We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +60 1800812339 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

In today’s fast-paced business environment, organisations constantly strive to stay ahead of the competition. As a result, they are turning to Agile. However, most organisations are still unaware of How to implement the Scaled Agile Framework.
As suggested in a survey by the University of Applied Sciences Koblenz on Status Quo, out of the organisations using SAFe worldwide, only 16 per cent of them reported that the improvement is more significant after applying the methodology.
Therefore, learning about effectively implementing SAFe will help you to enhance project delivery, collaboration, and customer satisfaction is crucial. Don’t know where to seek help from? Well, you need not scratch the surface anymore. Read this blog to understand How to Implement a Scaled Agile Framework for Your Organisation. Also, learn how to drive agility and success within your organisation.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe)
2) SAFe Implementation roadmap for organisational agility
3) How does SAFe function?
4) A brief comparison between SAFe and other Scaling Agile Frameworks
5) Reasons to Implement Scaled Agile Framework in your organisation
6) Conclusion
Understanding Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe)
Before discussing the implementation process, it is necessary to have an in-depth understanding of SAFe and scaled agile framework core values concepts. SAFe is a comprehensive framework that provides guidance on Scaling Agile principles and practices across multiple teams, departments, and even entire enterprises.
At its core, SAFe is based on the principles of Lean thinking and Agile Values. It embraces the idea of delivering value to customers quickly and frequently while also promoting collaboration, transparency, and continuous improvement.
Further, this Framework consists of three primary levels, each specifying roles, artifacts, and ceremonies to ensure effective coordination and alignment. These levels of SAFe are as follows
a) The Team level: Cross-functional teams work together to deliver value through short, iterative cycles known as iterations or Sprints.
b) The Program level: Multiple teams collaborate to deliver larger initiatives or projects, such as the Release Train Engineer (RTE) and Program Increment (PI) Planning.
c) The Portfolio level: Focuses on aligning the organisation’s strategic objectives with the Agile delivery of value.
SAFe Implementation Roadmap for Organisational Agility
Implementing the Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe) is a structured process that requires careful planning and execution. The following step-by-step guide will help you understand how to effectively Implement SAFe in your organisation and unlock the benefits of scaled agility:
Establishing a sense of urgency
The first step in Implementing SAFe is establishing a sense of urgency among employees and stakeholders. In simple terms, creating awareness about the need for organisational agility and the benefits of SAFe is key to driving the necessary momentum for change. Here’s what you can do:
a) Start by communicating the challenges that your organisation faces in the current business landscape.
b) Next, discuss market trends, evolving customer expectations, and competitive pressures that demand a more Agile and responsive approach.
c) Also, highlight the potential risks of not embracing agility, such as falling behind the competition or losing market share.
d) Further, demonstrate the competitive advantages and business opportunities of implementing SAFe.
e) Additionally, regularly communicate the urgency of implementing SAFe through various channels.
f) Emphasise the need for collective effort and the role that everyone can play in achieving organisational agility.
Defining the implementation strategy
A clear and powerful vision is essential for guiding the SAFe implementation. It should articulate the desired outcomes and benefits of Implementing SAFe in your organisation. Further, it should also align with the strategic objectives and priorities of the business. However, you need to consider the following while creating a vision:
a) Strategic alignment to the goal.
b) Embrace the core principles and values of Agile.
c) Clearly communicate the desired business outcomes.
d) Highlight the importance of delivering value to customers.
e) Acknowledge that SAFe Implementation is not just a process change but a transformative journey.
f) Promote a vision that fosters inclusivity and collaboration.
g) Incorporate the idea of continuous learning and improvement into the vision.
Moreover, once you have defined the vision, communicate it effectively to all employees. Also, revisit and reinforce the vision regularly, keeping it alive in employees’ minds.
Build Project Management proficiency with our Agile Project Management Foundation (AgilePM®) - start your Agile journey now!
Empowering employees
Empowering employees is a crucial step in effectively Implementing SAFe within your organisation. It helps create an environment that fosters ownership, collaboration, and innovation, leading to a successful SAFe Implementation. Here are key practices that you can follow to empower employees during the SAFe Implementation:
a) Offer comprehensive training programs to equip employees with the necessary skills and knowledge of Agile principles and SAFe practices. Ensure that the training is tailored to different roles within the organisation.
b) Foster a culture where individuals feel empowered to experiment, make independent choices, and take responsibility for their outcomes.
c) Implement collaborative tools and practices, including regular stand-up meetings, retrospectives, and other Agile ceremonies to promote collaboration.
d) Create forums for knowledge sharing, such as communities of practice, where employees can exchange ideas, best practices, and lessons learned.
e) Acknowledge and celebrate the achievements of individuals and teams as they progress in their SAFe journey. This recognition boosts morale and encourages further engagement.
f) Identify and address any organisational barriers that hinder employee empowerment.
g) Streamline processes, remove bureaucratic hurdles, and foster a supportive environment.
Understand the fundamentals concepts of Scrum and boost productivity with our Scrum Certification Training - join now!
