We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on + 1-866 272 8822 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Have you ever needed a smart and simple way to store information but struggled to keep it organised? Enters Python Dictionaries—a magical box where each item has a unique label, allowing you to find what you need right away. Python Dictionaries serve as data storage in the form of key-value pairs. This makes it easy to retrieve, modify, and add information.
In this blog, we will dive into the world of Python Dictionaries. You’ll learn how to create, access, modify, add, and remove elements while exploring key restrictions and Dictionary methods. Ready to unleash the full power of Python's most adaptable database? Let's get in!
Table of Contents
1) What are Python Dictionaries?
2) Creating a Dictionary in Python
3) Accessing Elements of a Dictionary
4) Adding Elements to a Python Dictionary
5) Modifying Elements in a Python Dictionary
6) Removing Elements from a Python Dictionary
7) Restrictions on Python Dictionary Keys and Values
8) Dictionary Methods
9) What is the Difference Between a List and a Dictionary in Python?
10) What Are Python Dictionaries Good For?
11) Conclusion
What are Python Dictionaries?
Python Dictionaries are a powerful and versatile data structure in Python that stores key-value pairs of data, allowing for seamless data retrieval. They are highly efficient for storing large amounts of data, where you can easily access the relevant data without having to search through the entire data structure.
Additionally, they are easy to use and manipulate, as you can easily add and delete elements . For example, a Dictionary can be used to store a student's first and last name or to keep track of a student's grades.
Key Features of Python Dictionaries:
Below are the main features of Python Dictionaries:
a) Key-Value Pairs: Each element in a Dictionary is a pair comprising a unique key and a value.
b) Mutable: You can change, add, or remove items after the dictionary is created.
c) Unordered: The items are not stored in any particular order.
d) Dynamic: They can grow and shrink as needed.
Here’s a basic example:

In this Dictionary, Keys ("name", "age", "city") are strings, and the values are a mix of string and integer types.
Python Dictionaries are particularly useful when you want to access elements by a unique identifier (key) rather than by an index (like in lists or tuples).
Creating a Dictionary in Python
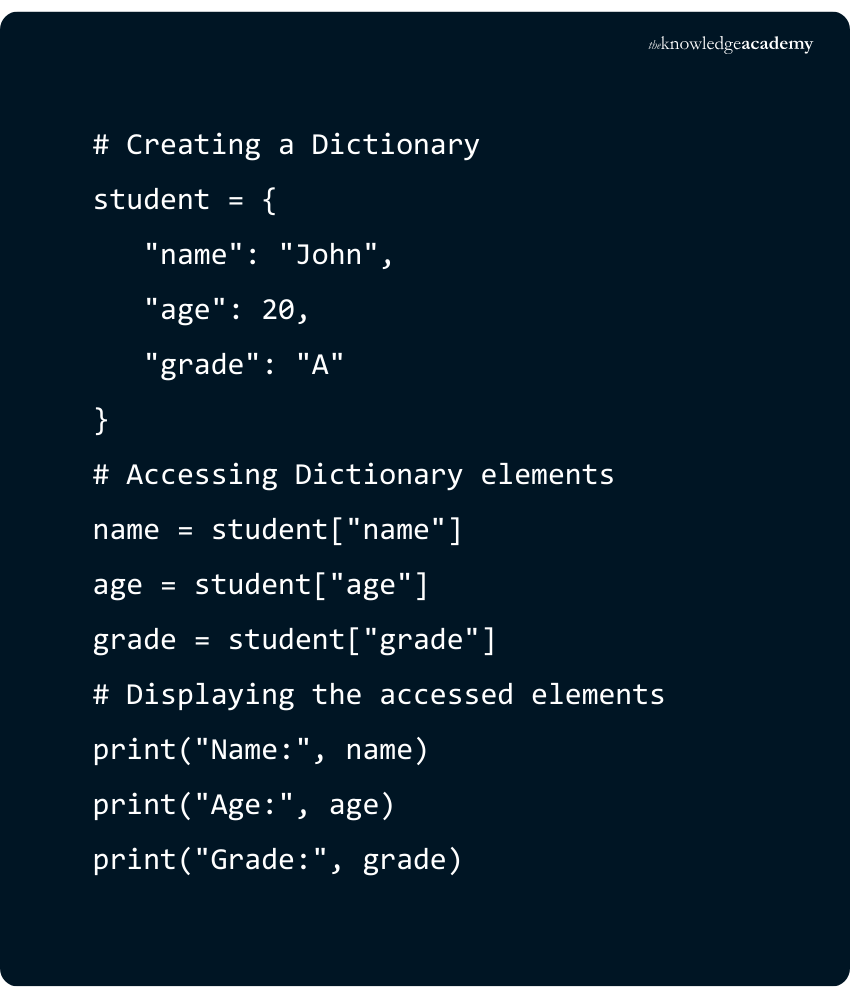
Creating a Dictionary in Python is done by enclosing a sequence of elements in curly braces {}. The elements are separated by a comma. In a Dictionary, each pair of values consists of a Key, followed by its corresponding value separated by a colon. The values in a Dictionary can be of any data type and can be repeated. However, the keys must be unique and cannot be changed.
Here is an example to create a Dictionary in Python:

