We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +60 1800812339 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Business Analytics and Business Analysis may seem like two sides of the same coin, but they are, in fact, two distinct currencies in the realm of corporate strategy. But, what differentiates Business Analytics vs Business Analysis?
Business Analytics is akin to a time machine, delving into the vast sea of historical data to unearth trends and patterns that can forecast the trajectory of future business landscapes. On the flip side, Business Analysis acts as a master key to unlock the potential within business processes, meticulously evaluating and recommending enhancements to propel a business forward.
As highlighted in the 2020 Global State Of Enterprise Analytics report, a striking 45% of organisations are now harnessing the power of data and analytics to sculpt new business models. Given this situation, you can read this blog to explore differences between Business Analytics vs Business Analysis and how they improve the business.
Table of Contents
1) What is Business Analytics?
2) Scope of Business Analytics?
3) What is Business Analysis?
4) Scope of Business Analysis?
5) Differences between Business Analytics vs Business Analysis
6) Examples of Business Analysis and Business Analytics approach to a task
7) Conclusion
What is Business Analytics?
Business Analytics involves analysing current business data using various tools, techniques, and skills to derive valuable insights for improving business performance. It encompasses working with large volumes of relevant data and includes predictive modelling, quantitative analysis, and multivariate testing. It also involves utilising Business Analysis Tools to enhance decision-making processes.
Scope of Business Analytics
Business Analytics is used extensively in domains where employees have to work in close proximity to a lot of customer data, like in financial institutions or hospitals. It is also used in IT to improve business, products and services.
Some examples of how Business Analytics is used are discussed below:
a) Analysing many complaints (data) about the app to determine the root problem. This can give insights into the root cause of many complaints or problems.
b) Business Analytics can be used to figure out how many users are likely to cancel a subscription.
c) Using statistical methods to understand how future sales can be based on past sales data
General applications and use-cases of Business Analytics are as follows:
a) Supply chain optimisation
b) Detecting frauds based on past data and trends
c) Establishing a price or cost for a product or service
d) Making a dashboard to track and analyse performance metrics
e) Simulations will be conducted to investigate various scenarios.
f) Data will be used to uncover new patterns and trends in the relevant industries
Learn how to evaluate, validate, document, and manage requirements and get certified in Requirements Engineering with BCS Certificate In Requirements Engineering.
What is Business Analysis
Business Analysis is the discipline which involves bringing change at the organisational level to improve business or align it with a goal. A key aspect of Business Analysis is to facilitate communication and collaboration among different business units, ensuring that everyone involved has a shared understanding of goals and objectives. This discipline is not only about problem-solving but also about anticipating future needs and aligning strategies to meet evolving business demands..
Business Analysis Techniques can also help you understand the business world more comprehensively Crudely speaking, a Business Analyst is akin to a “mega-supervisor” who supervises the entire business or unit.
A typical Business Analysis process includes the following:
a) Requirement gathering or understanding the needs of stakeholders or customers.
b) Understand the business objectives and manage the stakeholders’ expectations.
c) Collaborate with various departments to complete the tasks set during the planning phase of a project.
d) Manage and use business data to derive helpful data that can improve business processes or projects.
e) Help or guide the implementation of solutions.
Understand the difference between business analytics vs business analysis to better strategize your business goals.
Scope of Business Analysis
The need for understanding the business and implementing better solutions is universal irrespective of the sector or the type of business. This makes Business Analysts compatible everywhere.
Some examples of how Business Analysis is used:
1) Proposing a business case analysis to outline the changes needed in the organisation or business.
2) Establishing a benchmark of product performance to compare all future performance against the benchmark.
3) Analysing competitors or rivals in the same sector, industry or market to better understand them. For a specific example, comparing the delivery price of the rival brand can help make better decisions in the interest of the business
Dive into the world of Business Analysis with our host of BCS accredited Business Analysis Courses and certifications.
Difference between Business Analytics vs Business Analysis
Business Analysis primarily focuses on the business process analysis, techniques and functions, whereas Business Analysts focus on the data and statistical analysis of the relevant data. While Business Analysis as a whole considers the broader aspects of an organisation, including its strategy, structure, and objectives, Business Process Analysis narrows its scope to the detailed study of workflows, tasks, and activities involved in achieving specific business goals. Here are some key differences between Business Analytics vs Business Analysis.
Focus and purpose
Business Analysis involves assessing the present state of a business, recognising areas for enhancement, and specifying requirements for implementing alterations. Its aim is to connect business requirements with technological solutions, ensuring alignment with organisational objectives.
Conversely, Business Analytics centers on examining data, uncovering insights, and forecasting future trends. Its emphasis lies in utilising data to enhance decision-making, refine processes, and achieve a competitive advantage. Business analytics offers organisations a data-centric strategy for unveiling patterns, correlations, and avenues for advancement.
Get ready for your interview with our top business analyst interview questions.
Data usage
While both fields rely on data, they differ in usage and scope. Business Analysis involves gathering and analysing diverse sources like customer feedback and internal processes, tailored to the organisation's operations.
