We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203 999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Ever wondered why you feel drawn to certain brands or products over others? The secret lies in understanding What is Consumer Behaviour. Imagine walking into a store and instantly knowing which product you'll pick off the shelf—this decision-making process is deeply rooted in the study of Consumer Behaviour.
From the cultural influences that shape our choices to the personal preferences that define our tastes, understanding What is Consumer Behaviour unlocks the mysteries behind our purchasing decisions. Dive into the fascinating world of Consumer Behaviour and discover the psychological and social factors that guide what we buy and why we buy it.
Table of Contents
1) What is Consumer Behaviour?
2) Types of Consumer Behaviour
3) Significance of Consumer Behaviour
4) Guidelines for researching about Consumer Behaviour
5) Conclusion
What is Consumer Behaviour?
Consumer Behaviour examines the ways in which individuals, groups, or organisations make decisions about choosing, purchasing, utilising, and discarding goods, services, or experiences to fulfil their desires and requirements. This field covers various actions, starting from the initial acknowledgment of a need or desire to the ultimate disposal of the item. Grasping Consumer Behaviour is essential for companies to craft successful marketing strategies and to design products and services that align with consumer preferences.
Various factors influence Consumer Behaviour, including cultural, social, personal, and psychological factors. Cultural factors involve a person's culture, subculture, and social class, while social factors include reference groups, family, and social roles. Personal factors encompass age, occupation, lifestyle, and personality, while psychological factors involve motivation, perception, learning, and attitudes.
Consider a scenario where a customer is in the market for a new smartphone. The Consumer Behaviour journey begins with the recognition of a need—perhaps a desire for advanced features or a better camera. External factors, such as positive online reviews, play a crucial role in the information-gathering stage. Ultimately, the purchasing decision is made, and the chosen smartphone is brought into the consumer's life.
Key Components of Consumer Behaviour
Understanding consumer behaviour requires examining various components that influence how consumers make purchasing decisions. These components help marketers tailor their strategies to effectively meet consumer needs and preferences. Here are the key components of consumer behaviour:
1) Motivation
Motivation refers to the internal drives that prompt consumers to take action. It is the force that triggers consumers to fulfill their needs and desires. Motivations can be physiological such as basic needs like hunger and thirst or emotional needs like desire for happiness or security, or social wants such as need for belonging or status.
2) Perception
Perception is how consumers interpret and make sense of information and stimuli they encounter. It influences how they view products and brands. The perception process involves three stages: exposure (noticing the stimulus), attention (focusing on the stimulus), and interpretation (making sense of the stimulus).
3) Learning
Learning involves changes in consumer behaviour resulting from experiences. It affects future purchasing decisions. Learning can occur through conditioning (associating brands with positive experiences), observation (watching others), and cognitive processes (problem-solving and reasoning).
4) Beliefs and Attitudes
Beliefs are individual perceptions about products or brands, while attitudes are overall evaluations that influence buying behaviour. Positive beliefs and attitudes toward a brand can lead to increased loyalty and repeated purchases, whereas negative attitudes can deter consumers.
5) Lifestyle
Lifestyle reflects consumers' way of living, including their activities, interests, and opinions. Lifestyle segmentation helps marketers identify and target specific consumer groups based on shared characteristics and behaviours.
6) Personality and Self-concept
Personality encompasses the traits and characteristics that define an individual's behaviour. Self-concept is how consumers perceive themselves. Products and brands that align with consumers' personalities and self-concepts are more likely to be favoured.
7) Cultural Influences
Culture is a culmination of shared values, beliefs, and customs of a society that influence consumer behaviour. Subculture refers to subgroups within a culture that have distinct values and behaviours. Social class is the hierarchical division of society based on factors including income, education, and occupation, which affects consumer preferences and purchasing power.
Types of Consumer Behaviour
Consumer Behaviour can be categorised into several types based on various factors. Here are four key types of Consumer Behaviour:
1) Habitual Purchasing Behaviour
Habitual purchasing behaviour unfolds when consumers make routine purchases with minimal contemplation. This occurs as part of their everyday routine, where decisions are often driven by factors such as convenience, brand loyalty, and price. Marketers targeting this behaviour focus on repetitive, visually impactful advertisements and promotions to enhance brand familiarity and attract first-time buyers through discounts.
2) Variety-seeking Purchasing Behaviour
Variety-seeking purchasing behaviour is characterised by consumers actively seeking new products and experiences. In this scenario, individuals enjoy experimenting with different brands and products, driven by the desire for variety. Marketers tailor strategies to attract these consumers by emphasising innovation, differentiation, and promoting the unique features of their products.
