We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on + 800 908601 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Imagine owning a meme, a tweet or a piece of virtual land! Welcome to the world of Non-fungible Tokens (NFT), where ownership transcends the physical world and into the virtual one. Unlike traditional currency or Cryptocurrency, an NFT is a one-of-a-kind asset on the Blockchain, making it as unique as a collector’s item. From digital art to exclusive digital content, NFTs have revolutionised the concept of ownership for the modern era. This blog examines What is NFT, exploring its benefits, the buying process, NFT marketplaces and more. So read on and become a proud owner of collectables in the digital realm!
Table of Contents
1) What is a Non-fungible Token (NFT)?
2) What is an NFT?
3) History of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
4) How do NFTs Work?
5) Examples of NFTs
6) How is NFT Different From Cryptocurrency?
7) What is an NFT Marketplace?
8) Popular NFT Marketplaces
9) Benefits of NFTs
10) How do You buy NFTs?
11) Conclusion
What is NFT? What does NFT stand for?
An NFT is a digital asset that includes art, music, videos, in-game items or more. It is bought and sold online, often with Cryptocurrency, and is encoded through the same underlying software as many Cryptos. NFTs are becoming an increasingly popular method of buying and selling digital artwork.
NFTs have unique identifying codes and the key difference between them and most other digital creations is that the others are almost always infinite in supply.
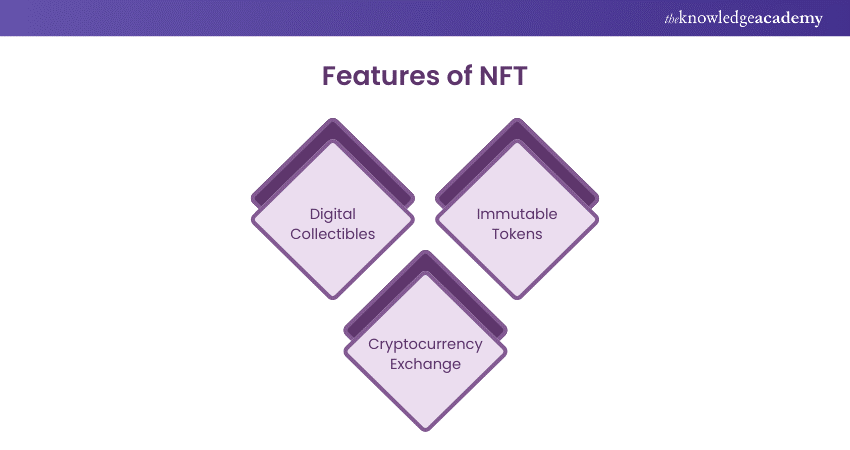
Here are some features of NFTs
a) Digital Collectibles: NFTs serve as digital collectibles for art, games, music, and more. They come with a unique digital certificate secured by Blockchain technology to verify authenticity.
b) Immutable Tokens: NFTs cannot be altered or tampered with once created, making them truly unique and irreplaceable.
c) Cryptocurrency Exchange: NFTs are traded exclusively using Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum on dedicated platforms.

History of Non-fungible Tokens (NFTs)
Here's a brief history of NFTs:
1) 2014: The first NFT ever sold was "Quantum". It was designed and tokenised by Kevin McKoy on one Blockchain (Namecoin).
2) 2014 to 2016: Significant development and experimentation took place in platforms built upon the Bitcoin Blockchain. It was the beginning of Ethereum’s initial reign over NFTs.
3) 2017-2021: NFTs go public. In 2021, Quantum was minted on Ethereum and sold in 2021.
How do NFTs Work?
NFTs mostly belong to the Ethereum Blockchain. Ethereum is a public ledger, and it keeps a record of all transactions. The information of the transaction is stored on the Blockchain, and it is stored as a token. There is a value set for the NFT, which makes it easier to buy and sell it just like any other commodity.
The creation of NFTs can be accomplished through contract-enabled Blockchains with some help from appropriate tools and support. Ethereum was among the first widely used EOS and NEO, and now it also includes NFT standards. The tokens and their Smart Contracts allow adding detailed information such as the owner's identity.
