We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +60 1800812339 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

ISO 22000 and ISO 9001 are the Quality Management Standard to control the internal Quality Management that can be used by many types of industries. They often provoke confusion due to their similar numerical designations and structural resemblances. However, a closer examination reveals that they serve different purposes and cater to distinct industries, making it crucial to grasp their disparities. ISO 9001 is the globally acclaimed standard for Quality Management Systems (QMS). It operates as a compass for organisations, ensuring they consistently meet customer expectations and regulatory requirements while striving to enhance customer satisfaction.
In contrast, ISO 22000 specialises in Food Safety Management Systems (FSMS), acting as a shield in the intricate web of the food supply chain, where safety is paramount. This blog will focus on ISO 9001 and ISO 22000, unravelling the key differences that make each standard uniquely suited to its designated domain.
Table of Contents
1) ISO 9001: Quality Management System
2) ISO 22000: Food Safety Management Systems
3) Key Differences Between ISO 22000 and ISO 9001
a) Focus and Objectives
b) Industry Specificity
c) Risk Management
d) Documentation
4) Conclusion
ISO 9001: Quality Management System
ISO 9001 is a universally recognised beacon of excellence in Quality Management Systems (QMS) emphasising the difference of ISO 9000 vs 9001. Its overarching purpose is to guide organisations in pursuing an unwavering commitment to quality and continuous improvement. With a comprehensive scope, ISO 9001 strives to ensure that businesses consistently meet customer expectations and stringent regulatory ISO 9001 Requirements.
This standard fosters a culture of excellence, emphasising the significance of customer satisfaction as the ultimate goal. Whether a manufacturing facility producing intricate machinery or a service-oriented company delivering impeccable customer support, ISO 9001 provides a robust framework for enhancing organisational efficiency and product or service quality.
Key requirements
ISO 9001 encompasses a set of key requirements, along with relevant ISO 9001 audit and the ISO 9001 Audit Checklist to ensure compliance and continuous improvement. These requirements encompass various facets of an organisation's operations, ensuring a holistic approach to quality:
a) Quality Policy and Objectives: ISO 9001 mandates the establishment of a clear quality policy and objectives, aligning the organisation's direction with a commitment to quality excellence.
b) Process Approach: Organisations must adopt a process-oriented mindset, emphasising the importance of identifying, documenting, and optimising their key processes to achieve efficiency and consistency.
c) Resource Management: Efficiently managing resources—both human and material—is vital. ISO 9001 encourages organisations to allocate resources effectively to meet quality objectives.
d) Continuous Improvement: Continuous improvement is at the core of ISO 9001. It requires organisations to implement processes for ongoing evaluation, corrective actions, and continual enhancement.
e) Monitoring and Measurement: Regular observation and measurement of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) ensure that organisations can keep track of their progress, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions in enhancing their QMS.
ISO 22000: Food Safety Management Systems
ISO 22000 is a specialised standard meticulously crafted to address the unique complexities of the food industry. Its primary purpose is to safeguard public health by verifying the safety of food products in the entire food supply chain. In an age where food safety is paramount, ISO 22000 is a robust framework that spans from the farm to the consumer's plate. Its scope covers food production, processing, packaging, distribution, and even the food services industry.
ISO 22000 aims to provide consumers with confidence in the safety of their food. By implementing these ISO Quality Standards, organisations within the food industry aim to mitigate and eliminate potential hazards, reduce foodborne illnesses, and uphold the highest standards of food safety
Key Requirements
ISO 22000 lays out a comprehensive set of key requirements that are essential for establishing an effective Food Safety Management Systems (FSMS):
a) Interactive Communication: Effective communication is the backbone of ISO 22000. Organisations must establish clear lines of communication within the food supply chain to ensure that relevant safety information is exchanged promptly and accurately.
b) Prerequisite Programs: ISO 22000 places significant importance on implementing prerequisite programs. These fundamental hygiene and safety practices serve as a foundation for food safety. Examples include sanitation, pest control, and employee hygiene.
c) HACCP: ISO 22000 incorporates the principles of hazard analysis and critical control points (HACCP), which involves identifying and assessing potential food safety hazards at every stage of the food supply chain. By doing so, organisations can determine critical control points and implement measures to manage and mitigate these risks effectively.
d) Management System: Similar to ISO 9001, ISO 22000 requires establishing a comprehensive management system that includes documented policies, procedures, and objectives related to food safety.
e) Verification and Improvement: ISO 22000 necessitates regular proof of the FSMS's effectiveness through internal audits, validation, and verification activities. Based on performance data and feedback, organisations are encouraged to improve their FSMS continually.
