We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203 999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Reflecting on the seismic shockwaves of the 2008 financial crisis, it became crystal clear that a robust regulatory framework was not just a need anymore – it was a necessity. Basel III stepped into the spotlight in 2010 to fortify the banking sectors from systemic shocks and the looming threat of bankruptcy.
The unexpected turbulence of a global pandemic in 2019 led to a recalibration of those initial Basel III Capital ratios (as reported by the Bank for International Settlements (BIS)). In this blog, we'll unravel the rippling effects of this adjustment on Basel III requirements and discuss the complex web of data processing systems. Let's get going!
Table of Contents
1) What is Basel III?
2) Important reforms of Basel III
3) Key Elements in Basel III
4) Basel III Implementation Timeline
5) Challenges and Considerations Associated with Basel III
6) Conclusion
What is Basel III?
Basel III is an internationally recognised regulatory framework designed by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS) to fortify the stability of the global banking sector. Unlike its predecessors- Basel I and II, Basel III addresses vulnerabilities exposed during the 2008 financial crisis. This framework enforces stringent capital requirements, ensuring that banks maintain substantial buffers to withstand economic downturns.
Additionally, it introduces liquidity standards and risk management guidelines, enhancing banks' ability to weather financial turmoil. The benefits of Basel III are to fosters a safer and more resilient financial environment. It also aims to prevent systemic risks and safeguard the integrity of the international financial system.
Important Reforms of Basel III
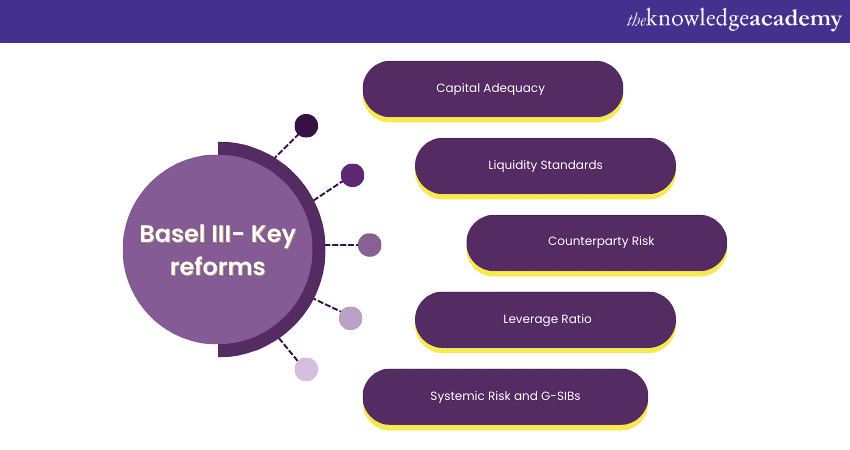
The reforms are carefully crafted to enhance the resilience of financial institutions, mitigate systemic risks, and ensure the stability of the international financial systems in Basel III. Below, we have listed the key reforms that define Basel III's transformative impact:
Capital Adequacy
Under Basel III, capital adequacy requirements were highlighted. The framework mandates banks to maintain higher capital levels, with a particular emphasis on Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1) capital. This means that banks must have a significantly greater proportion of their equity capital, which safeguards against unexpected losses. This higher capital requirement protects banks against economic downturns, reducing the probability of bank failures and taxpayer-funded bailouts.
Liquidity Standards
Recognising the emerging role of liquidity in financial stability, Basel III introduces liquidity standards that impose rigorous requirements on banks' ability to meet short-term and longer-term funding needs. The Liquidity Coverage Ratio (LCR) ensures banks have sufficient high-quality liquid assets to cover potential liquidity outflows during a 30-day stress state. The Net Stable Funding Ratio (NSFR) strengthens this by promoting funding profiles that are more stable and long-term.
Counterpart Risk
Basel III addresses the risks associated with derivatives and trading activities by introducing stronger capital requirements for these activities. The framework mandates banks to hold additional capital to cover potential losses arising from their trading activities. This measure encourages better risk management practices and reduces the potential for excessive risk-taking.
Leverage Ratio
To curb excessive borrowing and limit the reliance on leverage, Basel III implements a leverage ratio requirement. This ratio ensures that banks maintain a minimum capital levels with respect to their total assets, irrespective of the asset risk profiles. By preventing banks from becoming excessively dependent on capital, this reform strengthens the overall stability of the financial system.
