We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +91-181-5047001 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Kaizen and Six Sigma are methodologies renowned for driving process improvement and achieving operational excellence. While both aim to enhance efficiency and quality, their focus, approach, scope, implementation, and timeframe differ. Understanding the Difference Between Kaizen vs Six Sigma will help organisations determine the most suitable methodology for their needs.
By comparing these two methodologies, you can gain insights into their unique characteristics, approaches, and applications. In this blog, you will learn about the Difference between Kaizen vs Six Sigma, their principles, and their benefits.
Table of contents
1) What is Kaizen?
2) Key principles of Kaizen
3) Benefits of Kaizen
4) What is Six Sigma?
5) Key principles of Six Sigma
6) Benefits of Six Sigma
7) What are the differences between Kaizen vs Six Sigma?
8) Conclusion
What is Kaizen?
Kaizen, derived from the Japanese words "kai" (change) and "zen" (good), refers to the philosophy of continuous improvement. It is a methodology that emphasises making small, incremental changes to processes and systems for ongoing improvement. Kaizen encourages the active involvement of employees at all levels to contribute their ideas and suggestions for improvement.
The focus is on fostering a culture of continuous learning and improvement, where every individual within the organisation is empowered to identify and solve problems, eliminate waste, and streamline operations. By embracing the principles of Kaizen, organisations can create an environment that promotes efficiency, innovation, and sustainable long-term improvements.
Join our Kaizen Training courses to improve your understanding of the methodology and improve processes and systems within your organisation.
Key principles of Kaizen
The key principles of Kaizen are the foundational concepts that guide its implementation and drive continuous improvement within organisations. Here are its key principles:
a) Continuous improvement: Kaizen promotes the idea that there is always room for improvement in any process or system. It emphasises the mindset of continuously seeking better ways to do things.
b) Employee empowerment: Kaizen recognises that employees are the experts in their respective roles. It encourages empowering employees to identify problems, propose solutions, and actively participate in improvement.
c) Waste reduction: Kaizen focuses on identifying and eliminating waste in processes. It aims to reduce unnecessary steps, waiting times, defects, overproduction, inventory, motion, and transportation, thereby maximising efficiency.
d) Standardisation: Standardization is crucial in Kaizen. It involves establishing standardised processes, procedures, and best practices to ensure consistency and identify areas for improvement.
e) Small incremental changes: Kaizen advocates for making small, incremental changes rather than large-scale transformations. It recognises that small improvements, when accumulated over time, lead to significant positive outcomes.
f) Data-driven decision-making: Kaizen emphasises using data and objective analysis to drive decision-making. It encourages organisations to collect and analyse data to identify improvement opportunities and measure the impact of changes.
g) Cross-functional collaboration: Kaizen promotes collaboration and teamwork across different departments and levels of the organisation. It recognises improvement efforts are most effective when multiple perspectives and expertise are combined.
h) Total participation: Kaizen believes that improvement is everyone's responsibility. It encourages all employees to actively participate in the improvement process and contribute their ideas and suggestions regardless of their roles.
i) Continuous learning and training: Kaizen fosters a culture of continuous learning and skill development. It encourages providing employees training and development opportunities, enabling them to acquire new knowledge and skills for process improvement.
Become a Kaizen master with our Certified Kaizen Foundation & Practitioner course. Join now!
Benefits of Kaizen
Implementing Kaizen in an organisation can yield several benefits, including improved teamwork and collaboration. Let's take a look at some of them below:
a) Increased employee morale and job satisfaction: Kaizen promotes employee engagement and involvement in the improvement process. This can boost morale, job satisfaction, and overall motivation among employees.
b) Enhanced teamwork and collaboration: Kaizen encourages cross-functional collaboration and teamwork. By involving employees from different departments in problem-solving and improvement initiatives, Kaizen fosters a sense of unity and cooperation within the organisation.
c) Reduced waste and improved efficiency: Kaizen focuses on waste reduction and streamlining processes. Organisations can achieve improved operational efficiency and cost savings by eliminating unnecessary steps, reducing waiting times, and optimising resource utilisation.
