We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on + 800 908601 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Ready to transform your technical skills into a cybercrime-fighting career? Digital forensics is a must-have professional skill that allows you to solve cyber fraud through real-world data analysis applications. Coincidently, it is among the most demanding fields in the UK.
Based on a report by GOV.UK, there are approximately 73,439 shortages of professionals in digital forensics. This skills gap defines the increasing demand for digital forensics and cybersecurity expertise.
In this blog, we will explore the top 12 Digital Forensics Career choices and how you can start a career in this aspiring field!
Table of Contents
1) What is Digital Forensics?
2) 12 Digital Forensics Career Options
a) Information Security Analyst
b) Computer Systems Analyst
c) Forensic Computer Analyst
d) Security Consultant
e) Computer Forensic Analyst
3) Tips to Start a Digital Forensic Career
4) Conclusion
What is Digital Forensics?
Digital Forensics is a forensic science field specialising in solving criminal investigation cases through the vast applications of data analysis. It primarily involves collecting evidence from digital and networking devices, including smartphones, computers, laptops, and cloud computing to uncover valuable case-solving insights and conclusions.
To understand it better, let's look at a a real-world example. Suppose your computer got hacked, and all your personal files were stolen. You call a digital forensic expert. They examine the computer data and find clues like IP addresses, time stamps, and hidden files to track down the hacker. This way the whole digital forensic expertism works!
12 Digital Forensics Career Options
Digital forensic expertise is a broader profession. It is further divided into 12 major categories:
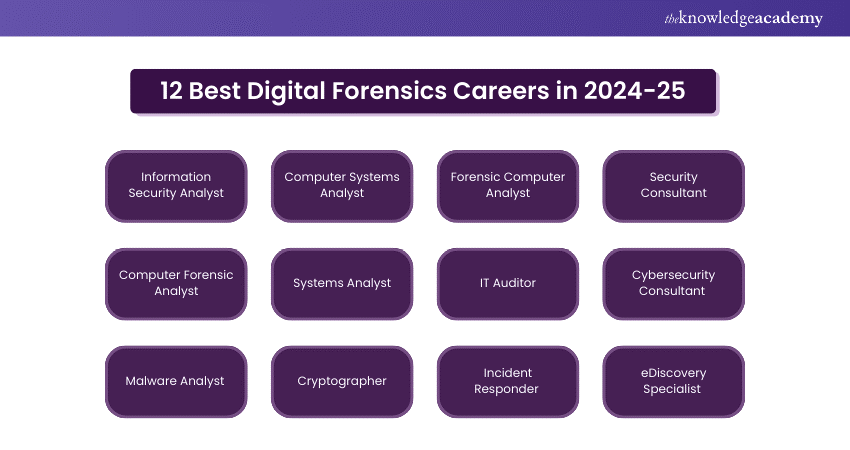
1) Information Security Analyst
They protect information systems and networks against cyber threats by monitoring suspicious activities, implementing security measures, and responding to security breaches.
2) Computer Systems Analyst
The computer systems analysts work closely with the IT team to manage the computer software and hardware.
3) Forensic Computer Analyst
They are responsible for gathering evidence by recovering lost data, such as deleted files, to trace cyber-attacks.
4) Security Consultant
Security consultants offer practical advice to organisations on the best practices for protecting their data and networks. They achieve this by identifying vulnerabilities and the relevant solutions in their computer systems.
5) Computer Forensic Analyst
They primarily work closely with Cyber Security Laws For Data Protection agencies to collect and examine digital evidence.
6) Systems Analyst
System analysts specialise in improving the efficiency of IT systems. They collaborate with various developers and stakeholders to implement and recommend system enhancements.
Master digital risk management with our Certified Cyber Security Professional Training- grab your seats today!
7) IT Auditor
IT auditors analyse computer systems to check whether they meet government regulatory requirements and industry standards.
8) Cybersecurity Consultant
They help organisations to protect their networks and data from cyber threats through implementing effective security strategies. They also conduct risk assessments and provide the necessary training to employees.
9) Malware Analyst
A malware analyst studies malicious software to analyse its workings and ways to create solutions to remove and defend against it.