This process provides NFTs with the attributes of scarcity and royalties that make them attractive when coupled with digital media:
Scarcity
It means that the owner gets to decide the scarcity of their assets. For example, let's take an example of a ticket to any sporting event or concert. The owner decides how many tickets are to be sold there. In the NFT token market, the creator can decide how many replicas should be there. So, these replicas are there with a slight difference in each one of them.
In another example of how to create non-fungible tokens, the owner can create an NFT token only once, making it a unique, rare collectable. In any case, each of the NFTs will have its unique identity, such as a bar code on every cloth or ticket that looks similar but uniquely different.
Royalties
NFTs are encoded with software code (known as smart contracts) that governs the prospects, including verifying the ownership and transferability management of the NFTs. Additionally, NFTs can get programmed beyond the basics of ownership like any software application that incorporates a variety of applications and functionality. For instance, a Smart Contract can be developed to ensure some NFTs automatically pay the royalties to the original owner.
Interested in knowing how NFTs work on Blockchain? You can learn that and so much more with our Blockchain Course!
Examples of NFTs
Arguably one of the most famous use case for NFTs is CryptoKitties. Launched in November 2017, CryptoKitties are digital representations of cats that has unique identifications on Ethereum's Blockchain. Each kitty has a different price and can "reproduce" with one another, creating new offspring with different qualities and valuations compared to their "parents."
CryptoKitties garnered a fan base that spent millions in Ether to purchase, feed, and nurture them in a few weeks. While much of the early market for NFTs was centred around digital art and collectables, it has since evolved significantly. For example, the popular NFT marketplace OpenSea offers a variety of NFT categories:
1) Photography: Photographers can tokenise their work and offer total or partial ownership.
2) Sports: Collections of digital art inspired by celebrities and sports personalities.
3) Trading Cards: Tokenised digital trading cards, some of which are collectibles while others can be traded in video games.
4) Utility: NFTs that represent membership or unlock benefits.
5) Virtual Worlds: Virtual world NFTs grant ownership of anything from avatar wearables to digital property.
6) Art: A general category of NFTs that includes everything from pixel to abstract art.
7) Collectibles: Examples include Bored Ape Yacht Club, CryptoPunks, and Pudgy Panda.

8) Domain Names: NFTs representing ownership of domain names for websites.
9) Music: Artists can tokenise their music, granting buyers specific rights as defined by the artist.
Learn how Bitcoins work and delve deeper into the Cryptocurrency ecosystem with our Bitcoin and Cryptocurrency Course!
How is NFT Different From Cryptocurrency?
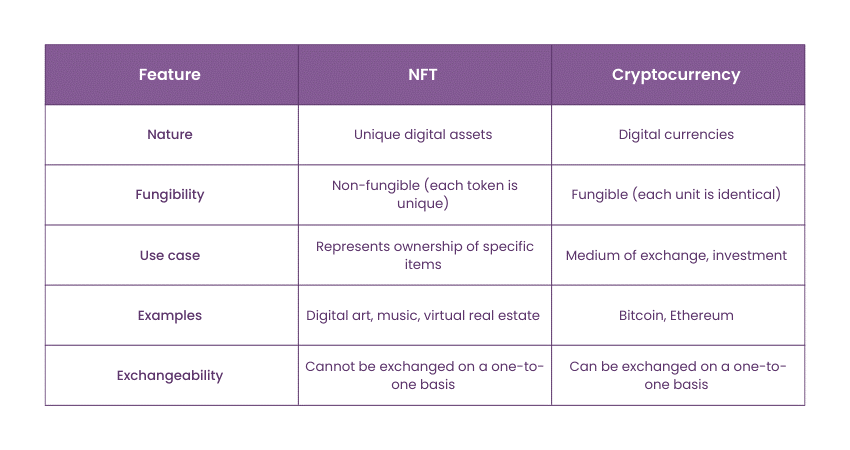
NFTs are unique digital assets that represent ownership of specific items like art, music, or virtual real estate, stored on a Blockchain. Each NFT is distinct and cannot be exchanged on a one-to-one basis.
Cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin or Ethereum, are digital currencies used for transactions and investments. They are fungible, meaning each unit is identical and can be exchanged equally.
What is an NFT Marketplace?