Output:
Elevate your skills with our Python Django Training - join now for in-depth learning!
Accessing elements of a Dictionary
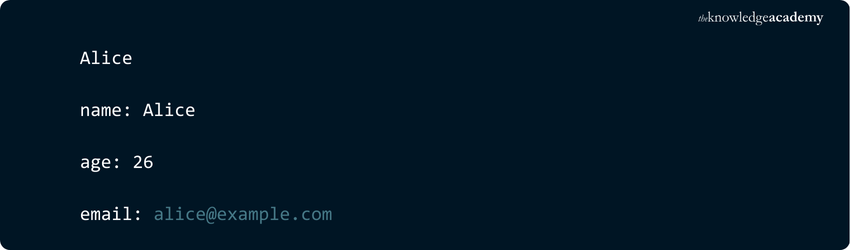
Accessing elements of a Dictionary can be done by a key and not by an index. This means that an element in a Dictionary cannot be accessed using its position but with the Dictionary key. Let us understand this with the help of an example:
Output:

In this example, we have a Dictionary called 'student' with three key-value pairs. We access the elements by using the keys as indices ("name", "age", and "grade") and assign them to variables ('name', 'age', and 'grade'). Then, we print out the values of these variables, which correspond to the values in the Dictionary.
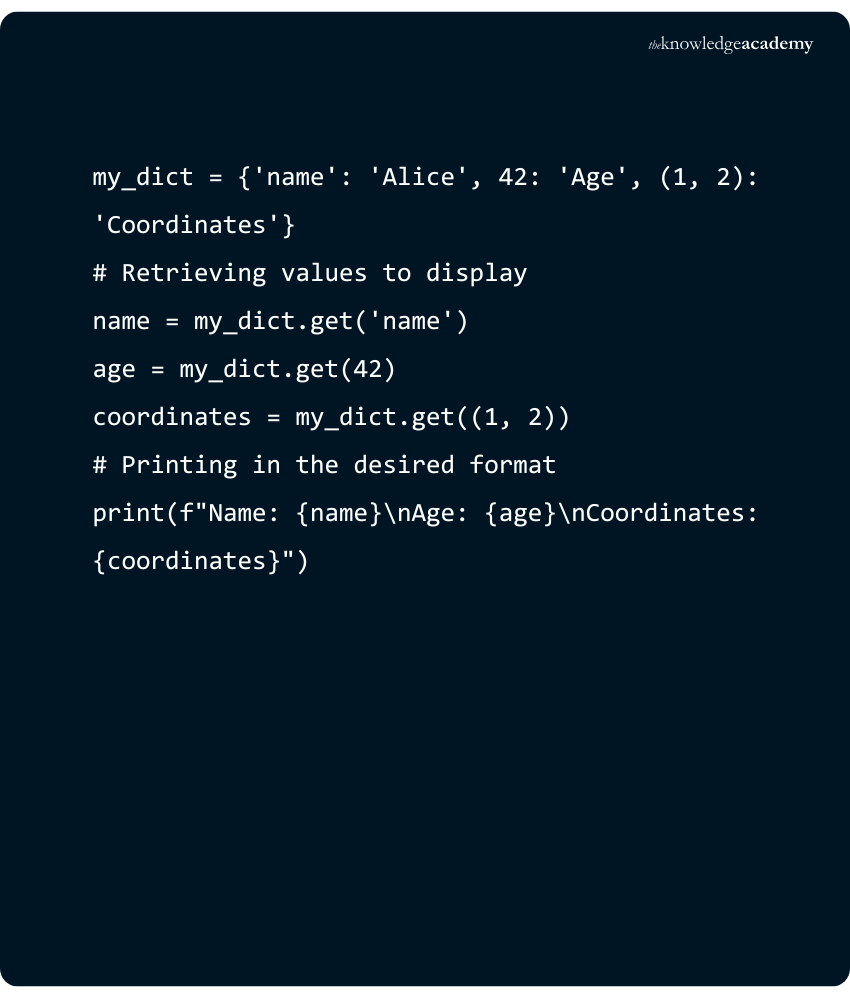
Accessing an Element with ‘get()’
Accessing an element can also be implemented using a method called 'get()'. Let us refer to an example to know how to use 'get()':

