We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +91-181-5047001 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Imagine a logistics company using Big Data to optimise delivery routes. By analysing traffic patterns and delivery times, they can reduce fuel consumption and speed up deliveries. This is just one example of how Big Data in Supply Chain Management can provide unprecedented insights and capabilities. It reveals hidden patterns, predicts trends, and enables data-driven decisions to enhance efficiency and innovation.
According to Statista, states that the Global Supply Chain Management market is anticipated to reach £24 billion by 2026. Given this context, this blog delves into the transformative impact of Big Data in Supply Chain Management, providing real-world examples and actionable insights. Let’s explore how Big Data is revolutionising the future of business.
Table of Contents
1) What is Big Data in Supply Chain Management?
2) Benefits of Utilising Big Data in Supply Chain Management
3) Applications of Big Data in Supply Chain Management
4) The Challenge of Supply Chain Data Management
5) Real Case Studies of Big Data in Supply Chain Management
6) Conclusion
What is Big Data in Supply Chain Management?
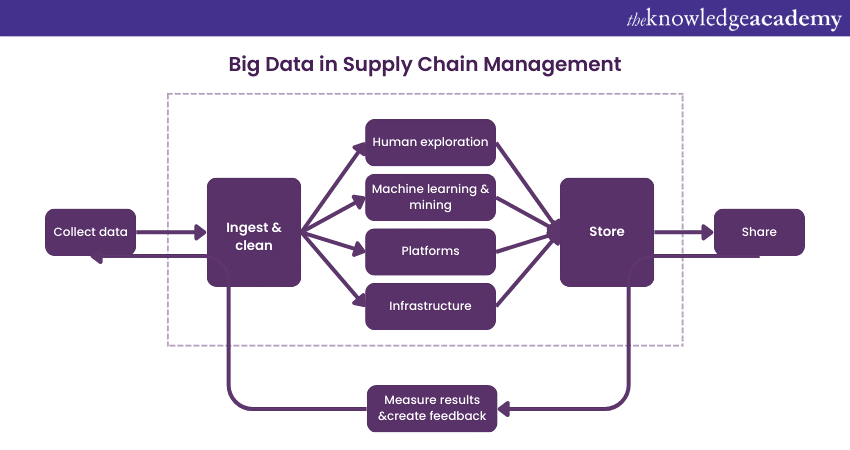
Big Data has a strategic role in Supply Chain Management where relevant information is valuable, and decisions are made based on it. It enables demand management, inventory optimisation, supply chain, and supplier relationship management.
Using Methodologies and technologies like Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence, organisations can extract intelligence from Big Data, which will make Supply Chain faster, efficient and more cost-effective.
Volume denotes the sheer scale of data generated, often surpassing the capacities of traditional storage and processing systems. Velocity heralds the speed at which data is generated and needs to be analysed to remain useful to the functioning of an organisation. Variety relates to the type of data, such as Database, social media and blog , XML or JSON or books.

Benefits of Utilising Big Data in Supply Chain Management
Big Data, with its ability to process and analyse vast amounts of information, has emerged as a game-changer in Supply Chain Management. Let’s explore its crucial advantages below:
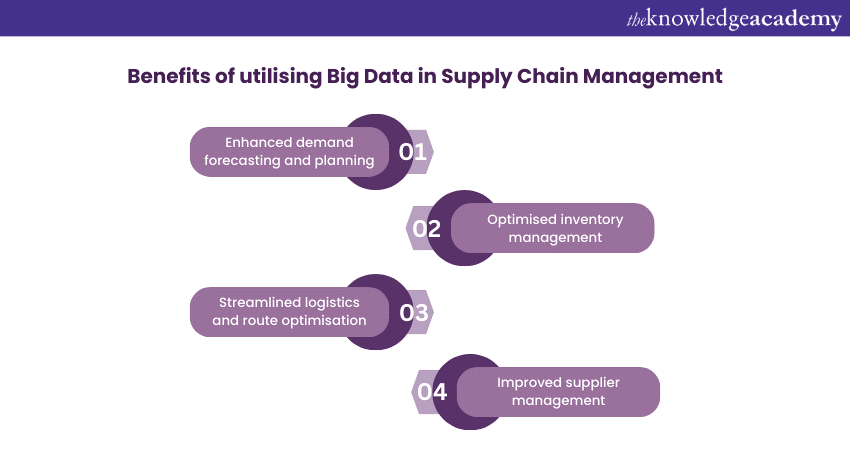
1) Enhanced Demand Forecasting and Planning
The application of Big Data in Supply Chain Management has prompted a significant evolution of demand forecasting and planning procedures. By conducting extensive research on large databases, firms can provide unique perspectives to consumers, including their preferences, market opportunities, and threats. Information updates further allow firms to rapidly adapt to production cycles and provide sequences and products in a timely manner that consumers demand.
