We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +91-181-5047001 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Power BI is a highly potent Business Intelligence (BI) software known for its features. Incremental Refresh in Power BI is one such feature that allows users to update and refresh large datasets efficiently, focusing only on the changed or newly added data. This approach offers several advantages, including improved performance, reduced data processing time, and optimised resource utilisation.
In this blog, we'll explore how Incremental Refresh works, its key benefits, challenges, and best practices for implementation in Power BI. So, let's dive in and unlock the full potential of smarter data refresh!
Table of contents
1) What is Incremental Refresh in Power BI?
2) Why Should We Use Incremental Refresh?
3) Full Refresh vs. Incremental Refresh
4) Performing Incremental Refresh in Power BI
5) SQL Queries for Incremental Refresh
6) Benefits of Incremental Refresh
7) Challenges of Incremental Refresh
8) Requirements for Incremental Refresh
9) Conclusion
What is Incremental Refresh in Power BI?
Incremental Refresh in Power BI is a feature that optimises data refreshes by updating only new or modified data rather than reloading the entire dataset. This approach enhances performance and reduces resource consumption, especially with large datasets.
By configuring parameters like RangeStart and RangeEnd, Power BI identifies and processes only the relevant data changes during each refresh cycle. This method ensures that reports and dashboards remain current without the overhead of full data reloads.
Why Should You Use Incremental Refresh?
We've all faced the challenge of data refresh at some point. Incremental Refresh is a game-changer that can save time, reduce resource usage, and enable real-time data updates. By refreshing only the new data, it significantly cuts down the time needed to load and process information.
This results in faster report generation and improved dashboard performance, which is especially valuable in industries where real-time data is crucial. Incremental Refresh also preserves historical data while updating only the new entries, making the refresh process much quicker.
In essence, Incremental Refresh streamlines data management, ensuring that your analytics are always up to date without the hassle of lengthy refresh times.
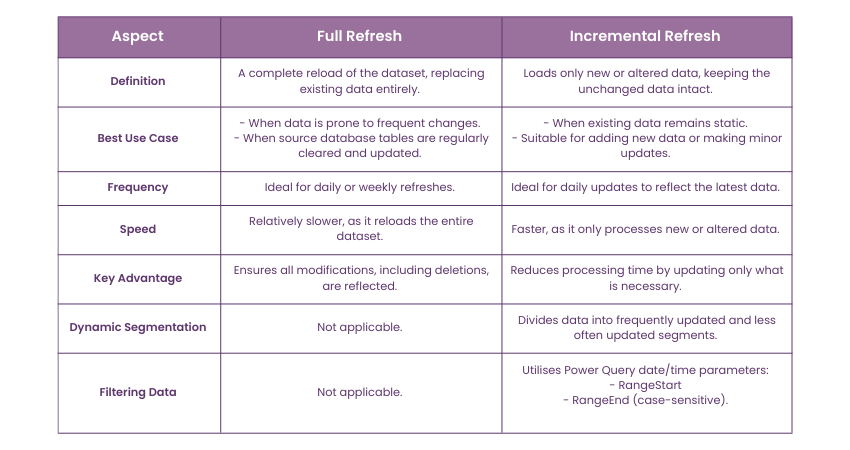
Full Refresh vs. Incremental Refresh
When transferring data into Power BI, users can choose between two methods: Full Refresh and Incremental Refresh.
Full Refresh reloads the entire dataset each time, replacing existing data. This is useful when data frequently changes or when source tables are cleared and repopulated. A Full Refresh ensures all modifications, including deletions, are reflected in reports.
Incremental Refresh loads only new or modified data while keeping unchanged data intact. This method is faster and ideal for daily updates, improving efficiency without reloading the entire dataset.