On the other hand, Business Analytics covers a wider array of data sources, employing advanced tools to extract insights for data-driven decisions.
Role within the organisation
A Business Analyst acts as a bridge between business needs and technical solutions, engaging with a range of stakeholders including management, operations, IT, and customers. Their duties encompass defining business requirements, process mapping, and designing functional solutions to address identified issues. They drive organisational change, ensuring alignment with strategic goals and delivering value.
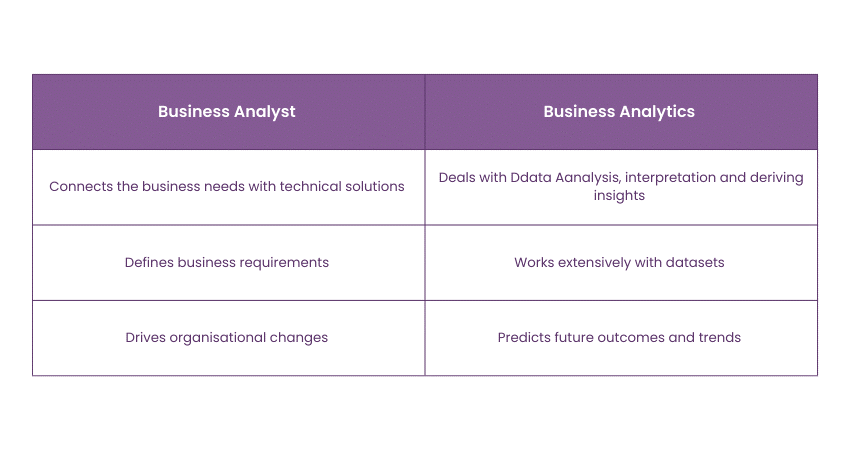
On the other hand, Business Analytics professionals primarily deal with Data Analysis, interpretation, and deriving insights. They work extensively with data sets, employing analytical models and tools to extract valuable information. Their focus lies in predicting future outcomes and trends, aiding organisations in anticipating market movements and customer behaviours a competitive edge and foster growth.
Outputs and deliverables
Business Analysis creates documents like business requirement documents, process models, and functional specifications, acting as guides for implementing changes and ensuring harmony between business needs and technology solutions.
Conversely, Business Analytics produces insights, reports, and visualisations aiding data-driven decision-making. This allows organisations to make informed choices and adapt to market shifts.
Dive into the Detailed Case Study of Business Analysis
Examples of Business Analysis and Business Analytics approach to a task
To better exemplify the distinction between Business Analysis and Business Analytics, let's delve into some specific instances.
Example 1: Addressing shopping cart abandonment for an e-commerce company
In tackling the challenge of shopping cart abandonment, a large ecommerce firm faces the need to uncover and address underlying reasons for customer drop-offs. Now, let's look at this from both the Business Analysis and Business Analytics approach:
a) Business Analysis approach: To uncover why customers abandon their shopping carts, a Business Analyst conducts customer interviews, analyses feedback, and collaborates with stakeholders like customer service, sales, and technical teams. They aim to understand the entire customer journey and pinpoint pain points causing drop-offs, suggesting solutions like simplifying checkout processes or adding trust indicators.
b) Business Analytics approach: On the other hand, a Business Analyst takes a data-centric approach, analysing like shopping cart abandonment rates and customer demographics using analytical tools. They aim to uncover recurring patterns or trends contributing to the problem, such as high abandonment rates on mobile devices or spikes during specific timeframes. With these insights, they propose data-driven solutions to address identified issues.
Example 2: Enhancing pricing strategy for a global retail chain
Let's consider a multinational retail corporation seeking to enhance its pricing strategy. Here, we have discussed both the Business Analytics and Business Analysis approach to this situation:
Business Analysis approach: Initially, a Business Analyst evaluates existing pricing strategies, analysing their effectiveness and factors influencing them. Upon gathering insights, they identify areas for improvement. For example, if pricing decisions heavily rely on cost-plus methods, they may recommend integrating value-based pricing. To address slow price adjustments to market changes, they might propose adopting more agile pricing strategies.
Business Analytics approach: A Business Analytics expert adopts a data-centric approach to refine the pricing strategy. By analysing historical sales data, customer purchase patterns, and pricing elasticity, they extract actionable insights. For example, their analysis might reveal products with lower price sensitivity, suggesting potential for price increases without significant sales declines.
Explore the Key Roles and Responsibilities of a Business Analyst Today!
Conclusion
Both Business Analytics and Business Analysis share the common goal of enhancing business operations. When the difference between Business Analytics vs Business Analysis is considered, Business Analytics is data-centric, delving into data to uncover insights, while Business Analysis zeroes in on business functions, employing various methods and techniques for improvement. Despite their differences, these disciplines often intersect and collaborate, contributing to the overarching aim of business optimisation.
Understand Business Analysis techniques and its practical application to business operations and flaunt your skills with BCS Certificate In Business Analysis Practice.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do Business Analysis and Business Analytics contribute to organisational success?

Business Analysis identifies areas for improvement, ensures effective communication, and drive organisational growth by optimising resources. Conversely, Business Analytics offers data-driven insights for strategic planning and operational efficiency. They empower decision-makers to respond to market changes and customer preferences.
How can organisations leverage Business Analysis and Business Analytics together?

Combining Business Analysis and Business Analytics enable organisations to maximise their data assets, streamline processes, and gain a competitive advantage. Business Analysis identifies improvement areas and suggests solutions, while Business Analytics offers data-driven insights for informed decision-making and strategic planning.
What are the other resources and offers provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is the Knowledge Pass, and how does it work?

The Knowledge Academy's Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are related courses and blogs provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Business Analysis Courses, including the BCS Certificate in Business Analysis Practice, BCS Foundation Certificate in Organisational Behaviour, and BCS Foundation Certificate in Business Analysis. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into the Benefits of Business Analysis.
Our Business Analysis Blogs cover a range of topics related to Business Analysis, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Business Analysis skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Business Analysis Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 BCS Certificate in Business Analysis Practice
BCS Certificate in Business Analysis Practice
Mon 17th Mar 2025
Mon 26th May 2025
Mon 1st Sep 2025
Mon 15th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