d) Higher product and service quality: Kaizen aims to improve the quality of products or services delivered by an organisation. Organisations can continuously seek and implement improvements to enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
e) Sustainable long-term improvements: Kaizen is not a one-time initiative; it promotes a continuous improvement culture. Organisations can achieve sustainable long-term growth and success by fostering a mindset of ongoing improvement.
f) Increased innovation and creativity: Kaizen encourages employees to contribute their ideas and suggestions for improvement. This stimulates innovation and creativity within the organisation, leading to new solutions and opportunities for growth.
g) Better problem-solving skills: Through Kaizen, employees develop and enhance their problem-solving skills. They learn to identify issues, analyse root causes, and implement effective solutions, which can be valuable assets in addressing future challenges.
h) Improved customer satisfaction: Kaizen ensures that customer needs and expectations are met and exceeded by focusing on continuous improvement. This leads to enhanced customer satisfaction, positive word-of-mouth, and increased customer loyalty.
i) Cost savings and financial benefits: Kaizen's emphasis on waste reduction and process optimisation can result in organisational cost savings. Organisations can achieve financial benefits by eliminating unnecessary expenses and improving operational efficiency.
j) Competitive advantage: Organisations that embrace Kaizen and consistently improve their processes gain a competitive advantage in the market. Continuous improvement allows them to adapt to changing customer demands, stay ahead of competitors, and drive business growth.
By leveraging the benefits of Kaizen, organisations can create a culture of improvement, foster employee engagement, and achieve sustainable success in today's dynamic business environment.
Learn the concepts and principles of Kaizen with our comprehensive Certified Kaizen Foundation course. Sign up now!
What is Six Sigma?
Originating in the 80s, it is a data-driven approach to quality management. It is widely recognised as a methodology focused on reducing process variations and defects to achieve near-perfect quality levels.
By following a structured problem-solving methodology and utilising statistical tools and techniques, Six Sigma aims to identify and eliminate the root causes of organisational problems. Its ultimate goal is to improve overall process efficiency, enhance customer satisfaction, and drive continuous organisational improvement.

Key Principles of Six Sigma
Six Sigma's key principles form its methodology's foundation and guide its implementation. Here are the key principles of Six Sigma:
a) Customer focus: Six Sigma strongly emphasises understanding and meeting customer needs and expectations. It involves identifying critical customer requirements and aligning process improvements to enhance customer satisfaction.
b) Data-driven approach: Six Sigma relies on the collection and analysis of data to drive decision-making. It emphasises the use of statistical tools and techniques to gain insights, measure process performance, and make informed improvement decisions.
c) Process focus: Six Sigma views organisations as a series of interconnected processes. It aims to identify and improve the key processes that significantly impact customer satisfaction, quality, and overall business performance.
d) Continuous improvement: Six Sigma promotes a culture of continuous improvement. It recognises that there is always room for enhancement and aims to achieve incremental and sustained process improvements over time.
e) Defect prevention: Six Sigma aims to prevent defects rather than just detecting and correcting them. It emphasises proactive measures, such as root cause analysis and process optimisation, to eliminate the causes of defects and variations.
f) Teamwork and collaboration: Six Sigma encourages cross-functional collaboration and teamwork. It recognises that involving employees with diverse skills and perspectives leads to more effective problem-solving and decision-making.
g) Leadership involvement: Successful implementation of Six Sigma requires strong leadership commitment and involvement. Leaders provide guidance, support, and resources to ensure the success of improvement initiatives.
h) Training and development: Six Sigma recognises the importance of training and developing employees in the methodology and tools. It ensures that individuals have the necessary knowledge and skills to participate effectively in improvement projects.
i) Project-based approach: Six Sigma employs a project-based approach to tackle specific improvement opportunities. Projects are selected based on their impact on business metrics and are managed using a structured methodology, such as Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve, and Control (DMAIC).
Master the DMAIC methodology and drive transformative improvements with our DMAIC Training - Signup now!