An NFT marketplace is a digital forum where you can:
1) Buy and sell NFT
2) Store and display NFTs
3) Mint NFTs (create them) in some cases
4) Own a piece of digital art or collectable
5) Trade unique digital assets
Most NFT marketplaces fall into these categories:
1) Open Marketplace: Anyone can sell, buy or mint NFTs. Open marketplaces typically mint NFTs for you, although creators can mint their works.
2) Closed Marketplace: Artists have to apply to join, and the marketplace typically undertakes the minting processes. However, selling and trading are more restricted.
3) Proprietary Marketplace: This marketplace sells NFTs trademarked or copyrighted by the company that operates it.
Popular NFT Marketplaces
Now that you have your essentials, where should you buy an NFT? Here are some popular NFT marketplaces, as mentioned earlier, that you can consider:
1) Rarible: A community-owned NFT marketplace, Rarible works with RARI tokens. All the active users receive RARI tokens, up to 75,000 RARI weekly. Digital creators can mint new NFTs to sell their works. Sneak peeks can display the collection with only the buyer getting the option

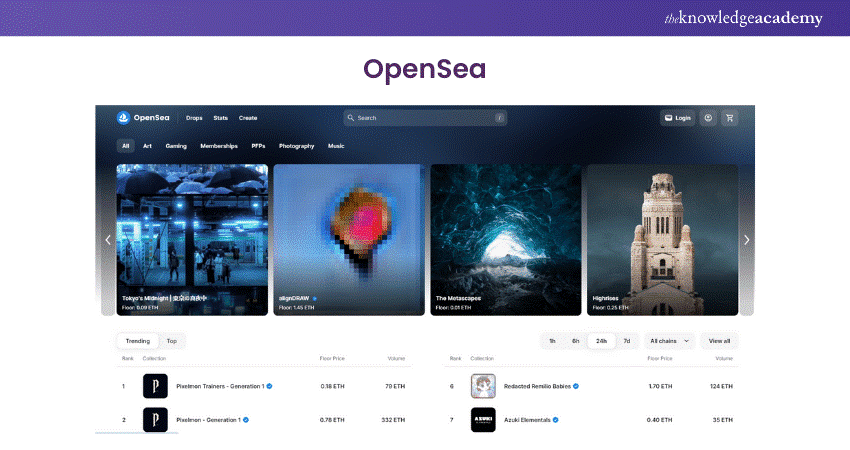
2) OpenSea - Possibly the largest NFT marketplace, OpenSea sells NFTs as art, domain names, sports, trading cards, collectables, etc. The platform has a minting tool through which creators can create their NFTs on Blockchain for free.
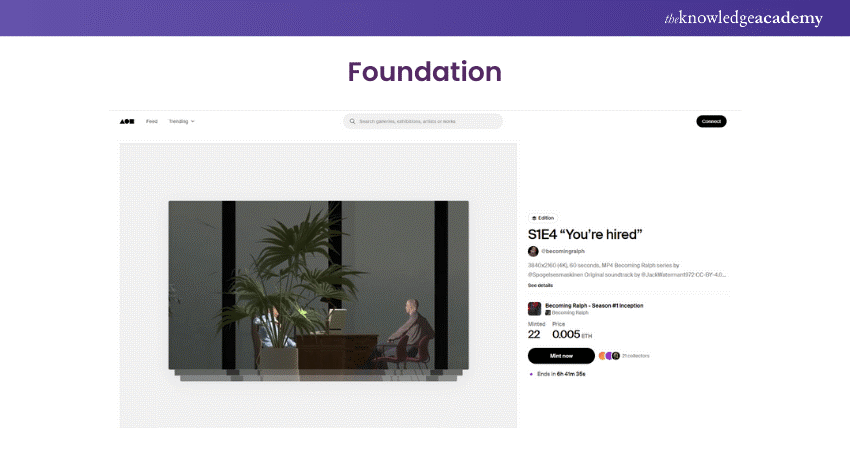
3) Foundation: The Foundation has brought together Digital Creators, Crypto Enthusiasts and Collectors.
