We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +91-181-5047001 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Have you ever wondered how companies like Netflix recommend your next favourite show or how financial institutions detect fraudulent transactions in real-time? The answer lies in Data Pipelines. But What is a Data Pipeline, and why is it so crucial? In this blog, you’ll have a clear understanding of how Data Pipelines work and their significance in modern Data Management.
In the Data Management realm, understanding What is a Data Pipeline can significantly enhance your ability to handle and analyse data efficiently. Let’s dive in and explore the fascinating world of Data Pipelines!
Table of Contents
1) Understanding the Concept of Data Pipeline
2) Types of Data Pipeline
3) How Does Data Pipeline Work?
4) What are the Benefits of a Data Pipeline?
5) Use Cases of Data Pipeline
6) Difference Between Data Pipeline and ETL Pipeline
7) Conclusion
Understanding the Concept of Data Pipeline
A Data Pipeline in Cloud Computing ingests raw data from various sources, transforms it, and stores it in a data lake or warehouse for analysis. This process includes filtering, masking, and aggregations to ensure data integration and standardisation, crucial for relational databases. Data Pipelines source data from Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), Structured Query Language (SQL)/NoSQL databases, and files, often requiring preparation.
Data lineage tracks relationships between enterprise data across environments like on-premises, data lakes, or warehouses. Data Scientists or Engineers handle data preparation, structuring it to meet business needs. Once processed, the data is stored and made available for various projects, including analyses, visualisations, and Machine Learning tasks.
Types of Data Pipeline
There are two primary types of Data Pipelines. Let’s explore them in detail:
a) Stream Processing Pipelines: These handle continuous, incremental data packets representing events over time, such as sensor data or financial transactions. They require low latency and high fault tolerance to process data in real-time, even if some packets are lost or arrive out of order.
b) Batch Processing Pipelines: These process and store large volumes of data in batches, ideal for tasks like monthly accounting. The Pipeline runs a series of sequenced commands on the entire batch, with each command’s output serving as the input for the next, before loading the batch into a data store.
Keen to have deeper knowledge of Data analytics, refer to our blog on "data Architecture"
How Does Data Pipeline Work?
Here is the step-by-step overview of how a Data Pipeline works. Let's explore them:
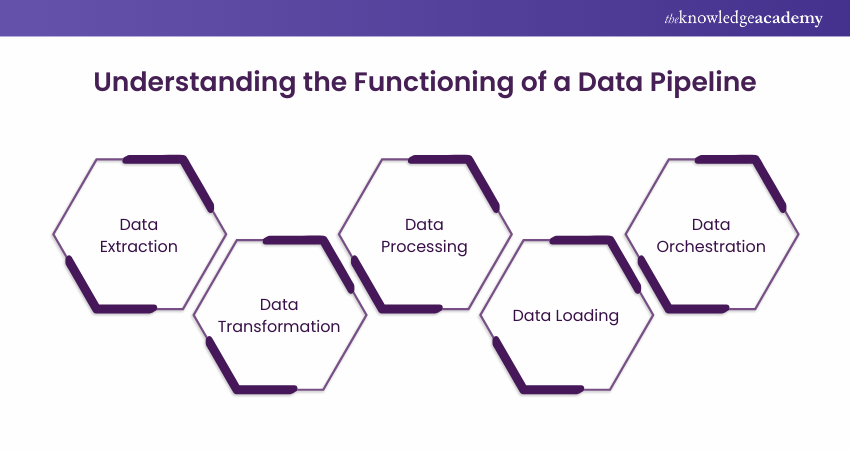
1) The procedure starts with extracting the data from one or more source systems. This involves different methods such as querying a database, reading data from files, fetching data from APIs or gathering data sensors and IoT devices.
2) Once the data is extracted, it is frequently required to be transformed to make it suitable for the intended use. Data transformation includes tasks like data cleaning, validation, enrichment and aggregation. This process makes sure that data is accurate, consistent and in the desired format.
3) In some cases, Data Pipelines may include data processing steps such as real-time streaming data processing or batch processing for complex computations. This process involves running algorithms, applying Machine Learning models or performing other data operations.
4) After the data is transformed and processed, it is then loaded into a destination system. The destination system is called a data warehouse, data lake, database or any other storage platform where the data will be stored for further analysis.
5) Data Pipelines are often complex workflows with many stages and dependencies. The tools and frameworks of data orchestration help in managing the flow of data through the Pipeline. They ensure that every step is in the proper order and can deal with failures and errors with the help of retrying and notifying errors.
Turn complex data into actionable insights with our Data Science Analytics Course – Sign up today!
What are the Benefits of a Data Pipeline?
Data Pipelines enable the integration of data from various sources and transform it for analysis, eliminating data silos and enhancing the reliability and accuracy of Data Analytics. Here are some key benefits of using a Data Pipeline:
1) Improved Data Quality
Data Pipelines clean and refine raw data, making it more useful for end users. They standardise formats for fields like dates and phone numbers, check for input errors, remove redundancies, and ensure consistent data quality across the organisation.