Output:

In the above example:
a) We have a Dictionary called 'student' with three key-value pairs.
b) We use the 'get()' method to access elements. When we use 'student.get("name", "Name not found")', it returns the value associated with the key "name" ("John" in this case). However, when we use 'student.get("major", "Major not found")', the key "major" does not exist in the Dictionary, so it returns the default value "Major not found."
Accessing an Element of a Nested Dictionary
Accessing an element of a nested Dictionary can be implemented with indexing [] syntax. Let us refer to an example to understand it:

Output:
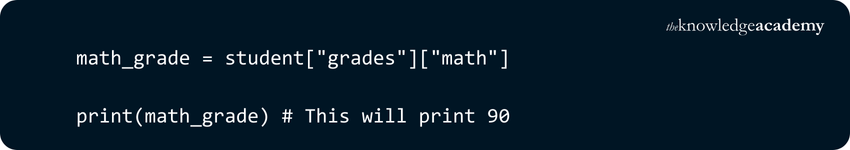
In the above example:
a) We have a nested Dictionary called 'student', where the "grades" key maps to another Dictionary containing subject grades.
b) To access the math grade, we first use "grades" as the key to access the inner Dictionary, and then we use "math" as the key to access the math grade.
c) Finally, we print the math grade, which is 90.
Learn PHP skills for web development, sign up for our PHP Programming Training now!
Adding Elements to a Python Dictionary
To add elements to a dictionary by assigning a value to a new key. If the key already exists, its value will be updated.
Example:

Output:

Explanation:
a) The new key 'city' with the value 'New York' is added to the dictionary.
b) The key 'major' doesn't exist, so the default message 'Major not found' is printed.
Modifying Elements in a Python Dictionary
To modify an element, simply assign a new value to an existing key. This will overwrite the old value.
Example:

Output:
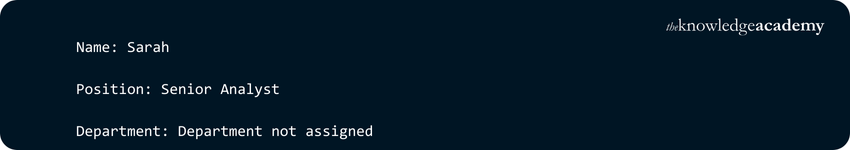
Explanation:
a) The value of the key 'position' is modified from 'Analyst' to 'Senior Analyst'.
b) The key 'department' doesn't exist, so the default message 'Department not assigned' is printed.
Removing Elements from a Python Dictionary
To remove elements using the del statement or the pop() method.
Example:

Output:
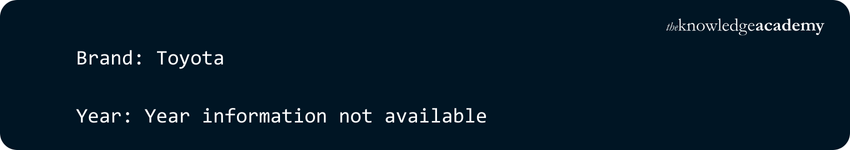
Explanation:
a) The key 'year' is removed from the dictionary.
b) Since 'year' no longer exists, the default message 'Year information not available' is printed.
Boost your career with Object Oriented Programming (OOPs) Course - register today for success!
Restrictions on Python Dictionary Keys and Values
Python Dictionaries have certain restrictions for keys and values, which must be followed for the dictionary to function properly. Let’s explore them in more detail.
a) Restrictions on Dictionary Keys
When working with Python Dictionaries, it's important to know that not all data types can be used as keys. There are specific rules governing which types are allowed. Let’s explore the restrictions on dictionary keys and why they exist to ensure smooth functionality in Python Dictionaries.