Furthermore, seasonal and trend analyses become more accurate and reliable with the addition of Big Data Database. Historical data patterns are examined with precision, enabling businesses to anticipate demand fluctuations during specific periods. This insight is invaluable for optimising production schedules, procurement, and resource allocation, ultimately reducing excess inventory and associated holding costs.
2) Optimised Inventory Management
Big Data transforms inventory management from a static process to a dynamic, data-driven strategy. Through continuous monitoring and analysis of stock levels, businesses can maintain an optimal balance between supply and demand. This leads to reduced instances of overstocking, minimising holding costs and mitigating the risks of obsolescence.
Additionally, Big Data analytics enables businesses to implement just-in-time inventory practices. By leveraging real-time market data, companies can fine-tune their procurement and production processes to respond directly to current demand trends. This approach not only reduces excess inventory and also enhances overall operational efficiency.
Stay ahead in the rapidly evolving data landscape by registering for our Big Data and Analytics Training – join us now!
3) Streamlined Logistics and Route Optimisation
Incorporating Big Data into Supply Chain Management enhances logistics operations. Real-time tracking and visibility of shipments provide unparalleled control over the movement of goods. This facilitates proactive problem-solving, allowing businesses to swiftly address delays or disruptions in transit.
Moreover, Big Data enables sophisticated route optimisation. By integrating traffic and weather data, businesses can dynamically adjust delivery routes to avoid congestion and unfavourable weather conditions. This not only ensures timely deliveries but also reduces fuel costs and carbon emissions, aligning with sustainability initiatives.
4) Improved Supplier Management
Big Data arms businesses with great tools to improve and manage supplier relationship and their supply chain performance. In fact, with the help of Vendor Performance Analytics, companies have an opportunity to remain fair and evaluate their suppliers based on such parameters as delivery on time, quality of provided products as well as correspondence to Service Level Agreements (SLAs). Centralised analysis of the data equates to increased transparency and accountability across the Supply Chain ecosystem.
Also, the use of Big Data enhances the management of risks in suppliers. While using historical records and environmental elements, the risk of certain suppliers can be established, and precautionary measures can be taken. It also regulates supply so that disruption can be easily dealt with as it does not happen regularly.
5) Enhanced Customer Service and Satisfaction
Leveraging Big Data leads to a substantial improvement in customer service and satisfaction levels. By analysing customer data, businesses can offer personalised experiences, tailored promotions, and product recommendations. This not only strengthens customer loyalty but also drives increased sales and revenue.
Accurate delivery timeframes, made possible through Big Data-powered logistics, further enhance customer satisfaction. Customers receive clear and reliable estimates for when their orders will arrive, reducing uncertainty and enhancing their overall purchasing experience. This level of transparency and reliability develops trust and fosters long-lasting customer relationships.
Applications of Big Data in Supply Chain Management
From sensing and responding to shifts in demand patterns to proactively maintaining equipment and ensuring product quality, Big Data offers a dynamic toolkit. Additionally, it plays a pivotal role in assessing and mitigating risks, fostering sustainability, and strengthening collaborative efforts with suppliers. Some of the important applications of Big Data in Supply Chain Management are:
1) Demand Sensing and Response
Demand sensing involves using real-time data and advanced analytics to gain immediate insights into consumer demand patterns. By leveraging Big Data, Supply Chain Managers can detect shifts in demand as they happen, allowing for agile and responsive adjustments to production, procurement, and inventory levels. This capability is particularly valuable in industries characterised by rapidly changing consumer preferences or seasonal fluctuations.
For instance, a retail company can utilise demand sensing to monitor buying trends in real-time. If an unexpected surge in demand for a particular product occurs, the system can trigger automatic reorders or production adjustments to meet the heightened consumer interest. This prevents stockouts and ensures that products are readily available when customers want them, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction and maximising revenue potential.
Join our comprehensive Data Science Analytics Course and stay competitive in the fast-evolving tech landscape.