Implement Agile practices
Effectively Implementing Agile practices enable teams to work collaboratively, deliver value iteratively, and respond to changing customer needs effectively. But How to Implement Agile appropriately? Well, here are key considerations when implementing Agile practices:
a) Organise teams into cross-functional units with a clear purpose and defined roles.
b) Implement Agile ceremonies such as daily stand-ups, Sprint planning, and retrospectives to facilitate collaboration and ensure alignment.
c) Embrace the iterative and incremental approach of Agile Methodologies by breaking down work into smaller, manageable units called iterations or Sprints.
d) Facilitate frequent integration of code changes and Automated Testing to ensure the continuous delivery of software increments.
e) Involve customers and stakeholders throughout development process to gain valuable insights and validate assumptions.
f) Utilise Agile planning techniques such as user stories, backlog prioritisation, and story point estimation to effectively manage and track work.
g) Monitor metrics such as velocity, lead time, and customer satisfaction to gauge the effectiveness of the implementation.
Implement ART and Value Stream Level practices
Implementing ART and Value Stream Level practices means ensuring alignment, coordination, and collaboration among teams to deliver value at scale. Here are key steps to effectively scale Agile Processes:
a) Create Agile Release Trains (ARTs), which are long-lived, cross-functional teams composed of multiple Agile teams. They help align and synchronise teams to deliver value at regular intervals, typically as Program Increments (PIs).
b) Clearly articulate a shared vision that aligns all teams within the ART. The vision should reflect the strategic objectives and provide a clear direction for implementation.
c) Create Communities of Practice (CoPs) to foster knowledge sharing, collaboration, and learning across teams. CoPs enable teams to exchange best practices, address common challenges, and drive continuous improvement.
d) Conduct regular PI Planning sessions where all teams within the ART can come together to plan and prioritise their work for the upcoming PI.
e) Implement communication and coordination mechanisms to ensure seamless collaboration among teams. Utilise Agile practices such as Scrum-of-Scrums.
f) Ensure that leaders are well-versed in Agile principles and practices and actively support the SAFe implementation.
g) Continuously monitor the progress of the implementation process and gather feedback from teams to identify areas for improvement and make necessary adjustments.
Expand to the Portfolio Level
Expanding the adoption of SAFe to the Portfolio Level is a significant milestone in achieving business agility and maximising the benefits of its Implementation. At the Portfolio Level, organisations align strategic initiatives, prioritise investments, and ensure the flow of value across Value Streams. Here are key considerations when expanding to the Portfolio Level:
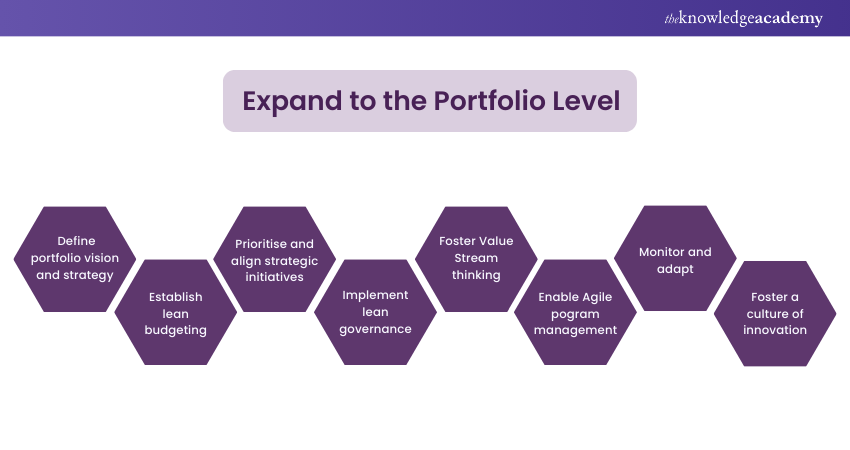
a) Align the Portfolio vision and strategy with the overall business strategy to ensure a cohesive approach.
b) Embrace a leaner, more dynamic approach to allocate budgets incrementally based on evolving priorities and actual progress.
c) Evaluate initiatives based on their alignment with the Portfolio vision, expected business value, market impact, and dependencies.
d) Establish governance boards or councils that provide guidance, oversight, and ensure compliance with organisational standards.
e) Foster collaboration and alignment across Value Streams to optimise the flow of value and minimise bottlenecks.
f) Implement large-scale coordination, cross-value stream planning, and dependency management to foster collaboration and optimise program outcomes.
Continuous improvement
Without ensuring improvement in the SAFe Implementation process, teams cannot determine its success. Therefore, continuous improvement is a fundamental principle of Implementing SAFe.
It involves an ongoing effort to identify areas for enhancement, make iterative changes, and drive incremental improvements. Here are a few key steps to facilitate continuous improvement:
a) Encourage individuals to continuously upgrade their skills, share knowledge with others, and seek feedback for personal and professional growth.
b) Implement feedback loops and retrospectives at various levels within the organisation to reflect on past iterations and identify areas for improvement.
c) Define relevant metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to measure the success of the SAFe implementation. Utilise the data derived to make informed decisions, identify bottlenecks, and drive targeted improvements.
d) Implement small-scale changes or pilots to test hypotheses. Also, gather data to create an environment where teams feel safe to try new approaches, learn from the results, and iterate.
e) Foster a sense of collective ownership and encourage teams to support each other in their continuous improvement efforts.
f) Provide support and resources to enable teams to implement changes and address impediments.
g) Acknowledge teams and individuals who have made significant contributions to continuous improvement.