Performing Incremental Refresh in Power BI
Implementing Power BI's Incremental Refresh involves steps and configurations to ensure the dataset is updated efficiently and only the necessary data portions are refreshed. By following a structured approach, organisations can leverage the benefits of Incremental Refresh and optimise their Data Analysis processes. The key steps to implement Power BI's Incremental Refresh are as follows:
a) Data Source Selection and Preparation: Begin by identifying the data sources that contain the dataset you wish to refresh incrementally. Verify the accessibility and compatibility of these data sources with Power BI's supported connectors. Prioritise data source preparation, including cleaning, transformation, and standardisation, to maintain data quality and consistency.
b) Partitioning Strategy: Conduct a comprehensive dataset analysis to identify logical divisions or partitions. Determine the key factors for partitioning, such as dates, geographical regions, product categories, or any other relevant criteria. Carefully select the partition columns that best align with the identified divisions and ensure they are readily available in the dataset.
c) Data Model Design: In Power BI Desktop, create or modify the data model to accommodate the Incremental Refresh process. Establish appropriate relationships between tables within the data model to ensure accurate synchronisation. Optimise the data model by eliminating redundant columns or tables, improving query performance.
d) Enabling Incremental Refresh: Access the "Modelling" tab in Power BI Desktop to activate the Incremental Refresh feature. Locate the "Incremental Refresh" button and enable it for the dataset you are working with. Specify the partition columns you identified in the previous step as the basis for an Incremental Refresh.
e) Defining Refresh Window and Granularity: Determine the refresh window, which establishes when data changes should be refreshed. Consider the granularity of data updates, whether hourly, daily, weekly, or at a different frequency. Align the refresh window and granularity with the business needs and the rate of data changes.
f) Configuring Retention and Discard Policies: Define the retention policy to determine how long incremental changes should be retained in the dataset. Establish a discard policy to determine when older data falling outside the retention window should be removed. Consider data storage constraints, compliance requirements, and the necessity for historical data preservation.
g) Testing and Validation: Create test scenarios that simulate incremental data changes to validate the Incremental Refresh setup. Monitor the refresh process closely to ensure only the relevant partitions are refreshed based on the defined policies. Validate the accuracy and consistency of the refreshed dataset by comparing it against the expected results.
h) Publishing and Scheduling Refresh: Save the changes made in the Power BI Desktop and publish the dataset to the Power BI service or the desired workspace. Access the dataset settings in the Power BI service to schedule the frequency and time for an Incremental Refresh. Choose an appropriate schedule based on the frequency of data updates and the specific requirements of your business.
i) Monitoring and Maintenance: Regularly monitor the Incremental Refresh process to ensure smooth operation and adherence to defined policies. Keep a close eye on the refresh history to identify errors, warnings, or anomalies that may require attention. Proactively adjust the partitioning strategy, refresh window, or other settings to optimise performance and address any issues.
Advance your career – by mastering Business Intelligence Analysis with an expert-led Business Intelligence Analyst Course today!
SQL Queries for Incremental Refresh
To perform Incremental Refresh of traces from an AppInsights instance using SQL, you would typically utilise the SQL query language supported by the database management system (DBMS) associated with your AppInsights instance. Since the exact structure and specific SQL syntax may vary depending on the DBMS, it's essential to reference the documentation specific to your system.
Let's assume you are using Microsoft Azure's Application Insights, and the associated DBMS is Azure SQL Database. In this case, an SQL query can be used to retrieve the traces based on a specific condition or time range. Here's a general example of an SQL query in Power BI:
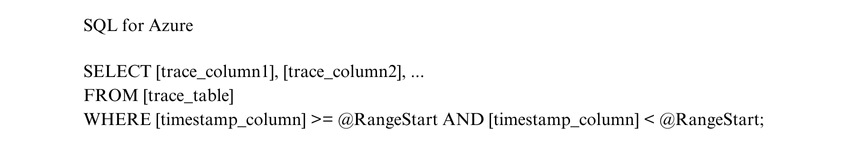
Learn Data Visualisation in Power BI with Microsoft Power BI Training - sign up now!
