We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +60 1800812339 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

"What is Photography?" At its essence, photography is a beautiful fusion of art and science. It captures fleeting moments and transforms them into timeless stories. Unlike traditional art forms that start with a blank canvas, photography begins with the rich tapestry of reality, allowing photographers to shape and express their unique visions.
A perfect photograph doesn’t just freeze a moment in time; it immortalises it, creating a lasting memory filled with visual eloquence. In this blog, we’ll answer the question "What is Photography?" and how photographers capture not just moments but emotions, stories, and diverse perspectives.
Table of Contents
1) What is Photography?
2) A Brief History of Photography
3) What is Photography Used for?
4) Essential Gear for Photography Beginners
5) Photography Composition Techniques
6) What is Photography Lighting?
7) Benefits of Learning Photography
8) Practical Application of Photography Skills
9) Conclusion
What is Photography?
Photography is the art and practice of capturing images using light. It involves using a camera to record moments, scenes, or subjects, either digitally or on film. Here are some key aspects of Photography:
1) Light: The fundamental element of Photography. The word itself comes from Greek, meaning “drawing with light.”
2) Camera: A device that captures light and records images. Cameras can be digital or film-based.
3) Lens: A crucial part of the camera that focuses light onto the sensor or film.
4) Composition: The arrangement of elements within a photograph. Good composition can make a photo more engaging and visually appealing.
5) Exposure: The amount of light that reaches the camera sensor or film. It is controlled by the aperture, shutter speed, and ISO settings.
6) Post-processing: Editing the captured images to enhance or alter them. This can be done using software like Adobe Photoshop or Lightroom.
Photography can be used for various purposes, including art, documentation, journalism, and personal expression. Whether you’re capturing a stunning landscape, a candid moment, or a portrait, Photography allows you to tell stories and preserve memories.
A Modern Canvas
Before Photography, artists endeavoured to capture reality or interpret their surroundings through paintings, sculptures, and drawings. These traditional mediums required a significant amount of time, skill, and interpretation. With the advent of the camera, artists found a new canvas, one that could instantaneously record reality with precision. This shift highlighted vision over handcraft in capturing unique perspectives.

Manipulating Reality
While a Photograph is often seen as a faithful representation of reality, it's also an avenue for surreal and altered perceptions. Techniques like double exposures and post-processing let Photographers blur the lines between reality and imagination. This transformation of the 'real' into the 'surreal' bridges Photography with traditional art forms were abstraction and interpretation reign supreme.
Evolving Genres
As the camera evolved, so did the genres of Photographic art. Portrait Photography delved deep into capturing the essence of a person, while landscape Photography aimed to encapsulate the grandeur of nature. Furthermore, abstract Photography allowed for freeform expression, playing with light, shadow, and form in ways reminiscent of abstract painting.
These genres, and countless others, have solidified Photography's place in art, demonstrating its versatility and depth.
A Brief History of Photography
Here’s a roadmap to explore the evolution and impact of photography, focusing on the transition from black and white to color photography:
Roadmap for Exploring the Evolution of Photography
1) Introduction to Photography
a) Brief overview of photography’s origins and its significance as an art form.
b) Introduction to early black and white photography.
2) The Rise of Color Photography
a) 1930s: Introduction of Kodachrome by Eastman Kodak.
b) Impact of Kodachrome on the accessibility and popularity of color photography.
3) Early Experiments in Color Photography
a) Exploration of pioneering photographers and their techniques for capturing color images before Kodachrome.
b) Highlight notable early color photographs from the 1800s and early 1900s.
4) Technological Advancements
a) Development of color film and its evolution over the decades.
b) Introduction of digital photography and its impact on color imaging.
5) Influential Figures in Photography
a) Profiles of key innovators and photographers who pushed the boundaries of the medium.
b) Contributions of these individuals to the art and science of photography.
6) Modern Photography
a) The role of digital technology in making photography more accessible.
b) Current trends and innovations in photography.
7) Exploring Historical Galleries
a) Recommendations for galleries and collections showcasing early color photographs.
b) Encouragement to explore these visual histories to appreciate the evolution of photography.
Capture the world through lens and elevate your photography skills with our Photography Course Join today!
What is Photography Used for?
Photography, over its storied history, has been utilised for numerous purposes, reflecting the multifaceted nature of the medium. Whether it's chronicling personal milestones or influencing global perceptions, the camera serves as a powerful tool in various spheres of life.
Documenting Moments
At the heart of Photography lies the simple act of documenting. Cameras turn milestones, like a child's first steps or a wedding day, into lasting memories. These personal keepsakes serve as visual diaries, helping individuals and families revisit and cherish moments of the long past.