Enhance your team’s expertise and drive continuous improvement with our ISO 22000 Training – sign up now!
Key Differences Between ISO 22000 and ISO 9001
Let us go over the Key Differences of ISO 9001 and ISO 22000:
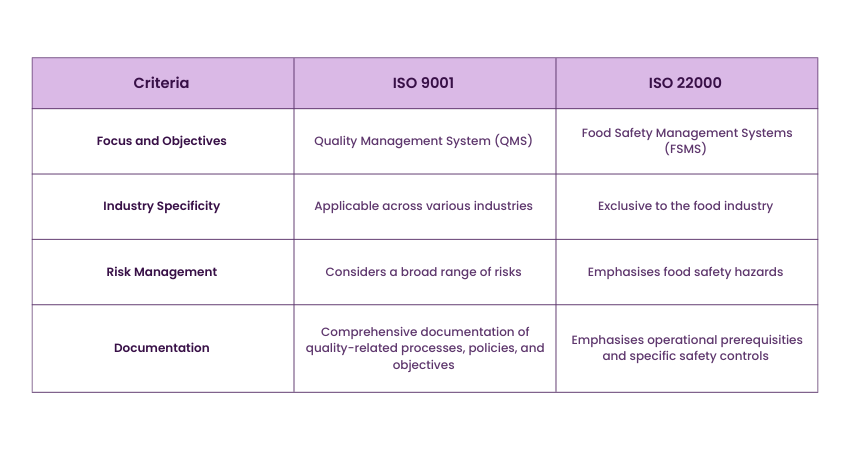
1) Focus and Objectives
The primary and most conspicuous difference between ISO 9001 and ISO 22000 lies in their focus and overarching objectives.
ISO 9001 can be described as a Quality Management System (QMS) and is designed to enhance overall quality across various industries. Its central goal is to ensure that organisations consistently meet customer expectations and regulatory requirements, strongly emphasising improving customer satisfaction. ISO 9001 acts as a compass for organisations seeking to achieve excellence in their products or services, fostering a culture of continuous improvement. Recognising the Benefits of ISO 9001, like better quality control and efficiency, is crucial for maximizing the standard's value.
ISO 22000, conversely, zooms in on Food Safety Management Systems (FSMS) and is specifically tailored to the food industry. While quality is essential in food production, ISO 22000's paramount objective is to guarantee the safety of food products in the total food supply chain. This standard is all about mitigating food safety hazards, reducing foodborne illnesses, and ensuring consumers build trust in their food.
Master ISO 9001 Foundations for quality excellence with our ISO 9001 Foundation Course – join now!
2) Industry Specificity
Another fundamental difference is the industry to which each standard is applied.
ISO 9001 is exceptionally versatile and can be implemented across various industries, including manufacturing, services, healthcare, and more. Its quality management ISO 9001 Principles are applicable wherever there is a need for consistent processes, customer satisfaction, and continual improvement.
ISO 22000, in stark contrast, is industry-specific and exclusively targets the food industry. This includes food production, processing, packaging, distribution, and even food services such as restaurants and catering companies. The specificity of ISO 22000 ensures it addresses unique challenges and risks associated with the food supply chain, making it indispensable.
3) Risk Management
ISO 22000 places a more pronounced emphasis on Risk Management, particularly concerning food safety hazards. It integrates the principles of Hazard Analysis Critical Control Points (HACCP) to identify, assess, and control potential hazards within the food supply chain. This proactive approach allows food organisations to prevent and mitigate risks that could lead to foodborne illnesses, ensuring food safety.
ISO 9001, while considering risks as part of its approach, delves less into hazard-specific Risk Management. Instead, it focuses on a broader range of risks organisations may encounter while striving for overall quality and customer satisfaction. The ISO 9001:2015 Monitoring and Measurement Procedure supports this by ensuring that quality and performance are consistently evaluated and improved.
4) Documentation
Documentation requirements also differ between ISO 9001 and ISO 22000.
ISO 9001 mandates comprehensive documentation of quality-related processes, policies, and objectives Emphasising the critical role that meticulous ISO 9001 Documentation plays in ensuring adherence to established standards and facilitating continuous improvement. This document is crucial for establishing a structured QMS and ensuring everyone acknowledges their roles and responsibilities in achieving quality goals.
ISO 22000, while still requiring documentation, places a more significant emphasis on operational prerequisites and specific safety controls within the food supply chain. This includes documenting procedures related to food safety hazards, prerequisite programs, and critical control points, ensuring a rigorous approach to food safety.
Become an Expert ISO 9001 Internal Auditor with our ISO 9001 Internal Auditor Training – sign up now!
Conclusion
While ISO 9001 and ISO 22000 share numerical similarities, they serve divergent purposes. ISO 9001 centres on enhancing quality and customer satisfaction across industries, while ISO 22000 prioritises food safety within the food supply chain. Choosing wisely to align your organisation's goals and industry focus with the appropriate excellence and safety standards can result in positive outcomes.
Excel as an ISO 9001 Lead Auditor with our ISO 9001 Certification Course– join today!
Frequently Asked Questions

ISO 22000's pillars include interactive communication, system management, Prerequisite Programs (PRPs), and the Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) principles, ensuring comprehensive Food Safety Management.

The 7 clauses of ISO 9001 are Context of the Organisation, Leadership, Planning, Support, Operation, Performance Evaluation, and Improvement, guiding organisations in achieving quality management.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various ISO 9001 Certifications, including the ISO 9001 Foundation Course, ISO 9001 Lead Auditor Course, and ISO 9001 Internal Auditor Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into ISO 9001 Principles.
Our Business Improvement Blogs cover a range of topics related to ISO 9001 Frameworks, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Business Improvement skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Health & Safety Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 ISO 9001 Foundation course
ISO 9001 Foundation course
Mon 10th Feb 2025
Mon 7th Apr 2025
Mon 2nd Jun 2025
Mon 11th Aug 2025
Mon 13th Oct 2025
Mon 8th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


