We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203 999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Are you struggling to understand the differences between Cost Accounting and Financial Accounting? These two key accounting practices play vital roles in managing a business’s financial health, yet they serve different purposes.
In this blog, we’ll explore the differences between Cost Accounting and Financial Accounting in detail. This will help you grasp how they impact your business strategy. Keep reading to learn which one is right for your company!
Table of Contents
1) What is Cost Accounting?
2) What is Financial Accounting?
3) Key Difference Between Cost Accounting and Financial Accounting
4) Similarities Between Cost and Financial Accounting
5) Conclusion
What is Cost Accounting?
Cost Accounting helps businesses understand about their production costs to support management’s decision-making. It gathers, analyses, and categorises data to optimise resource allocation, set pricing strategies, and manage expenses.
This thorough system depends on numerical data. It carefully examines every transaction, resource, and cost element to assess the cost-efficiency of various business activities. Key Features of Cost Accounting include:
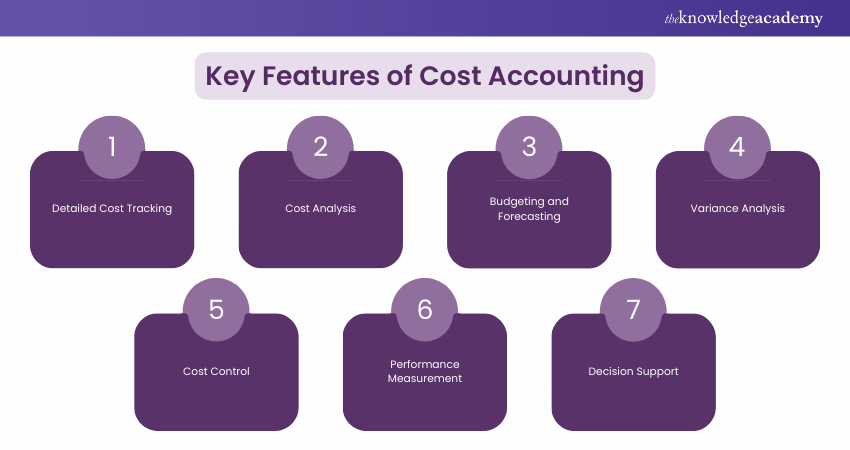
1) Detailed Cost Tracking:
Keeps track of all manufacturing costs, including materials, labour, and overhead.
2) Cost Analysis:
Breaks down costs to find inefficiencies and opportunities to save money.
3) Budgeting and Forecasting:
Helps create budgets and predict future costs for better financial planning.
4) Variance Analysis:
Compares actual expenses to budgeted ones to spot and explain differences.
5) Cost Control:
Puts measures in place to manage and reduce expenses, ensuring resources are used efficiently.
6) Performance Measurement:
Assesses how cost-effective different departments, processes, and products are.
7) Decision Support:
Provides detailed cost information to help with strategic decisions like pricing, outsourcing, and investments.
What is Financial Accounting?
Financial Accounting involves the collection, recording, summarisation, and reporting of business transactions to provide a clear picture of a company’s financial performance and position to external stakeholders. Here are the key elements:
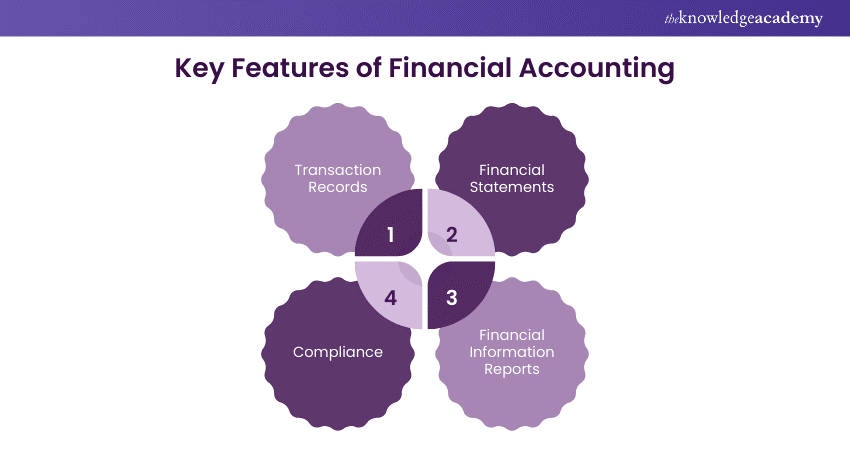
1) Transaction Records:
Detailed records of daily transactions over a fiscal year, including sales, purchases, investments, and expenses.
2) Financial Statements:
Specific information about the company’s financial status and performance.
a) Balance Sheet: Insights into assets, liabilities, and shareholder’s equity at a specific time.
b) Income Statement: Revenues, costs, and expenses over a period, indicating profit or loss.
c) Cash Flow Statement: Cash generated or used in operating, investing, and financing activities, showing cash management.