2) Predictive Maintenance and Quality Management
Big Data Analytics play a pivotal role in optimising maintenance practices within the Supply Chain. Through the analysis of equipment data, businesses can predict when machinery or vehicles might require maintenance or replacement parts. This proactive approach minimises costly downtime and prevents unexpected breakdowns that can disrupt operations.

Furthermore, in Quality Management, Big Data enables businesses to monitor and analyse various factors that impact product quality. By integrating data from sensors, production processes, and Quality Control checkpoints, organisations can identify potential issues early in the manufacturing process. This empowers them to take corrective action swiftly, ensuring that only high-quality products reach customers.
3) Risk Assessment and Mitigation
Big Data provides a powerful tool for assessing and mitigating Risks within the Supply Chain. By analysing historical data, market trends, and external factors, businesses can figure out potential Risks such as supplier disruptions, geopolitical issues, or natural disasters. With this information, contingency plans and Risk mitigation strategies can be developed and implemented.
For example, a company sourcing components from multiple suppliers across different regions can use Big Data Analytics to assess the potential impact of a disruption in one of those regions. With this foresight, they can adjust procurement strategies, diversify suppliers, or implement backup plans to ensure a consistent supply of critical components.
4) Sustainable and Green Supply Chain Initiatives
Sustainability is a significant priority for both consumers and businesses. Big Data can be instrumental in implementing and monitoring sustainable practices within the Supply Chain. It enables organisations to track and analyse environmental metrics, that include carbon emissions, water usage, and waste generation.
Through Data Analysis, businesses can identify areas of improvement and implement sustainable initiatives, such as optimising transportation routes to reduce emissions or implementing recycling programs for packaging materials. By incorporating sustainability into Supply Chain Management, organisations not only reduce their environmental impact but also satisfy the growing demand for eco-friendly products and practices.
Master the skills to turn complex data into actionable insights by joining our Advanced Data Analytics Course – sign up now!
Supplier Collaboration and Visibility
Big Data facilitates enhanced collaboration and visibility with suppliers, leading to stronger and more efficient Supply Chain relationships. Through shared access to relevant data and analytics, suppliers can gain insights into demand patterns, production schedules, and inventory levels. This enables them to align their operations with the needs of the business, resulting in improved Supply Chain efficiency.
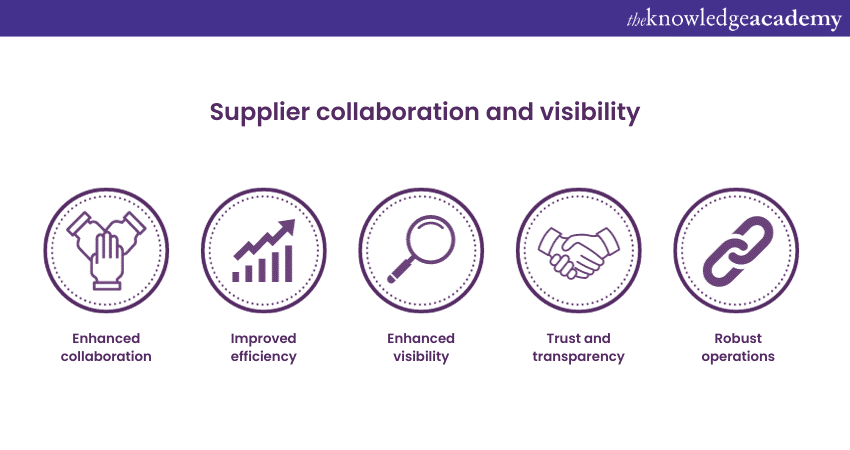
Moreover, increased visibility into supplier performance allows for more informed decision-making. By analysing data on factors like on-time delivery, product quality, and compliance with contractual agreements, businesses can objectively evaluate supplier performance and make strategic decisions about supplier relationships.
By leveraging Big Data for supplier collaboration and visibility, organisations foster transparency and trust throughout the Supply Chain ecosystem, ultimately leading to more robust and reliable supply chain operations.