Systemic Risk and G-SIBs
Global Systemically Important Banks (G-SIBs), institutions whose distress or failure could pose significant risks to the global financial system, are subjected to additional regulatory requirements. Basel III mandates G-SIBs to maintain higher capital buffers and meet stricter risk management standards. This targeted approach helps to mitigate the potential impact of a G-SIB's failure on the wider financial system.
Navigate financing journey confidently - register in our Introduction to Basel IV Training.
Key Elements in Basel III
Basel III is a crucial aspect of financial stability and protection. Below, we listed the key elements in Basel III to help you gain a clearer picture:
a) Capital Requirements: Basel III ensures that banks have enough money (called Equity Tier 1) to cover financially stressful situations.
b) Leverage Ratio: This rule prevents the bank from borrowing more than the permissible limit in comparison to its own money.
c) Liquidity Standards: Basel III requires a bank to have enough assets to instantly convert to cash during emergency financial situations.
d) Risk-Weighted Assets: Basel III improves the way banks calculate investment risks to cover potential financial losses efficiently.
Basel III implementation Timeline
The journey of Basel III, from its conception to global implementation, involves multiple stages characterised by careful development, regulatory adjustments, and ongoing monitoring. This timeline outlines the critical stages in implementing Basel III, highlighting its significance in reshaping the financial outlook.
1) 2008-2010: Post-Crisis Reflection and Framework Formulation
The 2008 financial crisis exposed the vulnerabilities within the global banking system. As a response, the Basel Committee started to protect the industry against unforeseen circumstances. This led to the establishment of Basel III during the period 2008–2010. However,prior to its creation, the era was characterised by lengthy discussions and consultations on the execution of this solid structure.
2) 2010-2017: Refinement and Finalisation of Basel III
During this phase, regulators and experts worked diligently to refine the reforms outlined in Basel III. The committee conducted several impact assessments and altered the technical details to balance robustness and feasibility. These efforts resulted in the adoption of the Basel III framework, which outlined comprehensive reforms to improve capital adequacy, liquidity standards, and risk management practices.
3) 2013-2019: Initial Implementation Phase
With the Basel III framework in place, national regulatory bodies started to incorporate it into their regional banking laws. Financial institutions started adapting to the new standards by revamping their capital structures, bolstering liquidity buffers, and implementing enhanced risk management practices. This phase marked the initial steps towards transforming the industry's practices and strengthening its resilience.
2020-Present: Ongoing Implementation and Adaptation
The COVID-19 pandemic introduced unexpected challenges to the Basel III Implementation. Recognising the exceptional circumstances, regulators provided extensions and adjustments to some deadlines, allowing banks to manage the crisis effectively. These reforms came into existence on 1 January 2023 and will be phased in over the next five years. Furthermore, as economies recover and stabilise, the process of implementing Basel III will continue, with regulatory bodies globally working to make sure that financial institutions comply with the regulations.
Minimum Capital Requirements Under Basel III
Minimum Capital Requirements under Basel III are the set of rules that tell banks how much money they need to keep aside to cover bankruptcy situations. This money, known as “Capital,” acts as a financial cushion that helps banks stay strong in the event of a financial loss.
The safest and most important type of money banks need to keep is “Common Equity Tier 1,” which acts as a foundation to keep them strong and able to navigate bankruptcy.
In addition, Basel III also requires banks to have extra money (also called Buffers) to compensate for extremely severe financial problems. By having more capital, banks are less likely to fail during financial crises. This helps protect the entire regional economy where the bank is based.
How are Basel Standards Implemented and Evaluated?
There are multiple steps banks can take to implement and evaluate Basel Standards. However, before, let’s check out how they are implemented and evaluated in the upcoming sections:
Implementation: Regulatory Consistency Assessment Program (RCAP)
In 2012, the Basel Committee established the Regulatory Consistency Assessment Program (RCAP) to monitor and assess how financial institutions implement and adopt its standards. The committee also encouraged a transparent and predictable regulatory environment to support international banks.
The Regulatory Consistency Assessment Program (RCAP) was established by the Basel Committee in 2012 to monitor and assess the implementation and adoption of its standards by financial institutions. The committee also encouraged a transparent and predictable regulatory environment to help international banks.
Evaluation
In 2021-2022, the Basel Committee published three evaluation reports. These reports were framed to determine if the implemented Basel III reforms achieved their objectives. The report also aimed to improve the banking sector's resilience and gather evidence through extensive research.
Upgrade your organisation's security: register now in our Security Governance and Compliance Training!
