We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +91-181-5047001 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Risk Management is a fundamental component of Information Security, and the ISO 27005 Standard provides guidelines for effectively managing risks. Within ISO 27005, organisations have the option to either retain or accept certain risks, depending on their specific context and risk tolerance. In this blog, we explore the concepts of Risk Retention and Risk Acceptance in ISO 27005, highlighting their definitions, strategies, and implications.
Table of contents
1) Understanding risk in ISO 27005
2) Risk Retention in ISO 27005
3) Risk Acceptance in ISO 27005
4) Comparing Risk Retention and Risk Acceptance in ISO 27005
5) Conclusion
Understanding risk in ISO 27005
Before understanding Risk Retention and Risk Acceptance, it's crucial to understand how ISO 27005 defines and conceptualises risk. ISO 27005 defines risk as the "effect of uncertainty on objectives" and emphasises the need for organisations to identify and manage risks to achieve their Information Security goals.
Risk Retention in ISO 27005
Risk Retention involves consciously accepting a certain level of risk and bearing the consequences if the risk materialises. This concept acknowledges that not all risks can be removed or reduced to an acceptable level and that some risks may be more cost-effective to retain.
Risk Retention strategies
ISO 27005 provides several strategies for Risk Retention, including:
a) Self-insurance: Organisations set aside funds to cover potential losses associated with specific risks.
b) Reduced protection measures: Organisations may choose to reduce security measures in certain areas due to cost or operational constraints.
c) Accepting legal and compliance risks: Some risks related to legal and regulatory compliance may be retained if the organisation believes the cost of compliance is excessive.
Benefits and drawbacks
Let’s first have a look at benefits of Risk Retention:
a) Cost-effectiveness: Retaining certain risks can be more cost-effective than implementing extensive risk mitigation measures.
b) Strategic decision-making: Allows organisations to make informed strategic decisions regarding risk tolerance and resource allocation.
c) Flexibility: Provides flexibility in adapting to changing risk landscapes.
Now let us have a look at the drawbacks of Risk Retention:
a) Financial exposure: Organisations bear the financial burden of losses when risks materialise.
b) Reputational damage: Certain risks, if realised, can lead to reputational damage.
c) Uncertainty: Retained risks can introduce uncertainty into an organisation's operations.
Enhance your Information Security expertise with our ISO 27001 Foundation Training – your gateway to a more secure future.
Risk Acceptance in ISO 27005
Risk acceptancez is the conscious decision to acknowledge the existence of a risk without taking specific actions to mitigate it. This strategy is often chosen when the cost of mitigation exceeds the potential impact of the risk or when mitigation measures are impractical.
Risk acceptance criteria
ISO 27005 recommends establishing clear criteria for Risk Acceptance, which may include:
a) Impact thresholds: Determining at what level of impact a risk is considered acceptable.
b) Cost-benefit analysis: Evaluating whether the cost of mitigating a risk outweighs its potential impact.
c) Legal and regulatory compliance: Ensuring that Risk Acceptance aligns with applicable laws and regulations.
Benefits and drawbacks
Benefits of Risk Acceptance include:
a) Cost savings: Avoids unnecessary expenses on risk mitigation for risks with a low potential impact.
b) Focus on critical risks: Allows organisations to concentrate resources on mitigating high-priority risks.
c) Simplicity: Simplifies Risk Management processes for certain risks.
Drawbacks of Risk Acceptance include:
a) Increased exposure: Risks are accepted as they are, potentially leading to negative consequences.
b) Loss of stakeholder confidence: Stakeholders may lose confidence in the organisation's ability to manage risks.
c) Reputation risk: High-impact risks that are accepted can damage an organisation's reputation.
Secure your organisation's future with our comprehensive ISO 27001 Training – fortify your cybersecurity knowledge today.
Comparing Risk Retention and Risk Acceptance in ISO 27005
ISO 27005, as a comprehensive standard for Information Security Risk Management, provides a structured approach to managing Risk Retention and Risk Acceptance. Let's break down how ISO 27005 addresses these critical aspects of Risk Management:
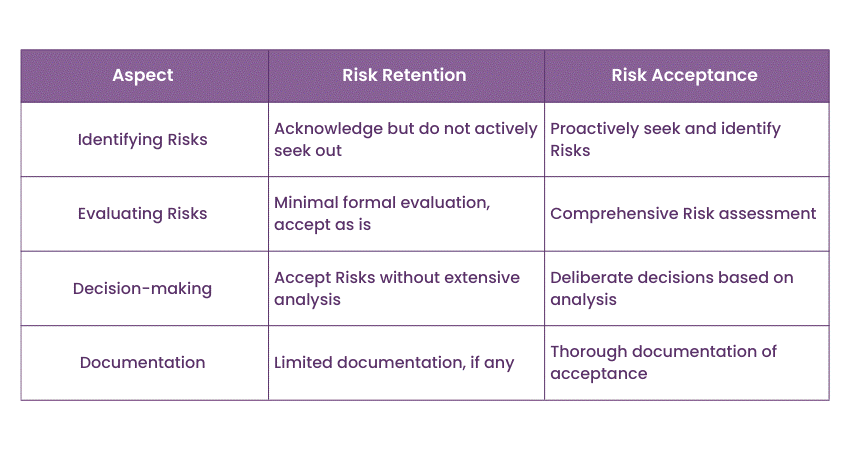
Identifying Risks
ISO 27005 begins by emphasising the importance of identifying risks comprehensively. This involves systematically identifying potential threats, vulnerabilities, and the potential consequences of these risks. It encourages organisations to create a comprehensive inventory of risks that may affect their Information Security.
Evaluating Risks
Once identified, ISO 27005 guides organisations in evaluating risks. It provides methodologies and tools for assessing the severity and likelihood of each risk. This evaluation process helps organisations prioritise risks based on their impact and the likelihood of occurrence.
Decision-making
ISO 27005 then moves to the decision-making phase. It highlights the need for organisations to make informed decisions regarding Risk Retention and Risk Acceptance. This involves considering factors such as the organisation's risk appetite, cost-benefit analyses, and strategic alignment. ISO 27005 encourages organisations to document these decisions to ensure transparency and accountability.
Documentation
Finally, ISO 27005 underscores the importance of documentation throughout the Risk Management process. It requires organisations to maintain comprehensive records of identified risks, risk assessments, and the decisions made regarding Risk Retention and Risk Acceptance. This documentation serves as a crucial reference for ongoing risk monitoring and review.
Conclusion
Risk Retention and Risk Acceptance in ISO 27005 provides structured framework for organisations to follow when dealing with Risk Retention and Risk Acceptance. By following these steps, organisations can make informed decisions about which risks remain based on their risk tolerance and strategic objectives. They can also choose to accept certain risks with full awareness of the potential consequences.
Lead the way in cybersecurity excellence – Register in our ISO 27001 Lead Implementer Course course and transform your organisation's security posture.
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 ISO 27005 Foundation
ISO 27005 Foundation
Mon 6th Jan 2025
Mon 31st Mar 2025
Mon 30th Jun 2025
Mon 6th Oct 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