3) Complex Purchasing Behaviour
Complex purchasing behaviour involves in-depth decision-making and research, typically associated with significant purchases. Consumers engaging in complex behaviour carefully evaluate options, gather extensive information, and weigh various factors before deciding. Businesses targeting complex purchasers focus on providing detailed information, building trust, and delivering a seamless buying experience.
4) Dissonance-reducing Purchasing Behaviour
Dissonance-reducing purchasing behaviour arises when consumers experience post-purchase doubts or anxiety. This commonly happens when there are multiple appealing alternatives, making the decision-making process challenging. To alleviate this cognitive dissonance, consumers seek additional information or reassurance after the purchase. Businesses address this behaviour through effective communication, customer support, and follow-up initiatives to reduce buyer's remorse and enhance confidence in their decision.
Enhance your marketing prowess with our Marketing Research Masterclass and elevate your strategic skills for business success!
Significance of Consumer Behaviour
Let’s discuss the significance of Consumer Behaviour.
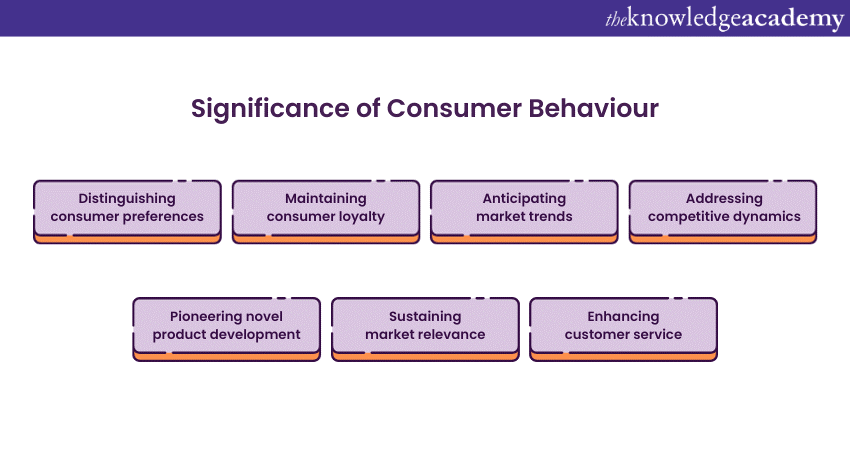
1) Distinguishing Consumer Preferences
When businesses understand consumer preferences, they uncover what customers like and dislike when purchasing. This insight is similar to discovering the recipe for success in the marketplace.
For instance, if a company discerns customers prefer eco-friendly products, they can adjust their offerings accordingly. This might involve creating items with minimal environmental impact, aligning with the eco-conscious trend. Beyond the product, businesses can tailor their marketing strategies to emphasise these environmentally friendly aspects.
2) Maintaining Consumer Loyalty
Maintaining consumer loyalty is the art of building enduring relationships between customers and brands. It resembles having a reliable go-to brand or shop, where businesses strive to create an experience that consistently attracts customers. This involves a deep understanding of customer preferences and expectations, achieved through feedback analysis and studying purchasing behaviours.
Brands actively listen to customer feedback, aiming to enhance products and services continually. The goal is to deliver consistency in quality, value, and positive experiences, fostering trust.
3) Anticipating Market Trends
This is like predicting what's going to be popular in the future. By understanding what people are starting to like or want, businesses can prepare and offer products or services that meet these emerging trends.
It's about staying ahead in the world of shopping and providing what customers will soon be looking for. This strategic foresight not only enhances a company's competitiveness but also ensures it remains a trailblazer in meeting the dynamic expectations of the market.
4) Addressing Competitive Dynamics
Addressing competitive dynamics involves a strategic understanding of how consumers make choices among various brands or products in the market. It's like peering into the consumer's decision-making process and deciphering the factors that influence their preferences. When businesses grasp these dynamics, they gain a competitive edge by positioning their products or services more effectively.
This understanding allows companies to identify and highlight the unique features or qualities that set their offerings apart from the competition. It's not just about having a product; it's about showcasing why that product is the best choice. This could be based on quality, price, innovation, or a combination of factors that resonate with the target audience.
Transform your marketing brilliance with our Integrated Marketing Masterclass. Sign up now!
5) Pioneering Novel Product Development
Pioneering novel product development is like being a trendsetter in the world of innovation. It involves using insights gained from understanding Consumer Behaviour to create fresh and appealing products that meet unmet needs or desires. This process begins by keenly observing consumer preferences and identifying gaps in the market—areas where existing products might not fully satisfy consumer demands.
Businesses delve into the intricacies of Consumer Behaviour, seeking to uncover latent desires or areas where improvements can be made. This thorough understanding allows companies to generate inventive ideas that resonate with consumers' wants but have yet to find in the market.