10) Cryptographer
Cryptographers develop algorithms to encrypt data by making it secure for authorised access. They are crucial in securing sensitive information like financial transactions and personal data.
11) Incident Responder
Incident responders are the first real-time responders to cyber threats, who analyse and mitigate security incidents. They work jointly to remove threats and prevent further damage to the organisation’s digital assets.
12) eDiscovery Specialist
eDiscovery specialists identify, collect, and preserve digital evidence for legal cases. They assist legal teams by providing relevant data from electronic sources to support litigation and regulatory investigations.
Become a complex forensic case analysis specialist with our Computer Forensics Foundation Training—join today!
Tips to Start a Digital Forensic Career
You can start a bright career in Digital Forensics by following certain fundamental yet strategic tips. These tips are described in the following sections:
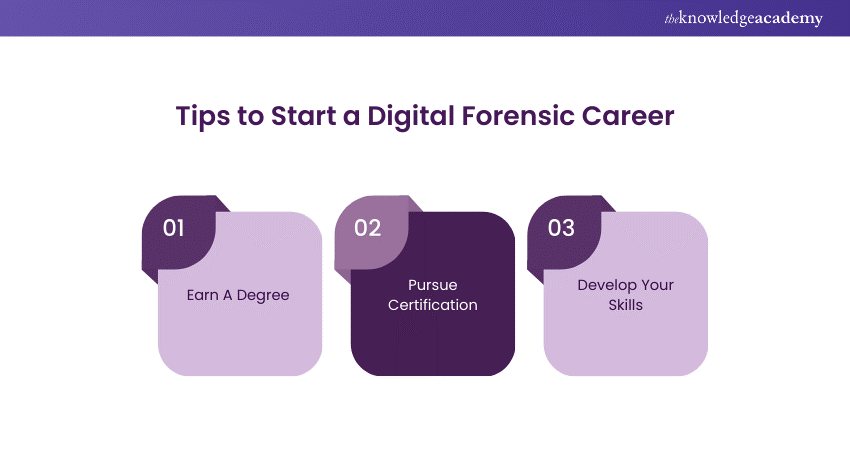
1) Earn A Degree
Begin by enrolling in bachelor's courses in computer science, Cyber Security for Business, or digital forensics. This education will help you learn how computers work and how digital evidence is gathered.
2) Pursue Certification
In addition to formal education, you should also pursue essential certifications like CFCE or CISSP. These will improve your credibility and give you a competitive advantage over other candidates.
3) Develop Your Skills
Working closely on real-world cases or simulations develops problem-solving and analysis skills. This ensures that you have implemented the right digital forensics techniques into a practical stage.
Upskill yourself in fraud data analytics with our Fraud Analytics Training—register now!
Conclusion
We hope you understand the top 12 Digital Forensics Career options. Digital forensics is a field filled with growth opportunities as diverse career paths for aspirants, ranging from security consultants to malware analysts, each playing a crucial role in combating cybercrime. Moreover, with the steep professional demands and skills gap, now is the right time to start a fulfilling career in this aspiring field.
Decode malicious code seamlessly with our Malware Analysis Training—sign up right away!
Frequently Asked Questions

Digital forensics is known as computer forensics. They are both used interchangeably. Computer forensics is a sub-category of digital forensics addressing digital devices, including computers and mobile phones. While digital forensics focuses on a broader prospect towards networking and cloud environments.

The goal of digital forensics is to identify, preserve, analyse, and present digital evidence from electronic devices. By providing actionable insights and maintaining data integrity, it can help solve cybercrimes, recover lost data, and support legal investigations.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Cyber Security Training, including Digital Forensics Training, Fraud Analytics Training Course, and Malware Analysis Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Top 30 Network Security Interview Questions & Answers.
Our IT Security & Data Protection Blogs cover a range of topics related to cybersecurity strategies and data protection techniques, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your IT security and data protection skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course




 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