Benefits of Six Sigma
Implementing Six Sigma within an organisation offers several benefits. Here are the key benefits of Six Sigma:
a) Improved quality: Six Sigma reduces process variations and defects, leading to improved product or service quality. This, in turn, enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty.
b) Increased efficiency and productivity: Six Sigma improves operational efficiency and productivity by optimising processes and reducing waste. It streamlines workflows, eliminates unnecessary steps, and enhances resource utilisation.
c) Cost reduction: Six Sigma aims to minimise defects, rework, and inefficiencies, resulting in cost savings for organisations. Organisations can reduce operational costs and improve their bottom line by identifying and eliminating waste.
d) Enhanced customer satisfaction: Six Sigma's emphasis on quality improvement directly impacts customer satisfaction. Organizations can strengthen their reputation and gain a competitive edge by consistently meeting or exceeding customer expectations.
e) Data-driven decision-making: Six Sigma relies on data analysis to drive decision-making. This ensures that decisions are based on objective information rather than subjective opinions, leading to more effective and informed choices.
f) Improved process control: Six Sigma provides tools and techniques for monitoring and controlling processes. Organisations can identify process deviations and take proactive measures to maintain control by implementing statistical process control methods.
g) Cultural transformation: Implementing Six Sigma requires a cultural shift towards a mindset of continuous improvement and data-driven decision-making. This cultural transformation fosters employee engagement, accountability, and a commitment to excellence.
h) Employee development: Six Sigma offers training and development opportunities for employees. It equips them with valuable skills in problem-solving, data analysis, and process improvement, enhancing their professional growth and marketability.
i) Strategic alignment: Six Sigma aligns improvement initiatives with strategic business goals. By focusing on critical processes and metrics directly impacting organisational success, Six Sigma ensures that improvement efforts are targeted and impactful.
j) Organisational learning: Six Sigma promotes a culture of learning and knowledge sharing. Through cross-functional collaboration and project-based work, employees gain key insights and learn about best practices that can be applied across the organisation.
By leveraging the benefits of Six Sigma, organisations can achieve operational excellence, drive continuous improvement, and deliver high-quality products or services to meet or exceed customer expectations.
Learn the core concepts of DMAIC with our Six Sigma Green Belt course. Join now!
What are the differences between Kaizen vs Six Sigma?
Six Sigma and Kaizen are two popular methodologies used in organisations to drive process improvement and achieve operational excellence. While both approaches aim to enhance efficiency and quality, there are some key differences between Kaizen vs Six Sigma. Let's compare them:
Focus
When comparing Six Sigma vs Kaizen, it's important to understand their respective focuses and how they approach process improvement. Here's an overview of the key differences in their areas of focus:
Six Sigma:
a) Six Sigma primarily reduces process variations and defects to achieve consistent, high-quality outputs.
b) It strongly emphasises statistical analysis and data-driven decision-making to identify and address the root causes of problems.
Kaizen:
a) On the other hand, Kaizen emphasises continuous improvement through small incremental changes in processes.
b) It directs its attention towards employee involvement, waste reduction, and identifying improvement opportunities at all levels of the organisation.
By understanding the focus of each methodology, we can delve deeper into their specific approaches and applications in driving process improvements.
Approach
The approach taken by Six Sigma and Kaizen in implementing process improvements differs in their methodologies and levels of flexibility. Here's an examination of their distinct approaches:
Six Sigma:
a) Six Sigma follows a structured problem-solving methodology known as DMAIC.
b) It employs a rigorous approach that involves extensive data analysis, statistical tools, and project-based improvement initiatives.
Kaizen:
a) Kaizen promotes a more flexible and organic approach to improvement.
b) It encourages a bottom-up approach, where employees actively participate in problem-solving, generate ideas, and implement small changes daily.
While Six Sigma provides a systematic framework for making breakthrough improvements, Kaizen fosters a culture of continuous improvement through employee empowerment and the constant pursuit of small incremental changes.
Are you a Six Sigma beginner? Join our Six Sigma Yellow Belt course.