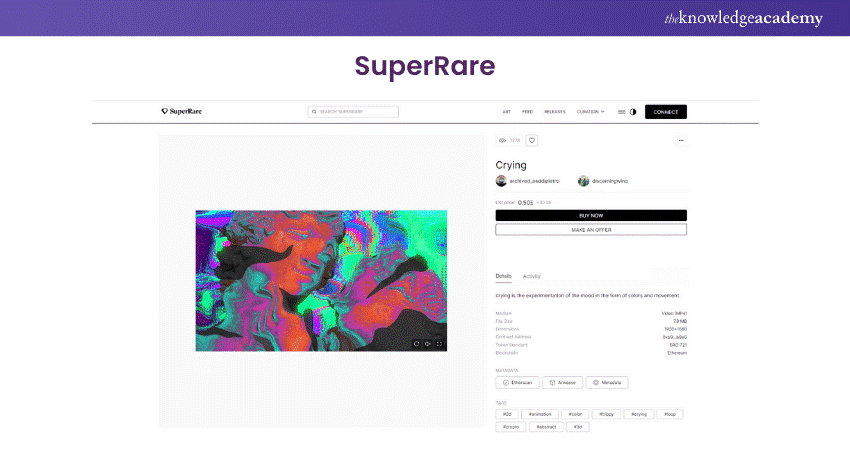
4) SuperRare - As the name suggests, SuperRare has fashioned itself as a platform that facilitates buying and selling unique digital assets only available as a single edition. The platform has moved forward and turned into a social network for creators and traders.
Master strategies for profitable trading with our comprehensive Cryptocurrency Trading Training – Sign up now!
Benefits of NFTs
The biggest benefit of NFTs is market efficiency, as tokenising a physical asset streamlines sales processes and removes intermediaries. NFTs representing physical or digital artwork on a Blockchain can bypass the need for agents and enable sellers to connect directly with their target audiences.
Investing
NFTs can streamline investing, as exemplified by real estate property being parcelled into multiple sections, each containing different characteristics. For example, one section might be on a lakeside, while another may be closer to the forest. Depending on the features, each piece of land could be priced differently and represented by an NFT.
Security
Non-fungible tokens are helpful in identity security. For example, personal information stored on a Blockchain can't be accessed or used by anyone who doesn't have the keys. Additionally, NFTs can democratise investing by fractionalising physical assets.
How do You Buy NFTs?
If you are thinking of buying NFTs, it’s essential to have a clear understanding of the process. Let’s explore the steps involved:
1) Open a Crypto Exchange Account: You begin by opening your account on a Crypto exchange or platform. A Crypto exchange is the online platform where buying and selling of Cryptocurrencies occur.
2) Open a Crypto Wallet: It stores the keys that grant access to your digital assets. Users are given a unique seed phrase (a recovery phrase) to access their wallet. Crypto Wallets may be hosted on an exchange or even operated independently. Whichever Crypto wallet you choose must be compatible with the Ethereum (ETH) Blockchain, since that's the network on which most NFTs are sold.
3) Transfer Ethereum Into a Crypto Wallet: Once you've chosen an NFT exchange and bought ETH, you must transfer it to a wallet. This process varies depending on the exchange through which ETH is bought, the wallet, and the marketplace where you plan to trade NFTs.
4) Buy NFTs: Once the wallet is connected and funded, you can start buying NFTs. You gain ownership of an NFT once you buy it because it becomes your property. But the NFT holder doesn’t hold other rights to the work, including the right to adapt or reproduce it, unless that's part of the direct agreement between the buyer and the creator.
Conclusion
In conclusion, NFTs have redefined the digital landscape by providing an innovative way to own, create and trade digital assets. By combining the individuality of collectables with the power of Blockchain technology, NFTs have opened new doors for gamers, artists, investors and more. As the digital world continues to evolve at breakneck speed, learning What is NFT is becoming an essential skill in the field of ownership.
Get trained in the fundamentals of Blockchain and Ethereum. Join our Ethereum Developer Training today!
Frequently Asked Questions

No, NFTs are not Cryptocurrency. NFTs are unique digital assets representing ownership of specific items, while Cryptocurrencies are fungible digital currencies used for transactions and investments.

NFT digital art is unique digital artwork authenticated by Blockchain. Each NFT art piece has a distinct, Non-fungible Token, ensuring its originality and ownership, and can be bought, sold, or traded.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Blockchain Courses, including Blockchain Training, Bitcoin And Cryptocurrency Course and Ethereum Developer Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into the Different Types of Blockchain.
Our Advanced Technology Blogs cover a range of topics related to Blockchain, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Blockchain Training skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