Journalistic Endeavours
Photography's impact isn't just limited to personal spheres. Photojournalism brings stories to life, chronicling events and offering visual testimony to moments that shape history. From war zones to historic events, Photojournalism offers a tangible, unfiltered view of global narratives.
Commercial Uses
In the business realm, Photography plays an indispensable role. Companies leverage high-quality images to showcase their products, creating appealing visuals that boost sales and establish brand identity. Fashion, food, product, and real estate Photography are just a few domains where a well-captured Photo can significantly impact consumer perceptions and decisions.
Educational and Scientific Documentation
The world of academia and research, too, benefits immensely from Photography. Documenting experiments, recording phenomena, or capturing species in the wild, Photographs aid in illustrating concepts, facilitating learning, and corroborating scientific claims. This visual evidence serves as a cornerstone in many academic and scientific endeavours.
Promoting Change
Beyond commerce and documentation, Photography has the profound power to incite change. Social activism and advocacy often employ powerful images to spotlight issues, generating awareness and galvanising action. From highlighting the plight of refugees to bringing attention to environmental degradation, Photography stands as a potent tool in the hands of change-makers.
Essential Gear for Photography Beginners
Starting with the basics can make photography much more approachable. Here’s a deeper dive into the essential gear every budding photographer should consider:
Camera: The Heart of Photography
Every Photographer's primary tool is the camera. But which one to choose?
1) Smartphones: Many contemporary smartphones boast impressive camera capabilities. For those on a tight budget or keen on mobile Photography, they can serve as a practical starting point.
2) Point-and-shoot Cameras: Compact and user-friendly, these cameras are an upgrade from smartphones. They often offer better optical zoom and image quality without the complications of interchangeable lenses.
3) DSLR/Mirrorless Cameras: For those ready to invest more, entry-level DSLRs or mirrorless cameras provide greater control, enhanced image quality, and lens flexibility.
Lenses: Seeing Through Different Perspective
For interchangeable lens cameras, the lens plays a pivotal role in how you capture the world.
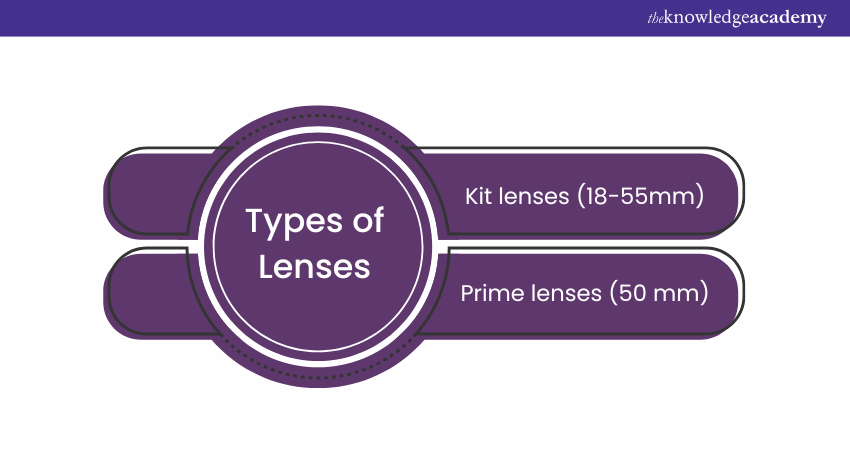
1) Kit Lenses - Typically ranging from 18-55mm, they're versatile enough for various scenarios like landscapes, portraits, and general Photography.
2) Prime Lenses - With fixed focal lengths, such as 50mm, they deliver sharper images and better low-light performance, ideal for achieving smooth background blur (bokeh).
Tripod: stability and Precision
While it might seem like an accessory, a tripod is essential. From capturing landscapes during the golden hour to trying long exposure shots of cityscapes or starry nights, a tripod ensures sharp, blur-free images.
Camera bag: Safety and Organisation
A beginner might overlook the significance of a camera bag, but as you accumulate gear, you’ll appreciate having a dedicated space. Apart from protection against physical damage, it also offers organisation, ensuring lenses and other accessories are always within arm's reach.
Editing Software: Perfecting the Final Image
The magic of Photography doesn't end after pressing the shutter. Post-processing allows Photographers to enhance, correct, or artistically alter their Photos. Beginners can start with free software like GIMP or invest in popular options like Adobe Lightroom for more advanced capabilities.
Discover your passions and deepen your skills with our range of Hobbies and Interests Courses . Explore now!