1) Keys Must be Immutable:
Dictionary keys must be of an immutable data type, meaning they cannot be changed after being created. Immutable types include:
a) Strings (str)
b) Numbers (int, float)
c) Tuples (tuple)
Example:
Output:

2) Keys Must Be Unique:
In a dictionary, keys must be unique. If you use the same key more than once, the last value assigned to that key will overwrite the previous value.
Example:
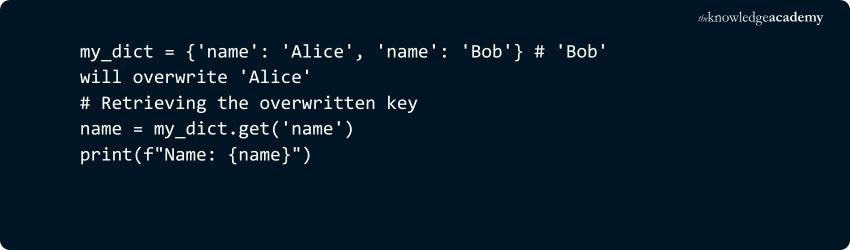
Output:

b) Restrictions on Dictionary Values
Unlike keys, dictionary values have fewer restrictions. However, understanding the flexibility and limitations of values in Python Dictionaries can help you manage your data efficiently. Let’s look into the guidelines for using values in dictionaries.
1) Values can be of any Data Type:
Unlike keys, values in a dictionary can be of any data type. You can have strings, integers, lists, or even other dictionaries as values.
Example:
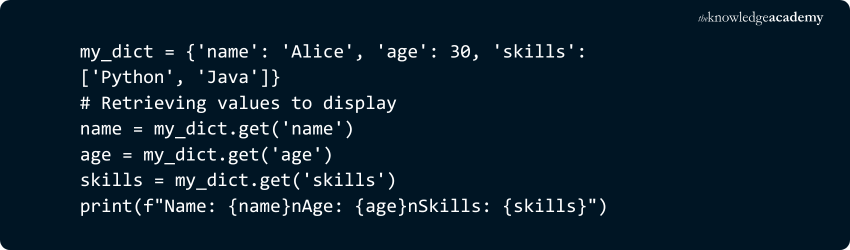
Output:

2) Values can be Mutable:
Dictionary values can be mutable, which means you can use lists, dictionaries, and other mutable types as dictionary values.
Example:
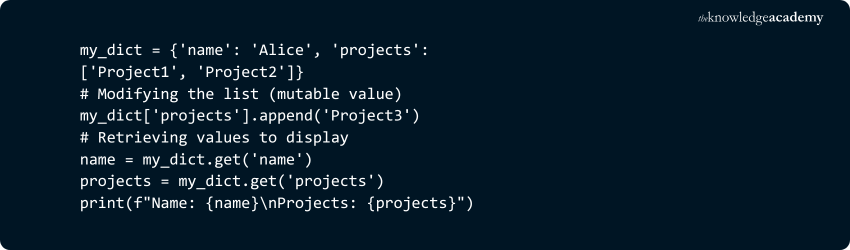
Output:
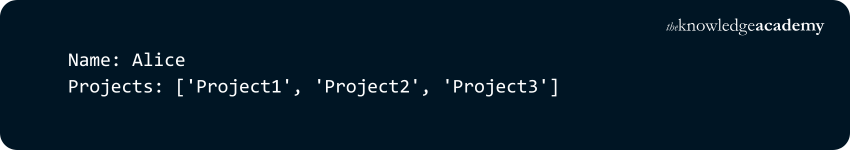
3) Values can be Duplicated:
Unlike keys, values in a dictionary do not have to be unique. You can have the same value assigned to different keys.
Example:
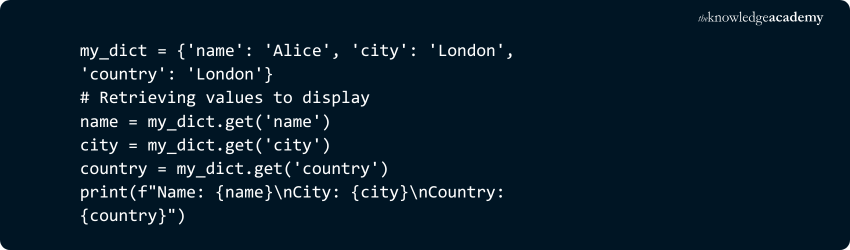
Output:

Dictionary Methods
Python provides multiple built-in methods to manipulate Dictionaries. These methods are utilised for adding, removing, and changing values of Dictionary keys. Dictionary methods are a robust way to work with Dictionaries. Understanding these methods becomes essential in working with Dictionaries effectively to store and manipulate data.
1) dict.get(key, default=None)
Retrieves the value of the specified key. If the key does not exist, it returns the default value (which is None by default).
Example:

Output:

2) dict.keys()
Returns a view object containing all the keys in the dictionary.
Example:
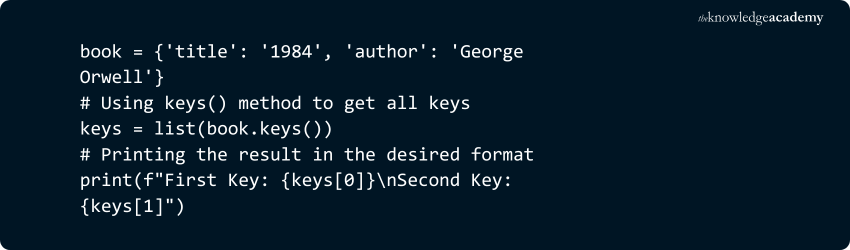
Output:

3) dict.values()
Returns a view object containing all the values in the dictionary.
Example:
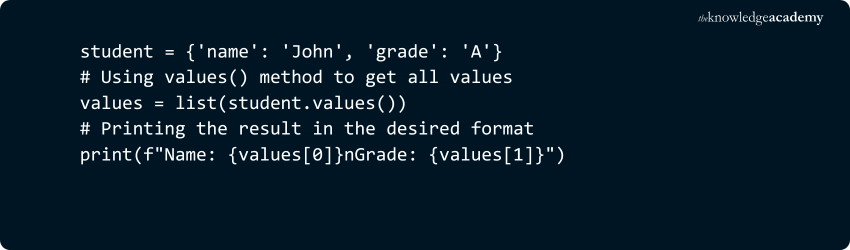
Output:

4) dict.items()
Returns a view object that displays a list of dictionary’s key-value pairs as tuples.
Example:

Output:

5) dict.pop(key, default=None)
Removes and returns the value associated with the specified key. If the key doesn’t exist, the default value is returned. If no default is provided, it raises a KeyError.
Example:
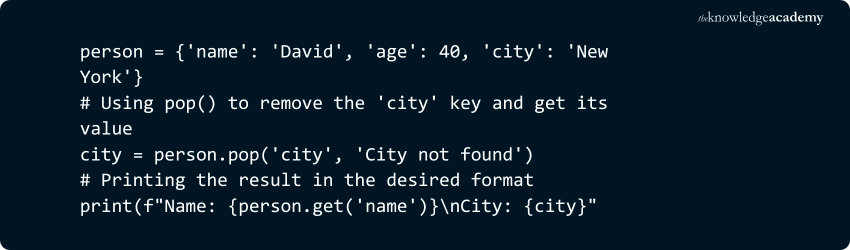
Output:

6) dict.popitem()
Removes and returns the last key-value pair inserted into the dictionary as a tuple. It raises a KeyError if the dictionary is empty.
Example:
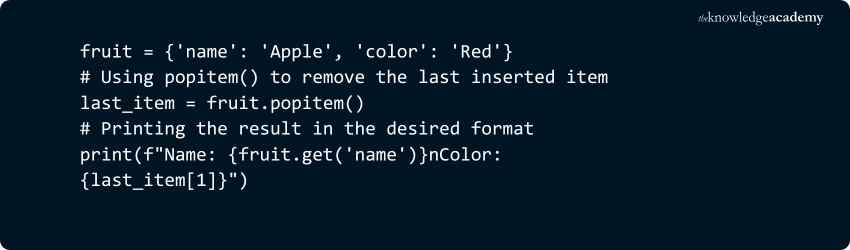
Output:

7) dict.update([other])
Updates the dictionary with elements from another dictionary or an iterable of key-value pairs. Existing keys will have their values updated, and new keys will be added.
Example:
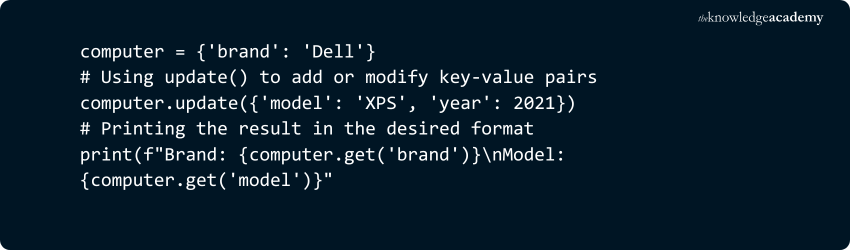
Output:

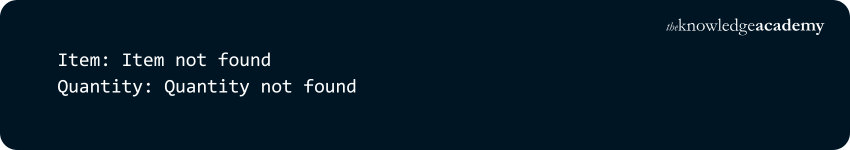
8) dict.clear()
Removes all elements from the dictionary, leaving it empty.
Example:
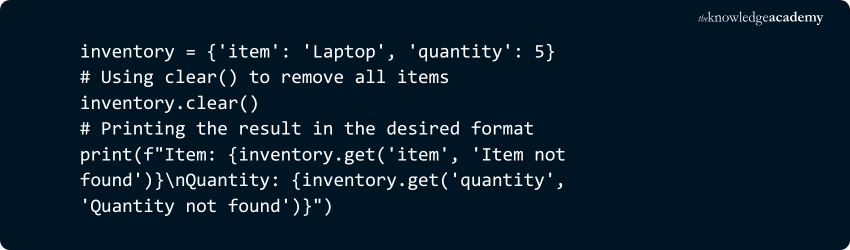
Output:
9) dict.copy()
Returns a shallow copy of the dictionary.
Example:
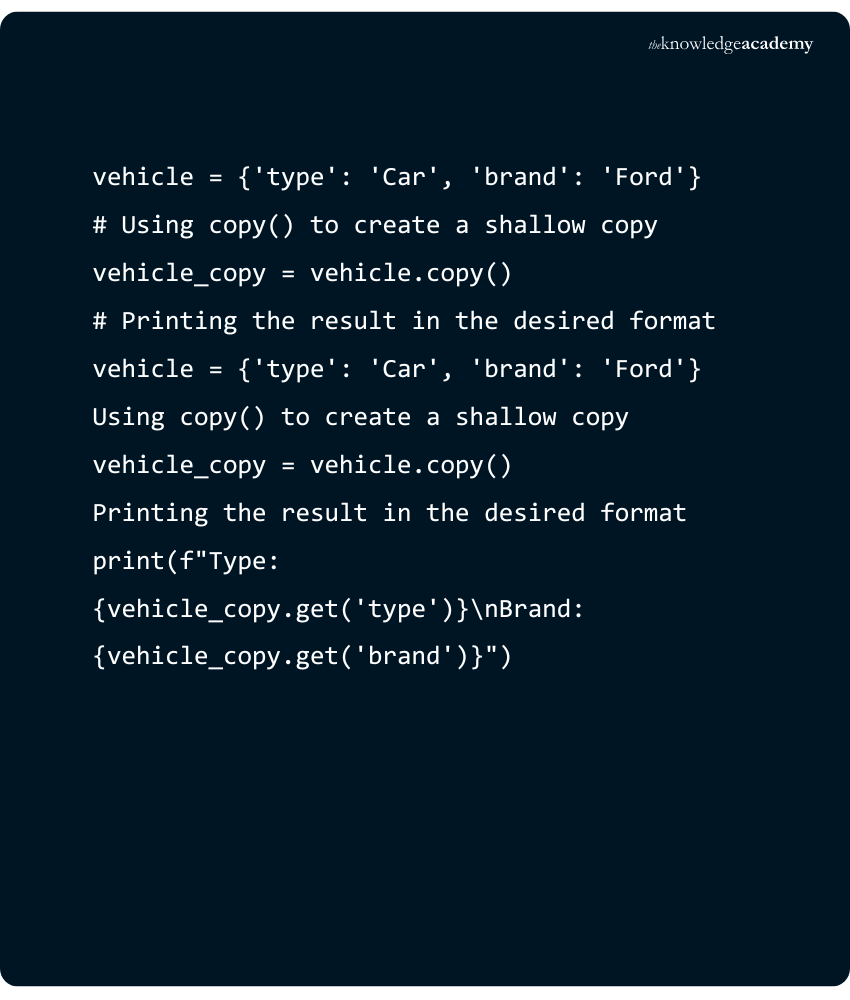
Output:

