We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203 999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Picture a healthcare provider using Data Analytics to predict patient outcomes and improve treatment plans. This is just one of the many ways Big Data Analytics can drive innovation and efficiency. The advantages are vast, from optimising supply chains to enhancing customer satisfaction. Wondering what are its different types, and how can they be leveraged in various sectors?
This blog will explore the definition, benefits, and diverse types of Big Data Analytics, offering a thorough insight into its transformative potential. Dive in and see how it can revolutionise your business strategies and decision-making processes.
Table of Contents
1) What is Big Data Analytics?
2) How Big Data Analytics Works?
3) Types of Big Data Analytics
4) The Benefits of Big Data Analytics
5) Tools Used in Big Data Analytics
6) Careers in Big Data Analytics
7) Conclusion
What is Big Data Analytics?
Big Data Analytics merges the principles of Big Data and Analytics, focusing on the vast amounts of structured and unstructured data that businesses accumulate daily. The emphasis is not on the sheer volume of data but on how organisations utilise it, encompassing everything from transaction data to social media content and machine logs. Analytics involves the systematic computational analysis of this data.
Big Data Analytics aids in uncovering new opportunities, making better business decisions, improving operational efficiency, boosting revenues, and enhancing customer satisfaction. It is a real-time activity that employs techniques such as Machine Learning, Predictive Analysis, and Data Mining to support decision-making.
How Big Data Analytics Works?
Big Data Analytics involves the collection, processing, cleaning, and analysis of large datasets to help organisations operationalise their Big Data Integration. Let’s explore their working strategy:
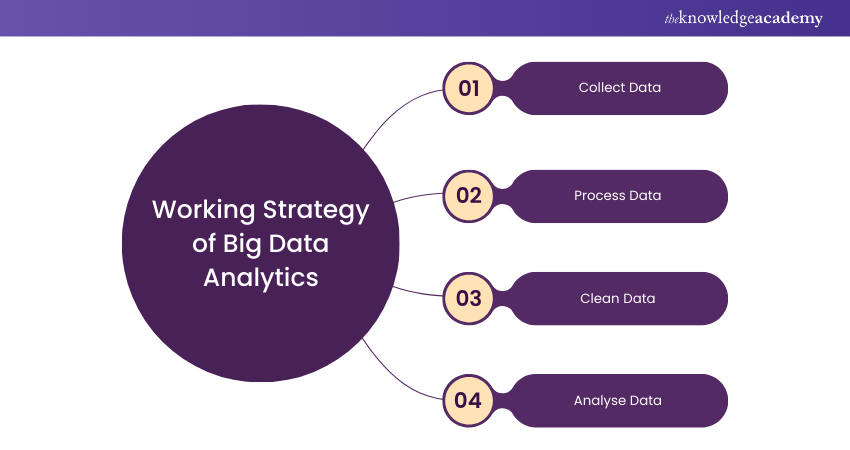
1) Organisations gather structured and unstructured data from various sources like cloud storage, mobile apps, and IoT sensors. Data is stored in warehouses or data lakes, depending on its complexity.
2) Data must be organised for accurate analysis. Batch processing handles large data blocks over time, while stream processing analyses small batches in real-time for quicker decisions.
3) Data needs scrubbing to improve quality. This involves formatting correctly and removing duplicative or irrelevant information to avoid misleading insights.
4) Preparing Big Data for analysis takes time. Once ready, advanced analytics processes can transform Big Data into valuable insights.
Types of Big Data Analytics
Big Data Analytics can be classified into four primary types, each serving a unique purpose and offering different insights. These types are Descriptive Analytics, Diagnostic Analytics, Predictive Analytics, and Prescriptive Analytics. Let's discuss each type in further detail, as follows:
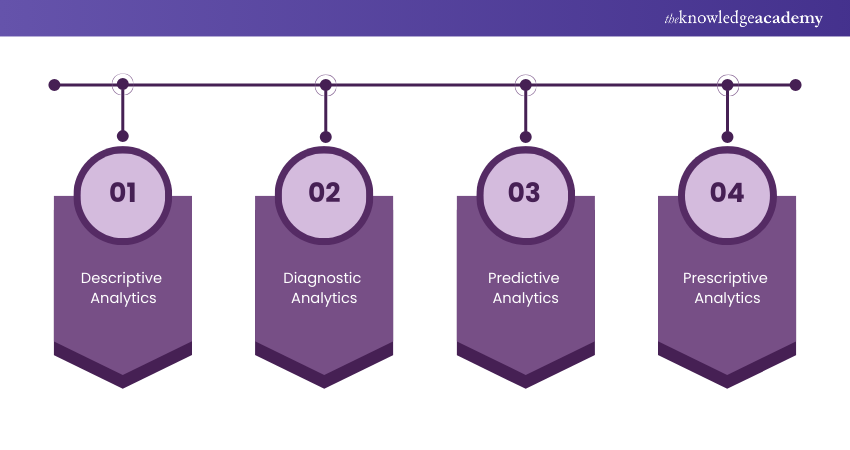
1) Descriptive Analytics
Descriptive Analytics is the basic form of Big Data Analytics, focusing on processing historical data to understand what has happened in the past. It utilises data aggregation and data mining techniques to provide a clear view of past performance by summarising raw data from multiple sources and converting it into a user-friendly format.