Photography Composition Techniques
Effective composition can transform an image, adding depth, emotion, and intrigue. Delving deeper into these techniques provides a clearer understanding.
Rule of Thirds: Balanced Framing
Divide your frame into a 3x3 grid. By positioning subjects at the intersections or along these lines, Photos become balanced. It creates visual interest and can make images more engaging, preventing central, predictable placements.
Leading Lines: Guiding the Viewer
Lines naturally pull the viewer's gaze in a particular direction. Whether it's a winding road, a row of trees, or architectural details, they lead the viewer's eye. This technique organically guides attention, emphasising the Photo's primary subject or showcasing depth and perspective.
Framing: Highlighting the Subject
Using objects or elements to surround your main subject creates a natural 'frame'. Trees, arches, windows, or even shadows can work. It helps to focus the viewer's attention directly on the framed subject, offering context and increasing the subject's prominence.
Symmetry: Creating Harmony
Symmetry provides a sense of balance, making Photos pleasing to the eye. Whether it's a building's reflection in still water or a butterfly's wings, symmetry can evoke feelings of stability, harmony, and order, making images captivating.
Depth: Layered Storytelling
By incorporating elements in the foreground, midground, and background, images attain depth. This layering not only gives Photos a three-dimensional feel but also tells a richer story, providing context and a sense of place.
Negative Space: Simplifying the Scene
Utilise empty or uncluttered spaces in an image to emphasise the primary subject. Negative space provides breathing room, reduces distractions, and can evoke powerful emotions, from loneliness to the vastness of a scene.
Patterns and Textures: Adding Intrigue
Repetitive patterns and diverse textures capture attention. The predictability of patterns can be soothing, while breaking these patterns can be striking. Textures, whether rough tree bark or smooth water ripples, add tactile depth.
Fill the Frame: Emphasising Details
By moving closer or zooming in, distractions are minimised. This technique highlights finer details, textures, and nuances, offering an intimate look at subjects, from portraits to macro-Photography.
Juxtaposition: Telling Contrast Stories
Place opposing or contrasting elements together. This unexpected combination can create surprise, telling visual stories of difference or highlighting the uniqueness of each element within the frame.
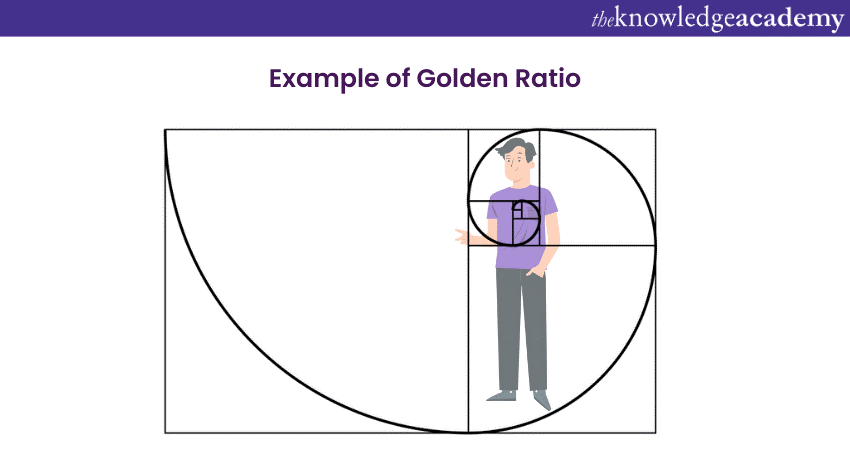
Golden Ratio: Beyond the Thirds
An ancient mathematical concept, the Golden Ratio (or Phi) is roughly 1.618 to 1. The frame is split into a spiral based on this ratio. Placing subjects along this spiral creates compelling, harmonious compositions, offering an alternative to the Rule of Thirds.
What is Photography lighting?
In the world of Photography, light is the invisible brush that paints the image. It's the foundational element that can elevate an ordinary scene into a masterpiece or diminish a compelling subject into obscurity. Delving into the essence of Photography lighting reveals its nuanced complexities and its profound impact on the final image.
Natural vs. Artificial Light
At its core, Photography lighting can be divided into two primary categories: Natural and artificial.
Natural light emanates from the sun and encompasses the golden warmth of a sunset or the soft, diffused glow on an overcast day. It's unpredictable and ever-changing, making it both a challenge and a delight for Photographers. Shooting in natural light demands adaptability but offers unparalleled authenticity and mood.
