefits of Digital Forensics are described below:
1) Uncovering and Preserving Evidence
a) Purpose: Recover and preserve crucial digital evidence.
b) Application: Used in criminal investigations to recover deleted files, trace communications, and analyse device data.
c) Outcome: Helps law enforcement build stronger cases and provides critical information for legal proceedings.
2) Improving Cyber Security
a) Purpose: Improve Cyber Security through data breaches and cyberattacks analysis.
b) Application: Identify the occurrence of intrusions and the exploited vulnerabilities
c) Outcome: Strengthens security measures, closes gaps, and prevents future attacks.
3) Supporting Corporate Investigations
a) Purpose: Address internal issues like employee misconduct, data theft, and fraud.
b) Application: Examine digital evidence from company systems.
c) Outcome: Uncover wrongdoing, enforce policies, and protect company assets.
4) Enhancing Incident Response
a) Purpose: Contain and mitigate damage from security incidents.
b) Application: Rapid forensic analysis to assess the situation and implement preventative measures.
c) Outcome: Minimises disruption and helps organisations recover swiftly from incidents.
5) Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
a) Purpose: Support compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
b) Application: Audit data handling practices and ensure adherence to regulations.
c) Outcome: Legal repercussions avoidance and building trust with clients and stakeholders.
Start your forensics journey – register for our Computer Forensics Foundation Training!
Drawbacks of Digital Forensics
As with the benefits, Digital Forensics comes with certain drawbacks. These drawbacks are described below:
1) Complexity and Evolving Technology
a) Challenge: Rapid technological advancements can quickly render forensic tools and techniques outdated.
b) Impact: Continuous skill and tool updates are resource-intensive and challenging.
2) High Costs
a) Challenge: Digital Forensics involves expensive tools, software, and skilled experts.
b) Impact: High costs can be a barrier for smaller organisations or individuals.
3) Privacy Concerns
a) Challenge: Accessing and analysing personal data can raise privacy issues.
b) Impact: Balancing effective forensic practices with privacy respect is delicate.
4) Legal Scrutiny
a) Challenge: Forensic results can be challenged in court regarding reliability and accuracy.
b) Impact: Legal disputes over findings can affect the outcomes of proceedings.
5) Data Recovery Limitations
a) Challenge: Some data may be too damaged, encrypted, or deleted beyond recovery.
b) Impact: Limits the effectiveness of forensic investigations and case resolutions.
Conclusion
Digital Forensics is an important field that leverages the combination of technology and investigative skills to discover valuable digital evidence. Despite its key benefits, Digital Forensics is prone to numerous challenges, such as evolving technology, elevated costs, concerns about privacy, and data recovery limitations. Understanding its critical processes, applications, and drawbacks will help you better understand What is Digital Forensics and how it contributes to modern investigations and security.
Strengthen security strategies- join today for our Cyber Security Risk Management Training!
Frequently Asked Questions

Yes, Digital Forensics is a part of Cyber Security. It consists of analysing digital evidence, detecting and responding to cyber threats, supporting investigations, and improving security measures.

The degrees and certifications required in Digital Forensics are Degrees in Computer Science or Cyber Security and Certified Computer Forensics Examiner (CCFE) and Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP).

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Cyber Security Training, including the Digital Forensics Training, Certified Cyber Security Professional Training, and Computer Forensics Foundation Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Whaling Attacks.
Our IT Security & Data Protection Blogs cover a range of topics related to Cyber Security and data privacy, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Cyber Security skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Digital Forensics Training
Digital Forensics Training
Fri 14th Feb 2025
Fri 11th Apr 2025
Fri 13th Jun 2025
Fri 15th Aug 2025
Fri 10th Oct 2025
Fri 12th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