Moreover, this type of analytics helps businesses understand trends and patterns in their historical data. For instance, a company might use Descriptive Analytics to analyse past sales data to identify which products were most popular and during which time periods. Essentially, Descriptive Analytics translates raw data into meaningful information.
2) Diagnostic Analytics
Diagnostic Analytics delves deeper into data to understand the root cause of observed events. It's the "why" behind the "what" that Descriptive Analytics provides. Diagnostic Analytics employs techniques such as data discovery, correlations, and data mining. It's akin to a detective sifting through clues to identify the cause of an event. For example, if a company experienced a sudden drop in sales in a specific month, Diagnostic Analytics would be used to uncover the reason behind this decrease. It might reveal that a competitor's promotional campaign during that period was a significant factor. Hence, Diagnostic Analytics helps explain why certain trends or patterns occurred.
3) Predictive Analytics
Predictive Analytics takes past and present data and employs statistical models and algorithms to forecast future outcomes. It tries to answer the question, "What might happen in the future?" It's a step towards proactive decision-making, helping organisations anticipate future events based on data patterns.
For example, a business might use Predictive Analytics to forecast future sales trends based on past sales data and market conditions. Techniques like Machine Learning, regression analysis, and pattern matching are commonly used in Predictive Analytics. Although it can't predict the future with 100% certainty, Predictive Analytics can provide an educated forecast that businesses can utilise for strategic planning.
4) Prescriptive Analytics
Prescriptive Analytics is deemed the most advanced form of Big Data Analytics. It not only predicts future outcomes but also suggests the best course of action to take based on those predictions. It's like a GPS for decision-making, providing directions on how to reach the desired goal. If Predictive Analytics forecasts a decrease in sales, Prescriptive Analytics might suggest strategies to mitigate this, such as adjusting pricing or enhancing marketing efforts.
Furthermore, Prescriptive Analytics utilises advanced techniques and technologies like Machine Learning, Artificial Intelligence, algorithms, and mathematical models to analyse data and generate recommendations. It enables proactive decision-making, thereby driving better business outcomes.
Benefits of Big Data Analytics
Big Data Analytics offers a wealth of benefits across various sectors and industries. By analysing vast amounts of data quickly and efficiently, organisations can improve their decision-making processes, increase operational efficiency, and gain a competitive advantage. Here are some of the key benefits:
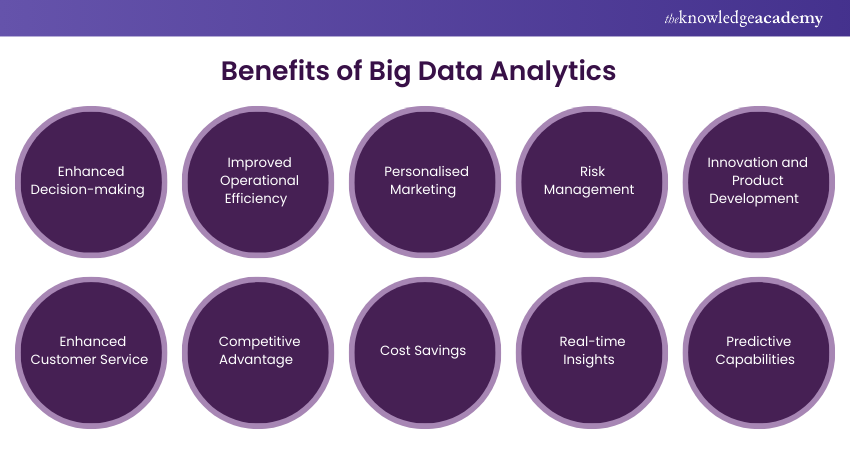
1) Enhanced Decision-making
Big Data Analytics allows businesses to make informed, data-driven decisions, moving away from intuition and guesswork. This leads to improved efficiency, better resource allocation, increased productivity, and greater success.
2) Improved Operational Efficiency
By analysing large datasets, businesses can identify inefficiencies and optimise workflows, resulting in reduced costs, increased productivity, and faster turnaround times. This enhances overall efficiency and competitiveness.
3) Personalised Marketing
Big Data Analytics tailors marketing strategies to individual customer preferences and behaviours, delivering targeted content. This increases customer engagement, satisfaction, and loyalty, leading to higher marketing Return on Investment (ROI).
4) Risk Management
Big Data Analytics helps businesses identify, assess, and mitigate risks by detecting early warning signs of threats. This enables proactive risk management, safeguarding assets and ensuring continuity.
Equip yourself with the knowledge and tools to excel in the data-driven world – sign up for our Big Data Analysis Training today!
5) Innovation and Product Development
By analysing customer preferences and market trends, businesses can identify opportunities for new products and services. This fosters continuous improvement and agility, leading to customer-centric products and sustained growth.