Scope
When it comes to the scope of improvement, there is a massive difference between Kaizen and Six Sigma varies greatly, with each methodology addressing different aspects of an organisation's processes. Here's a closer look at their contrasting scopes:
Six Sigma:
a) Six Sigma projects typically have a defined scope and focus on specific processes or areas that require improvement.
b) It aims for breakthrough improvements and targets critical business metrics, such as reducing defects, cycle time or improving customer satisfaction.
Kaizen:
a) Kaizen takes a holistic approach, encompassing all areas and processes within the organisation.
b) It encourages a culture of continuous improvement where even small improvements in various processes contribute to overall organisational growth.
Implementation
The implementation of Six Sigma and Kaizen involves different strategies and levels of employee involvement. Let's delve into the distinct difference between Kaizen and Six Sigma in implementing process improvements:
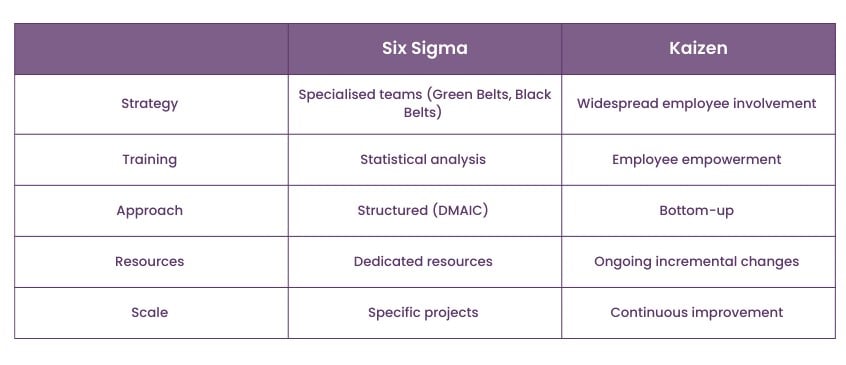
Six Sigma:
a) Six Sigma is often implemented through specialised teams, such as Green Belts and Black Belts, who undergo extensive statistical analysis and project management training.
b) Projects are carried out with a structured approach, following the DMAIC methodology.
c) Dedicated resources and time-bound project schedules are allocated to ensure the successful completion of improvement initiatives.
Kaizen:
a) Kaizen encourages widespread employee involvement and participation in improvement initiatives.
b) It promotes a bottom-up approach, where employees at all levels are empowered to identify problems, propose solutions, and implement changes daily.
c) Improvement efforts are typically ongoing and implemented through small, incremental changes rather than large-scale projects.
Elevate your problem-solving skills and become a catalyst for organisational success with our comprehensive Six Sigma Black Belt Training – Signup now!
Timeframe
The timeframes associated with Six Sigma and Kaizen initiatives differ due to the nature of their implementation and the duration of their improvement efforts. Let's explore the difference between Kaizen and Six Sigma’s temporal aspects:
Six Sigma
a) Six Sigma projects tend to have specific start and end dates, with a defined timeline for completion.
b) Due to the comprehensive data analysis and statistical tools involved, Six Sigma projects often require a longer completion time.
c) The rigorous approach and the focus on achieving breakthrough improvements contribute to the longer timeframe.
Kaizen:
a) Kaizen is an ongoing process that fosters a culture of continuous improvement.
b) It emphasises making small, incremental changes regularly without the constraints of specific start and end dates.
c) Improvement efforts are integrated into daily operations, allowing for continuous progress and flexibility in implementation.
Strengthen your black belt in Six Sigma with our Six Sigma Black Belt Upgrade course. Sign up now!
Conclusion
We hope you read and understood the Difference Between Kaizen vs Six Sigma. They are two distinct methodologies with different focuses and approaches to process improvement. While Kaizen focuses on continuous improvement, while Six Sigma targets reducing variations and defects. Understanding their differences enables organisations to choose the most suitable approach for their specific improvement needs.
Take a leap towards process excellence and unlock your organisation's potential with our Six Sigma Certification Training Courses.
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Business Improvement Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Certified Kaizen Foundation & Practitioner
Certified Kaizen Foundation & Practitioner
Wed 2nd Apr 2025
Wed 6th Aug 2025
Wed 5th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