Benefits of Incremental Refresh
Implementing Power BI's Incremental Refresh offers several significant benefits that enhance Data Analysis processes and optimise system performance. Here are the key advantages of using Incremental Refresh:
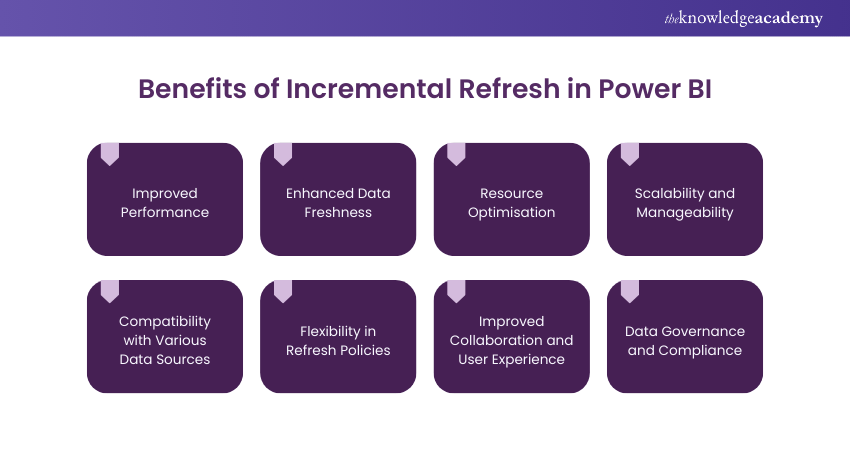
a) Improved Performance: Incremental Refresh minimises the time required for refreshing data in Power BI compared to full data refreshes, leading to improved performance. Refreshing only the necessary portions of the dataset reduces the processing overhead and enhances the overall responsiveness of reports and dashboards. Users can access updated information swiftly, making timely decisions using the latest data.
b) Enhanced Data Freshness: Incremental Refresh ensures that reports and dashboards are based on the latest available data. By swiftly incorporating incremental changes into the dataset, organisations can stay ahead of dynamic business conditions and make well-informed decisions. Maintaining data freshness improves the accuracy and relevance of reports, driving more effective data-driven decision-making.
c) Resource Optimisation: Incremental Refresh optimises the utilisation of system resources, improving efficiency and reducing unnecessary load. Refreshing only the relevant portions of the dataset minimises storage requirements, reducing the overall disk space consumed.
It also reduces the amount of data transferred over the network during refresh operations, resulting in lower bandwidth usage. This resource optimisation allows organisations to allocate their computing resources and use network bandwidth more efficiently, optimising overall system performance.
d) Scalability and Manageability: Incremental Refresh supports handling large and complex datasets more effectively. Organisations can manage and maintain their data more efficiently by partitioning the dataset based on logical divisions, such as dates or regions.
Each partition can be refreshed independently, allowing for scalable data analysis processes without sacrificing performance. This scalability enhances the ability to handle growing data volumes and provides flexibility in accommodating evolving business needs.
e) Compatibility with Various Data Sources: Incremental Refresh is highly adaptable, and therefore it can be used with a wide range of data sources, providing flexibility and consistency across different platforms. Whether the data resides in SQL databases, Excel files, SharePoint lists, or other supported sources, it can be implemented seamlessly.
This compatibility allows organisations to leverage Incremental Refresh consistently, regardless of the underlying data source, promoting a unified data analysis approach.
f) Flexibility in Refresh Policies: Incremental Refresh offers flexibility in defining refresh policies for different partitions. Organisations can customise each partition's refresh frequency and window based on their specific requirements.
This flexibility allows for fine-tuning the refresh process to align with data update frequencies, ensuring that data is updated at the desired intervals. By tailoring the refresh policies, organisations can strike the right balance between data freshness and resource utilisation.
g) Improved Collaboration and User Experience: Incremental Refresh enhances collaboration among users working on shared reports and dashboards with faster data refresh. Users can access updated reports in real-time, facilitating collaborative data analysis and enabling more efficient workflows. This improved user experience fosters better team engagement and productivity, leading to more effective data-driven decision-making.
h) Data Governance and Compliance: Incremental Refresh supports organisations' data governance and compliance efforts. It allows for the retention and discarding of data based on defined policies, ensuring adherence to data retention regulations and guidelines. Organisations can implement data retention and discard policies that align with their governance frameworks, promoting data compliance and security.