6) Enhanced Customer Service
Analysing customer data allows businesses to provide personalised and proactive support, leading to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty. Real-time Data Analysis enables prompt responses to queries and issues.
7) Competitive Advantage
Leveraging data insights gives businesses a comprehensive understanding of their market and competitors, enabling strategic decisions and innovative products. This helps maintain a dominant market position and drive growth.
8) Cost Savings
Big Data Analytics helps businesses streamline processes, reduce wastage, and optimise resource allocation, leading to lower operational costs. Predictive maintenance and targeted marketing further enhance cost efficiency.
9) Real-time Insights
The ability to analyse data as it is generated allows businesses to make immediate decisions based on up-to-date information. This is crucial for responding swiftly to market changes and staying competitive.
10) Predictive Capabilities
Predictive capabilities in Big Data Analytics allow businesses to forecast future outcomes by analysing historical data and patterns. This enables proactive decision-making and strategy development, providing a competitive edge across various industries.
Register for our Big Data and Hadoop Solutions Architect Training and become a key player in the Big Data world!
Tools Used in Big Data Analytics
Utilising all that data requires specialised tools. Let’s explore some of the crucial Big Data Analytics tools:
a) Hadoop: An open-source framework for storing and processing Big Data sets, capable of handling both structured and unstructured data.
b) Spark: An open-source cluster computing framework used for real-time data processing and analysis.
c) Data Integration Software: Programmes that streamline Big Data across various platforms, such as MongoDB, Apache, Hadoop, and Amazon EMR.
d) Stream Analytics Tools: Systems like Kafka that filter, aggregate, and analyse data stored in different platforms and formats.
e) Distributed Storage: Databases like Cassandra that can split data across multiple servers and identify lost or corrupt data.
f) Predictive Analytics Hardware and Software: Systems that process large amounts of complex data using Machine Learning and algorithms to predict future outcomes, such as fraud detection, marketing, and risk assessments.
g) Data Mining Tools: Programmes that allow users to search within structured and unstructured Big Data.
h) NoSQL Databases: Non-relational data management systems ideal for handling raw and unstructured data.
i) Data Warehouses: Storage solutions for large amounts of data collected from various sources, typically using predefined schemas.
Careers in Big Data Analytics
As organisations across industries strive to leverage data for decision-making, operational efficiency, and enhanced customer experiences, the demand for skilled professionals in Big Data Analytics has surged. Here are some prominent career paths in this field:
a) Data Scientist: Data Scientists analyse complex digital data to aid business decisions. They use their training in Data Science and advanced analytics technologies, such as Machine Learning and predictive modelling, to uncover hidden insights.
b) Data Analyst: Data Analysts transform data into information and insights. They employ statistical techniques to analyse data sets and extract meaningful trends, often to inform business strategies and decisions.
c) Data Engineer: Data Engineers prepare, process, and manage Big Data infrastructure and tools. They develop, maintain, test, and evaluate data solutions within organisations, often working with massive datasets to support analytics projects.
d) Machine Learning Engineer: These engineers focus on designing and implementing Machine Learning applications. They develop sophisticated algorithms that learn from and make predictions based on data.
e) Business Intelligence (BI) Analyst: BI Analysts help businesses make data-driven decisions by analysing data to produce actionable insights. They use BI tools to convert data into easy-to-understand reports and visualisations for stakeholders.
f) Data Visualisation Specialist: These specialists focus on the visual representation of data. They create visualisations that help end users understand the significance of data by placing it in a visual context.
g) Data Architect: Data Architects design, create, deploy, and manage an organisation’s data architecture. They define how data is stored, consumed, integrated, and managed by different data entities and IT systems.
Conclusion
In a world overflowing with data, Big Data Analytics is the key to unlocking actionable insights and driving innovation. By harnessing the power of data, businesses can make smarter decisions. Harness its power to turn your data into a strategic asset for future success!
Unlock the strategy between Big Data and Data Science with our Big Data Analytics & Data Science Integration Course – book your spot now!
Frequently Asked Questions

Big Data Analytics can be complex due to the vast volumes of data, diverse data sources, and the need for advanced tools and techniques. However, with proper training, understanding key concepts, and mastering analytical tools, it becomes manageable.

The four types of Big Data Analytics are descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive. Descriptive analytics summarises past data, diagnostic analytics identifies reasons behind outcomes, Predictive Analytics forecasts future trends, and prescriptive analytics recommends actionable strategies.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Big Data and Analytics Trainings, including the Advanced Data Analytics Course, Big Data Analysis Course, and Data Science Analytics Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Data Reconciliation.
Our Data, Analytics & AI Blogs cover a range of topics related to Big Data Analytics, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Data Analytics and Artificial Intelligence (AI) skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Data, Analytics & AI Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Hadoop Big Data Certification
Hadoop Big Data Certification
Thu 23rd Jan 2025
Thu 20th Mar 2025
Thu 22nd May 2025
Thu 17th Jul 2025
Thu 18th Sep 2025
Thu 20th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