3) Financial Information Reports:
Data for decision-making, such as investing, granting loans, setting policies, or determining taxes.
4) Compliance:
Ensures consistent and transparent practices for easier comparisons between companies and industries.
Financial Accounting provides valuable information for decision-making. However, it mainly focuses on past performance and does not predict future outcomes.
Become a successful manager with our Introduction to Management Course – Register now!
Key Difference Between Cost Accounting and Financial Accounting
There are many differences between Cost Accounting and Financial Accounting. Some of them are mentioned below:
1) Scope
Financial Accounting analyse the entire business and provides an overall picture of the financial health. It summarises financial transactions and prepare financial statements for external stakeholders like investors, creditors, and regulatory bodies.
Cost Accounting focuses on specific activities or processes, analysing the costs associated with products, departments, or projects. It is mainly used for internal decision-making to improve efficiency and cost control.
2) Categories of Costs Recorded
Financial Accounting records all business financial transactions, including revenues, expenses, assets, and liabilities. It adheres to standardised principles like GAAP or IFRS2.
Cost Accounting records costs related to the production process, including materials, labour, and overhead. It can use both historical and pre-determined costs to provide detailed insights into cost management.
3) Information
Financial Accounting provides information in monetary terms. It focuses on the financial performance and position of the entire business.
Cost Accounting provides detailed information on the costs incurred in specific areas of the business. It helps management make informed decisions about pricing, budgeting, and operational efficiency.
4) Objective
Financial Accounting's main objective is to offer an accurate financial picture to external parties. This will ensure transparency and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Cost Accounting helps internal management in controlling and reducing costs. This improves the efficiency and profitability of business operations.
5) Forecasting Capability
Financial Accounting typically does not involve forecasting. It focuses on historical data to prepare financial statements.
Cost Accounting frequently involves forecasting and budgeting to predict future costs and plan accordingly. This helps in making strategic decisions to optimise resources.
6) Stock Value
In Financial Accounting, stock is valued at cost or net realisable value, whichever is lower.
In Cost Accounting, stock is valued at cost, providing a more detailed view of the cost structure.
7) Profit Evaluation
Financial Accounting evaluates profit for the entire business over a specific period, typically a fiscal year.
Cost Accounting evaluates profit at a more granular level, such as for a particular product, job, batch, or process.
8) Time Frame
Financial Accounting focuses on reporting the results of completed reporting periods, usually annually or quarterly.
Cost Accounting can report on both past periods and make projections for future periods. This provides more frequent and detailed reports as needed.
9) Reporting Schedule
Financial Accounting personnel typically issue reports only at the end of a reporting period.
Cost Accounting staff can issue reports at any time and with any frequency based on management’s needs. For example, daily reports might track the output of a specific machine in the production area.
10) Privacy
Financial Accounting reports are publicly available and used by external stakeholders.
Cost Accounting reports are usually confidential and used internally by management.
11) Advantages
Financial Accounting ensures compliance with regulatory standards and provides a clear financial picture to external stakeholders.
Cost Accounting helps in cost control, budgeting, and improving operational efficiency. This provides valuable insights for internal decision-making.
Learn to make informed choices and analyse complex situations with our Management Courses – Register today!
Similarities Between Cost and Financial Accounting
Some similarities between Cost Accounting and Financial Accounting include:
1) Data Utilisation
Both financial and Cost Accounting utilise financial data to determine a company’s financial status and performance. They play crucial roles in helping an organisation understand its financial situation.
2) Profit Maximisation
Financial Accounting tracks the overall profitability and financial health of the company. At the same time, Cost Accounting focuses on controlling costs and identifying operational efficiencies.
3) Inventory Valuation
Both systems are involved in inventory valuation, but they approach it from different perspectives. Financial Accounting values inventory based on standardised principles. Meanwhile Cost Accounting provides a detailed view of the costs associated with inventory.
4) Improving Efficiency
Financial Accounting helps identify broader financial trends and the overall health of the business. In contrast, Cost Accounting pinpoints inefficient processes or products, aiding in operational improvements.
Join our Costing and Pricing Training today and master strategies to boost business performance and profits.
Conclusion
Understanding the Difference Between Cost Accounting and Financial Accounting is critical for effective financial control. While Cost Accounting specialises in internal efficiency and costs, Financial Accounting presents a basic financial picture for all the stakeholders. By using both, companies can increase sustainable growth and increase their decision-making.
Enhance your managerial skills and drive success with practical strategies from our expert-led Management Courses – Sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions





Upcoming Accounting and Finance Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Costing and Pricing Training
Costing and Pricing Training
Fri 20th Dec 2024
Fri 21st Feb 2025
Fri 25th Apr 2025
Fri 20th Jun 2025
Fri 22nd Aug 2025
Fri 17th Oct 2025
Fri 19th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