A brief comparison between SAFe and other Scaling Agile Frameworks
There are other Scaling Agile Frameworks that are also used by organisations other than SAFe. So, let’s discuss how these Scaling Frameworks are different from SAFe:
a) SAFe vs Scrum@Scale:
Refer to the following table to understand the difference between SAFe and Scrum@Scale:
|
Feature |
SAFe |
Scrum@Scale |
|
Primary scale of application |
Preferred by large organisations |
Not preferred by largesmall organisations |
|
Main principles used |
Lean-Agile principles |
Scrum principles |
|
Main roles |
Numerous specific roles |
Scrum roles, but scaled up |
|
Complexity |
Implement, it is quite complex and requires significant change |
It is relatively lex complex to implement |
|
Focus |
Focuses on aligning the entire company |
Focuses on scalable Scrum practices |
|
Customisation |
Cannot be customised entirely |
Can be customised according to organisational needs |
b) SAFe vs Large-Scale Scrum (LeSS):
Refer to the following table to understand the difference between SAFe vs Large-Scale Scrum (LeSS):
|
Feature |
SAFe |
LeSS |
|
Focus |
Aligns the entire organisation, especially large enterprises |
Simplifies and scales Scrum for larger teams |
|
Framework |
Highly structured |
Minimalist framework |
|
Complexity |
Complex |
Less complex |
|
Implementation |
Requires significant organisational changes |
Easier to adopt in Scrum teams |
|
Suitable for |
Larger organisations |
Medium to large organisations |
|
Scaling approach |
Top-down, generally hierarchical |
Bottom-up, generally organic |
c) SAFe vs Spotify model:
Refer to the following table to understand the difference between SAFe and Spotify models:
|
Feature |
SAFe |
Spotify model |
|
Framework |
Highly structured |
Less structured |
|
Scaling approach |
Perspective |
Organic |
|
Focus |
Aligns entire enterprise with Agile strategy |
Focuses more on culture and team empowerment
|
|
Governance |
More centralised |
Decentralised |
|
Cultural aspect |
Process-oriented |
Emphasises Agile culture |
|
Size |
Suited for very large organisations |
Suitable for various organisations |
|
Change management |
Top-down implementation |
Bottom-up implementation |
Reasons to Implement Scaled Agile Framework in your organisation
Even after learning How to Implement Scaled Agile Framework, you might be wondering what if you do not Implement the Framework properly? Worry no more. The following are some of the key factors to consider when Implementing SAFe:
a) SAFe helps in team alignment. There are many organisations that struggle to ensure that all the teams that are working on the same project, whether it be from the same or different departments, are dedicated towards the common goal. SAFe can help those organisations maintain a seamless collaboration.
b) SAFe helps in proper team planning so that organisations can tackle even the most complex agile challenges. It offers a solution by helping the organisations form Program Increment or PI planning.
c) If an organisation is struggling to provide enterprise-wide visibility, SAFe provides solutions to connect different backlogs. This helps them connect to the Kanban teams and provides enterprise-wide visibility.
d) If a business is struggling to handle complex and large-scale projects, it is necessary that the implementation of SAFe should be considered. It helps to handle and manage complex and large-scale projects which involve multiple teams efficiently.
e) SAFe helps maintain and improve the quality and productivity of teams. SAFe can be implemented here for continuous improvements, built-in quality practices and regular iteration.
Conclusion
Gaining a deep understanding of How to Implement Scaled Agile Framework can significantly benefit your organisation. It can enable you to effectively respond to market demands, deliver value, and foster a culture of collaboration and innovation. As a result, you can set your organisation on a path towards agility and success.
Frequently Asked Questions

SAFe Implementation Roadmap can be referred to as an overview graphic and a 12- article series which describes a strategy. It also consists of an ordered set of activities which are effective in implementing SAFe.

Before you Implement SAFe in an organisation, you need to recognise the development and operational value streams. This development Value Stream will help the organisation in building new products and the operational value stream will help the customers communicate with that organisation.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Agile courses, including Certified SAFe® Product Manager, Certified Scaled Agile Framework Leading SAFe® 6.0 Training and Exam, and Agile Project Management Foundation & Practitioner. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Agile methodologies.
Our Agile blogs covers a range of topics related toAgile, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Agile skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Project Management Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Certified Scaled Agile Framework Leading SAFe® 6.0 Training and Exam
Certified Scaled Agile Framework Leading SAFe® 6.0 Training and Exam
Thu 16th Jan 2025
Thu 22nd May 2025
Thu 24th Jul 2025
Thu 25th Sep 2025
Thu 20th Nov 2025
Thu 11th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