2) Efficient Data Processing
Data Engineers often perform repetitive tasks when transforming and loading data. Data Pipelines automate these tasks, allowing engineers to focus on deriving valuable business insights. They also help process raw data quickly, which is crucial as data can lose value over time.
3) Comprehensive Data Integration
A Data Pipeline abstracts data transformation functions to integrate datasets from different sources. It can cross-check values from multiple sources and fix inconsistencies. For instance, if a customer misspells their name on your digital service but not on your e-commerce platform, the Pipeline can correct this before the data is used for analytics.
Transform your data-driven insights into powerful business strategies with our Big Data Architecture Training – Join now!
Use Cases of Data Pipeline
There are versatile tools in Data Pipelines with a variety of use cases across different industries. Let’s understand.
1) Business Intelligence and Reporting: It is used for extracting data from various data sources, changing it into a certain format and then loading it into a data warehouse to create reports and dashboards. It helps in accurate reporting and making informed decisions.
2) IoT Data Processing: It is used to handle huge volumes of data generated by Internet of Things (IoT) devices for monitoring analysis and automation. It helps in getting real-time insights and keeping predictive maintenance.
3) Healthcare Data Processing: It is used in managing and analysing Electronic Health Records (EHRs), patient data and medical imaging for healthcare providers and researchers. It is beneficial in enhancing patient care and medical research advancements.
4) Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence (AI): It is used in creating and maintaining Pipelines for data preparations, model training and evaluation in Machine Learning and AI applications. It is helpful in automating model updates and real-time predictions.
5) Financial Data Processing: It is used in handling financial transactions, market data and risk analysis for banks, trading firms and financial institutions. This helps in Risk Mitigation and algorithmic trading.
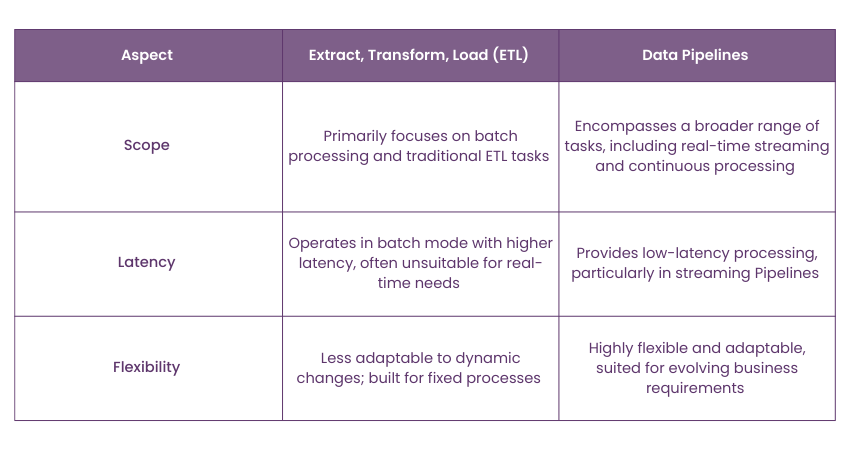
Difference Between Data Pipeline and ETL Pipeline
Although Data Pipelines and Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) processes have similarities, there are significant differences between them:
Conclusion
In essence, Data Pipelines are the lifeblood of modern Data Management, seamlessly transporting and transforming data to fuel insights and innovation. By understanding What is a Data Pipeline, you can unlock the potential to harness data’s full power. By ensuring that data flows efficiently from source to destination, they enable real-time analytics.
Unlock the potential of Big Data and Analytics to drive smarter decisions with our Big Data and Analytics Training – Join today!
Frequently Asked Questions

Tools like Apache Airflow, AWS Data Pipeline, and Google Cloud Dataflow are widely used for building and managing Data Pipelines. These tools streamline the process by automating data Extraction, Transformation, and Loading (ETL) across different systems and platforms.

A Data Pipeline is designed by identifying data sources, defining ETL processes, setting up scheduling mechanisms, and implementing monitoring tools. The Pipeline ensures seamless data flow from the source to the destination while considering scalability, error handling, and performance optimisation.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Big Data and Analytics Courses, including Advanced Data Analytics Course, Certified Artificial Intelligence for Data Analysts Training and Data Analysis Training using MS Excel. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Big Data Analyst Job Description.
Our Data, Analytics & AI Blogs cover a range of topics related to Data Pipeline, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Data Analytics skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Cloud Computing Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Cloud Computing Training
Cloud Computing Training
Thu 13th Feb 2025
Thu 10th Apr 2025
Thu 12th Jun 2025
Thu 14th Aug 2025
Thu 9th Oct 2025
Thu 11th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