The Challenge of Supply Chain Data Management
Managing supply chain data effectively is crucial for maintaining smooth operations and making informed decisions. However, organisations often face significant challenges in this area. Let’s delve into some of the key challenges of Supply Chain Data Management:
a) Data Silos: Information is often stored in separate systems, making it difficult to get a unified view of the supply chain.
b) Data Accuracy: Ensuring the reliability and accuracy of data can be challenging due to manual entry errors and outdated information.
c) Real-Time Data: The need for real-time data to make informed decisions can be hindered by delays in data collection and processing.
d) Integration Issues: Integrating data from different sources and systems can be complex and time-consuming.
e) Data Security: Protecting sensitive supply chain data from cyber threats and breaches is a critical concern.
f) Scalability: Managing and scaling data systems to handle increasing volumes of data as the supply chain grows.
g) Compliance: Ensuring data management practices comply with industry regulations and standards.
Real Case Studies of Big Data in Supply Chain Management
Big Data has revolutionised Supply Chain Management by providing deeper insights, enhancing efficiency, and enabling predictive analytics. Here are some real case studies that highlight the transformative impact of Big Data in Supply Chain Management:
1) How Amazon Utilises Big Data to Improve Its Supply Chain Operations?
Amazon leverages various Big Data solutions to enhance its supply chain operations. One key approach is through real-time Data Analytics to optimise inventory management. By analysing sales, inventory, and delivery systems, Amazon can accordingly predict product demand and adjust inventory levels. This strategy helps prevent stockouts and reduces excess inventory, saving millions in storage costs.
Additionally, Amazon employs Predictive Analytics and Machine Learning to optimise its delivery network. By gathering data on weather, traffic, and shipping routes, managers can determine the fastest and most efficient delivery routes. This ensures timely package deliveries and reduces shipping costs. Furthermore, Amazon uses customer data to personalise shopping experiences by analysing preferences, shopping habits, and feedback.
2) How does Procter & Gamble (P&G) Collaborate with Suppliers to Share Data and Improve Efficiency?
Procter & Gamble (P&G) collaborates with its suppliers to share data and increase efficiency. P&G utilises technology to share data with suppliers, improving forecast accuracy and reducing inventory levels. They have also developed a Supplier Environmental Sustainability Scorecard to help suppliers measure and enhance their environmental impact.
Moreover, P&G’s Connect + Develop programme lets the company work with external partners to drive innovation. This initiative enables collaboration with suppliers, universities, and start-ups to re-design new products and improve existing ones. P&G also focuses on creating value and sustainable growth by working closely with suppliers to make sustainable solutions for packaging, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and improve supply chain visibility.
3) How does UPS use Data Analytics to Optimise its Delivery Routes?
UPS employs Data Analytics to optimise its delivery routes by gathering data from various sources, such as package destinations, weights, and weather patterns. This data is analysed to create the most efficient delivery routes, saving time and money.
UPS uses a combination of GPS tracking, handheld devices, and sensors to gather delivery data, creating detailed maps that update in real-time based on changing conditions. The company has also implemented a package flow technology called ORION (On-Road Integrated Optimisation and Navigation). ORION uses algorithms to analyse delivery route data and driver movements, reducing the number of miles driven and saving time and fuel costs. UPS reports that ORION has saved over 39 million miles and reduced CO2 emissions by 20,000 metric tonnes.
Conclusion
The integration of Big Data in Supply Chain Management marks a transformative leap forward in operational efficiency, responsiveness, and sustainability. By harnessing real-time insights, businesses can finely tune their strategies, ensuring products reach customers with precision and speed.
Master the required skills to handle massive datasets – sign up for our Hadoop Big Data Certification today!
Frequently Asked Questions

Big Data in Supply Chain Management enhances efficiency through real-time tracking, demand forecasting, and predictive analytics. It enables better inventory management, reduces operational costs, and improves supplier relationships, leading to more responsive and resilient supply chains.

Big Data drives informed decision-making in Supply Chain Management by offering detailed insights into market trends, risks, and operational inefficiencies. It supports data-driven strategies, optimises resource allocation, and enables proactive Risk Management.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Big Data and Analytics Trainings, including the Advanced Data Analytics Course, Data Analytics With R Course, and Big Data Analysis Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Chai vs Character.
Our Data, Analytics & AI Blogs cover a range of topics related to Big Data and Analytics, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Data, Analytics and Artificial Intelligence (AI) skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Data, Analytics & AI Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Hadoop Big Data Certification
Hadoop Big Data Certification
Thu 23rd Jan 2025
Thu 20th Mar 2025
Thu 22nd May 2025
Thu 17th Jul 2025
Thu 18th Sep 2025
Thu 20th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