Challenges of Incremental Refresh
While Incremental Refresh in Power BI provides significant benefits, it is important to understand its limitations and potential challenges. Being aware of these constraints helps ensure smooth implementation and avoids unexpected issues. The key limitations and challenges of Power BI’s Incremental Refresh include:
a) Data Source Limitations: The underlying data sources determine the overall effectiveness of the capabilities and limitations of Incremental Refresh. Some data sources in Power BI may not support native partitioning or incremental updates, limiting its applicability. Organisations need to assess the compatibility and suitability of their data sources to ensure seamless implementation.
b) Compatibility Constraints: It has certain compatibility constraints when it comes to data transformations and Power Query operations Power BI. Certain transformations, such as merging or appending data, can invalidate the Incremental Refresh capabilities. It is crucial to thoroughly evaluate the compatibility of data transformations and ensure they align with its requirements.
c) Complexity in Partition Management: Managing partitions can become complex Power BI, particularly when dealing with large and rapidly changing datasets. Determining the right partitioning strategy and maintaining partitions require careful planning and ongoing monitoring. Organisations should allocate resources to handle partition management effectively and ensure optimal performance and data accuracy.
d) Maintenance Overhead: Incremental Refresh introduces additional maintenance overhead compared to full data refresh in Power BI. Regular monitoring and management of partitions, refresh policies, and data model optimisation are necessary for seamless operation. Organisations should allocate sufficient resources and establish efficient processes for ongoing maintenance tasks associated with Incremental Refresh.
e) Dependency on Data Update Patterns: The effectiveness of Power BI's Incremental Refresh is closely tied to the data update patterns of the underlying dataset. If the data updates are sporadic or irregular, its benefits may be limited. Organisations need to evaluate the frequency and consistency of data updates to determine the viability and effectiveness of incremental Refresh.
f) Performance Trade-offs: While Incremental Refresh significantly improves performance for data retrieval, it introduces additional overhead during the refresh process in Power BI. Partitioning and maintaining multiple partitions can impact refresh performance and resource utilisation. Organisations need to balance the benefits of Incremental Refresh and the potential impact on system performance.
g) Learning Curve and Expertise: Effectively implementing incremental Refresh requires a solid understanding of Power BI concepts and best practices. Setting up and managing Incremental Refresh, particularly for organisations new to the feature, can involve a steep learning curve. Acquiring the necessary expertise or training resources can help overcome implementation challenges and ensure successful adoption.
h) Data Governance and Compliance: Incremental Refresh may present data governance and compliance challenges. Organisations must ensure that incremental updates align with data retention and privacy policies. You should handle sensitive data appropriately and adhere to regulatory requirements during the refresh process.
Requirements for Incremental Refresh
Incremental Refresh is a versatile feature supported for all datasets. However, if you need real-time data updates using Direct Query, a Premium workspace is required.
1) Date Filtering: Ensure your table includes a date column, either in date/time or integer format. This is crucial for effective date filtering and optimising the refresh process.
2) Single Data Source: All queries must originate from a single data source to enable Incremental Refresh.
3) Query Folding: This refers to Power Query's ability to generate a single query statement to retrieve and transform source data efficiently.
By meeting these requirements, you can leverage Incremental Refresh to streamline your data management and keep your analytics up to date with minimal effort.
Develop necessary skills for Data Analysis with Business Intelligence Reporting - sign up today!
Conclusion
Incremental Refresh in Power BI is a valuable feature that provides substantial benefits. By optimising the data refreshing process, organisations can achieve improved performance, enhanced data freshness, and resource optimisation. This blog covered the details of utilising Incremental Refresh, which can significantly improve Data Analysis capabilities and empower organisations to make data-driven decisions based on current insights.
Master flowchart mapping techniques - enhance your Business Intelligence skills with expert-led Business Intelligence Reporting – sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Difference Between Direct Query and Incremental Refresh in Power BI?

Direct Query retrieves data from the source in real time without storing it in Power BI, while Incremental Refresh stores historical data in the Power BI dataset and updates only new or changed data, optimising performance for large datasets.
Can We Use Incremental Refresh in Direct Query?

No, Incremental Refresh is not applicable to Direct Query since Direct Query doesn’t store data in the dataset. It always queries data directly from the source, making real-time updates unnecessary for incremental processing.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Business Intelligence Reporting Courses, including Microsoft Power BI Course, Tableau Desktop Training, and DAX Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Power BI Slicers.
Our Office Application Blogs cover a range of topics related to Power BI, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Business Intelligence Reporting skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Office Applications Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Querying Data with Microsoft Transact-SQL DP080
Querying Data with Microsoft Transact-SQL DP080
Thu 10th Apr 2025
Thu 12th Jun 2025
Thu 14th Aug 2025
Thu 9th Oct 2025
Thu 11th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