6) Sustaining Market Relevance
Sustaining market relevance is a continual effort by businesses to stay relevant in the ever-evolving marketplace. It's akin to staying in tune with the latest tunes in a dynamic industry orchestra. To achieve this, companies vigilantly monitor how consumer preferences shift over time. This involves observing and actively engaging with changing trends, preferences, and expectations.
7) Enhancing Customer Service
Understanding how customers behave is the foundation of exceptional service. Businesses gain valuable insights by actively listening to customer feedback and studying their preferences. This knowledge allows companies to customise their services, ensuring they align precisely with customers' likes and dislikes. It's a personalised approach that transcends a one-size-fits-all mentality.
Tailoring services to meet customer needs is a proactive effort. Whether it's adjusting communication styles, refining products, or streamlining processes, this adaptability ensures that customers not only get what they want but also feel heard and valued.
Supercharge your marketing expertise with our Introduction to Marketing Training – Sign up today and propel your career forward!
What Influences Consumer Behaviour?
Factors influencing consumer behaviour encompass a range of internal and external elements that affect individuals' decisions and actions when selecting, purchasing, using, or disposing of products or services. Grasping these factors and their interactions can aid businesses and marketers in crafting more effective marketing strategies, customising products and services to meet consumer needs, and anticipating shifts in consumer behaviour.
Personal Factors
Personal factors play an important role in shaping consumer behaviour, as they are unique to each individual and significantly impact their purchasing decisions. These factors include:
a) Age and Life Cycle Stage: Different age groups and life stages have varying needs and preferences. For instance, teenagers may prioritise fashion and technology, while older adults might focus on health and comfort. Similarly, a single individual might have different purchasing habits compared to someone who is married or has children.
b) Occupation: A person's job influences their buying choices. For example, a professional might invest in formal attire and gadgets related to their work, while a student may spend more on educational materials and casual clothing.
c) Economic Situation: An individual's financial status, including income level and disposable income, affects their spending power and the types of products they can afford. Economic stability or instability also plays a significant role in shaping consumer behaviour.
d) Lifestyle: This reflects a person's way of living, including their activities, interests, and opinions. Lifestyle choices, such as being health-conscious, adventurous, or environmentally aware, influence the products and services consumers prefer.
e) Personality and Self-Concept: Personality traits, such as extroversion, agreeableness, and conscientiousness, influence consumer behaviour. Additionally, how individuals perceive themselves (self-concept) affects their buying decisions, as they often choose products that align with their self-image and aspirations.
Understanding these personal factors helps businesses and marketers tailor their strategies to meet the specific needs and preferences of their target segment, ultimately driving better engagement and customer satisfaction.
Psychological Factors
Psychological factors significantly impact consumer behaviour, affecting how individuals think, feel, and act when making purchasing decisions. These factors include:
a) Motivation: Motivation indicates the internal drives that prompt consumers to take action. It is the force that triggers consumers to fulfill their needs and desires, which can be physiological (basic needs like hunger and thirst), emotional (desire for happiness or security), or social (need for belonging or status).
b) Perception: Perception is how consumers interpret and make sense of information and stimuli they encounter. It influences how they view products and brands. The perception process involves three stages: Exposure (noticing the stimulus), attention (focusing on the stimulus), and interpretation (making sense of the stimulus).
c) Learning: Learning involves changes in consumer behaviour resulting from experiences. It affects future purchasing decisions. Learning can occur through conditioning (associating brands with positive experiences), observation (watching others), and cognitive processes (problem-solving and reasoning).
d) Beliefs and Attitudes: Beliefs are individual perceptions about products or brands, while attitudes are overall evaluations that influence buying behaviour. Positive beliefs and attitudes toward a brand can lead to increased loyalty and repeated purchases, whereas negative attitudes can deter consumers.
These psychological factors enables marketers to predict consumer responses, tailor their messages, and create strategies that resonate with their target audience, ultimately influencing their purchasing decisions.
Social Factors
Social factors play a prominant role in shaping consumer behaviour, as individuals are influenced by the people around them and the social contexts in which they operate. These factors include:
a) Family: Family members significantly impact consumer choices. The influence can be seen in preferences for products and brands, as family traditions and values often guide purchasing decisions. Parents, spouses, and children each play distinct roles in influencing what and how consumers buy.
b) Reference Groups: These are groups that individuals identify with or aspire to be part of, such as friends, colleagues, or social clubs. Reference groups provide points of comparison and can influence attitudes, behaviours, and purchasing decisions through peer pressure and social norms.
c) Social Roles and Status: An individual’s role in society (e.g., parent, manager, student) and their social status (which may be determined by occupation, income, education, and other factors) affect their buying behaviour. People often purchase products that reflect their role and status in society to maintain or enhance their image.
d) Social Networks: With the rise of digital platforms, social networks have become crucial in influencing consumer behaviour. Recommendations, reviews, and endorsements from friends, influencers, and online communities can significantly sway buying decisions.