Artificial light, on the other hand, encompasses studio lights, flash units, and other man-made light sources. The primary advantage here is control. Photographers can manipulate the direction, intensity, and colour of artificial light to craft a scene meticulously.
Direction and Quality of Light
The direction from which light hits the subject plays a pivotal role in shaping the image's mood and depth. Front lighting illuminates the subject head-on, reducing shadows and often giving a flat appearance. Side lighting emphasises textures and contours, while back lighting can create silhouettes or a halo effect around subjects.
Beyond direction, the quality of light—whether it's hard or soft—impacts the image. Hard light results in sharp, defined shadows and is often seen on bright sunny days or with unmodified artificial lights. Soft light, conversely, produces gentle, gradual shadows, often achieved with diffusers or during the 'golden hour' just after sunrise and before sunset.
Colour Temperature
Every light source has a colour temperature, usually measured in Kelvins (K). This spectrum ranges from the warm, reddish tones of a candle to the cool, blueish hues of a clear sky. Adjusting for colour temperature ensures Photos retain true colours or match the Photographer's vision.
Light Modifiers
The world of artificial lighting is expansive, with a plethora of tools and accessories designed to modify and shape light. Soft Boxes, reflectors, umbrellas, and grids are just a few. These modifiers allow Photographers to achieve specific effects, softening harsh lights, redirecting beams, or concentrating light on certain areas.
Benefits of Learning Photography
Learning photography offers a wide range of benefits, from personal enrichment to professional advancement.
Personal Growth and Development:
a) Creativity: Enhance your creativity and explore new forms of expression through photography.
b) Perspective: Gain a new perspective on the world, appreciating the beauty and intricacy of daily life.
c) Connections: Forge meaningful connections with others by sharing your visual stories.
Professional Development:
a) Career Skills: Strong photography skills are valuable in fields like marketing, advertising, and any profession that relies on visual communication.
b) Effective Messaging: Photographs are crucial for effectively communicating messages and ideas, helping businesses engage with their audience.
Additional Benefits:
a) Stress Relief: Photography can be a relaxing and therapeutic activity, providing a break from daily stress.
b) Memory Preservation: Capture and preserve important moments and memories.
c) Technical Skills: Learn and master technical skills related to camera operation, lighting, and editing.
d) Portfolio Building: Create a portfolio that showcases your work, which can be useful for personal satisfaction or professional opportunities.
Practical Applications of Photography Skills
Photography skills have a wide range of practical applications, making them valuable in both professional and personal contexts.
Business and Marketing:
a) Product Photography: High-quality images of products can make them more appealing and help businesses stand out in a competitive market.
b) Event Documentation: Capturing events can create engaging and memorable content for marketing purposes.
c) Branding: Effective use of photography can enhance a brand’s image and communicate its values to the audience.
Journalism and Documentary:
a) Capturing Events: Photography plays a crucial role in journalism, documenting significant events around the world.
b) Storytelling: Renowned photographers like Margaret Bourke-White and Robert Capa have used their skills to tell powerful stories, often in challenging and dangerous situations.
c) Insight into Human Experience: Through their work, photographers provide profound insights into various aspects of the human experience, from wars to natural disasters.
Preserving Memories:
a) Personal Milestones: Photography helps capture and preserve cherished moments with loved ones, such as holidays, birthdays, and special occasions.
b) Family History: Photos create a visual record of our lives, becoming treasured keepsakes that can be shared with future generations.
c) Strengthening Bonds: By documenting and sharing these moments, photography helps strengthen family bonds and fosters a sense of shared history.
Conclusion
“What is Photography?” is more than just a question—it’s an invitation to embark on a journey of discovery and expression. Each step, from understanding its essence to mastering its techniques, shapes a photographer’s unique vision. As an art form, photography offers boundless opportunities to explore and challenge oneself. Through the lens, moments, emotions, and stories come to life, creating a vivid tapestry of human experience.
Unleash the experience of film making and editing with our Filmmaking Course Sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions

In photography, the technical and creative aspects are intertwined. Each camera setting you choose is essentially an artistic decision. Your grasp of photography and your potential for artistic expression will greatly expand once you understand how your camera functions.

The main equipment's that are needed as a beginner are as follow:
a) Camera
b) Lens
c) Processing Software
d) Tripod Stand
e) Cleaning Kit
f) Batteries
These are the main basic equipments that are needed as a beginner to start and enhance your photography skills.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Hobbies & Interest, including the Filmmaking and Practitioner Course, and the Photography Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Photographer Job Description.
Our Business Skill Blogs cover a range of topics related to Photography, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Photography skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course




 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