10) dict.setdefault(key, default=None)
Returns the value of the specified key if it exists. If the key does not exist, it inserts the key with the specified default value and returns the default.
Example:
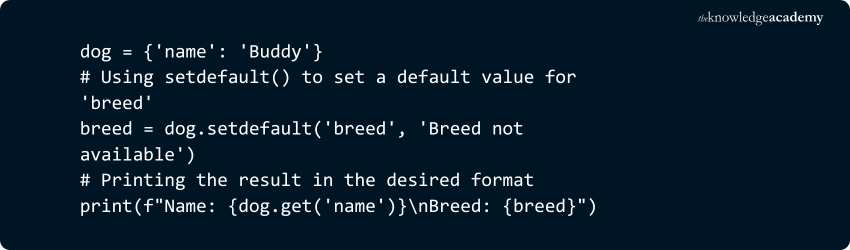
Output:

What Is The Difference Between a List and a Dictionary in Python?
In Python, a List is an ordered items collection that can be accessed using their index, making it ideal for sequential operations. In contrast, a Dictionary is an unordered collection of key-value pairs, accessed through unique keys, which makes it better suited for mapping relationships. Although both are mutable, they serve distinct purposes based on the type of data and the operations required.
What Are Python Dictionaries Good For?
Python Dictionaries are perfect for storing and managing data as key-value pairs, making them ideal for tasks requiring quick lookups, mappings, or associations. Unlike lists, which use numeric indices, Dictionaries allow efficient access to values through unique keys, providing a more intuitive and flexible way to organise data.
Boost your career with Object Oriented Programming (OOPs) Course - register today for success!
Conclusion
Python Dictionaries provide a versatile and efficient way to store and manage data through key-value pairs. By mastering their creation, modification, and key-value handling, you can streamline your coding tasks. Embrace the full potential of Dictionaries in Python and elevate your programming efficiency.
Enhance your skills with our comprehensive R Programming Course - join now!
Frequently Asked Questions
How to Print Dictionaries in Python?

To print a dictionary in Python, you can use the `print()` function, which displays the dictionary in a readable key-value format. This makes it easy to view its contents directly.
How to Declare a Dictionary in Python?

To declare a dictionary in Python, use curly braces `{}` to define key-value pairs separated by colons. For example, a dictionary is written as `my_dict = {'key': 'value'}`.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Programming Training, including Python Course, PHP Course, Python Django Training, R Programming Course and Visual Basic Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Phases of Compiler.
Our Programming & DevOps Blogs cover a range of topics related to Python, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your programming skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Programming & DevOps Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Python Course
Python Course
Thu 12th Jun 2025
Thu 7th Aug 2025
Thu 18th Sep 2025
Thu 27th Nov 2025
Thu 18th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