Understanding these social factors helps businesses and marketers create strategies that leverage social influences, fostering brand loyalty and driving consumer engagement by resonating with the social dynamics of their target audience.
Guidelines for Researching About Consumer Behaviour
Listed below are some of the guidelines for conducting research on Consumer Behaviour.
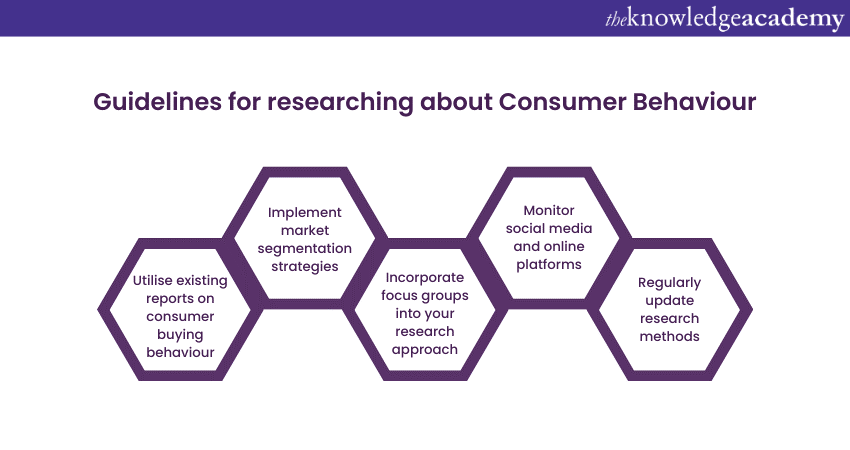
1) Guidelines for Researching About Consumer Behaviour
Leveraging existing reports provides a valuable starting point for understanding Consumer Behaviour. Analyse market research studies, industry reports, and consumer surveys. These sources can offer insights into trends, preferences, and buying patterns. It's like tapping into a wealth of knowledge that others have already gathered, giving your research a solid foundation and helping you identify areas for further investigation.
2) Implement Market Segmentation Strategies
Market segmentation divides a larger market into distinct groups based on similar characteristics or behaviours. By employing segmentation strategies, researchers can gain a more nuanced understanding of Consumer Behaviour within specific demographics or interest categories. This approach allows for targeted analysis, helping businesses iterate their products and marketing strategies to meet the unique needs of each segment.
3) Incorporate Focus Groups Into Your Research Approach
Engaging with focus groups provides a qualitative dimension to Consumer Behaviour research. These small, interactive gatherings of potential customers allow for in-depth discussions. By facilitating conversations, researchers can uncover detailed insights into attitudes, perceptions, and motivations.
It's like having a direct conversation with the target audience, providing a deeper understanding of the emotional and psychological aspects that influence consumer choices. Focus groups complement quantitative data, offering a more comprehensive view of Consumer Behaviour.
Conclusion
By understanding what makes customers tick and what triggers their buying decisions, companies can cook up new products and marketing magic to rake in profits. But here's the catch: to really nail it, companies need to have a chat with customers, keep an eye out for their bugbears, and, above all, figure out what they want and expect. So, in a nutshell, what is Consumer Behaviour? It's the compass guiding businesses to create stuff people love, ensuring a happy, loyal bunch of customers.
Elevate your E-mail marketing game with our comprehensive Email Marketing Course – Join now!
Frequently Asked Questions

Key components include psychological factors (motivation, perception, learning, beliefs, attitudes), personal factors (age, occupation, lifestyle, personality), social factors (family, reference groups, social roles, networks), cultural factors (culture, subculture, social class), and situational factors (context, environment, temporal effects).

The four psychological factors influencing consumer behaviour are motivation (drives that prompt consumers to fulfill needs), perception (how consumers interpret information and stimuli), learning (changes in behaviour from experiences), and beliefs and attitudes (individual perceptions and overall evaluations that shape decisions).

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Marketing Courses, including the Content Marketing Course, Pay Per Click Training, and Explainer Videos Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Pinterest Marketing.
Our Digital Marketing Blogs cover a range of topics related to Consumer Behaviour, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Marketing skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Digital Marketing Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Consumer Behaviour Course
Consumer Behaviour Course
Fri 24th Jan 2025
Fri 21st Mar 2025
Fri 2nd May 2025
Fri 27th Jun 2025
Fri 29th Aug 2025
Fri 3rd Oct 2025
Fri 5th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