Challenges and Considerations
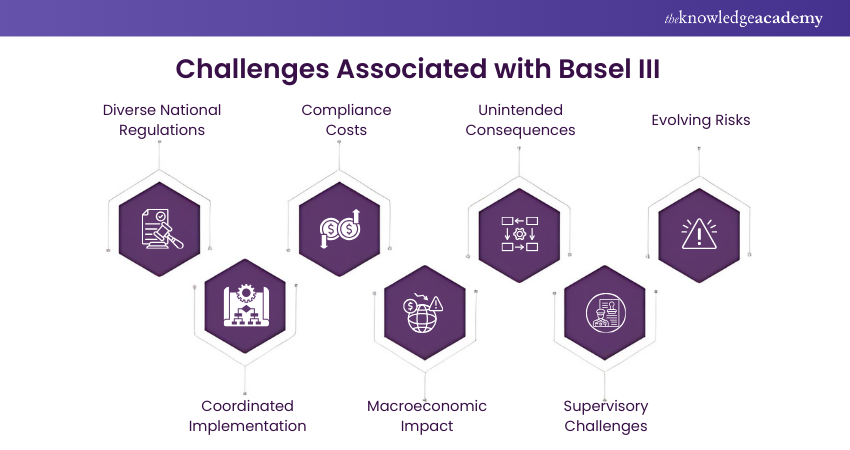
While the Basel III framework holds the promise of strengthening the global banking system, its implementation is not without challenges and considerations that demand careful attention. Let’s have a look at some of its challenges:
a) Diverse National Regulations: The adoption of Basel III reforms vary across nations, leading to a complex paradigm of regulations. Harmonising these standards across different jurisdictions is essential to avoid regulatory discrimination and ensure equal opportunities for all.
b) Compliance Costs: Adapting to Basel III's stringent requirements increases the financial and operational costs for financial institutions. This financial strain can be seen particularly on smaller organisations with limited resources.
c) Unintended Consequences: While stricter capital and liquidity requirements improve stability, they may have an unintended impact on lending to certain sectors of the economy. Finding the right balance between risk management and economic growth is a daunting task for these banks.
d) Evolving Risks: The financial landscape constantly changes with newer emerging risks. Basel III's effectiveness hinges on its ability to adapt and address emerging risks such as cyber threats, fintech innovations, and climate-related risks. This creates unprecedented risks for organisations.
e) Coordinated Implementation: Achieving consistent and coordinated implementation across jurisdictions is crucial to preventing regulatory fragmentation. Misaligned timelines and differing interpretations of the framework could impede its effectiveness.
f) Macroeconomic Impact: While the framework mitigates individual bank risks, it sometimes fails to minimise these on the broader economic spectrum. Striking a balance between systemic risks and allowing banks to fuel economic growth is a significant challenge for these financial institutions. g) Supervisory Challenges: Regulators and supervisors need to continuously monitor the effectiveness of Basel III reforms. Ensuring that banks adhere to the framework's requirements without stifling innovation or impeding economic growth is a concern that they must address.
Unravel the intricacies of Basel III with our Introduction To Basel III Course.
Conclusion
The Basel III Implementation marks a significant step towards a more stable and resilient global financial system. Its reforms address vulnerabilities exposed by the 2008 financial crisis and are designed to prevent a similar collapse in the future. Although challenges are never-ending battles, the ongoing efforts to harmonise regulations and bolster financial institutions' strength demonstrate the significance of these ammendments.
Navigate the world of compliance with confidence – Register now in our Compliance Training
Frequently Asked Questions

Basel III began its initial implementation in 2013. Its complete implementation was originally planned for 2015, but due to multiple reform amendments, it is now expected to become fully operational by January 1, 2025.

Professionals with Basel III Implementation skills can pursue careers as risk management specialists, regulatory compliance officers, or financial analysts. These roles involve assessing risks, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards, and optimising capital and liquidity to meet Basel III requirements.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Compliance Trainings, including the Introduction to Basel IV Training and compliance Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into the Pathways to Become a Compliance Officer.
Our ISO & Compliance Blogs cover a range of topics related to regulatory standards and best practices, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your compliance skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming ISO & Compliance Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 PCI DSS Implementer
PCI DSS Implementer
Thu 23rd Jan 2025
Thu 6th Feb 2025
Thu 3rd Apr 2025
Thu 5th Jun 2025
Thu 7th Aug 2025
Thu 2nd Oct 2025
Thu 4th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


