We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203 999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

In today’s digital era, Information Security Management is the bulwark of data integrity, serving as a vigilant protector of our digital domain. It transcends mere protocol, embodying a steadfast commitment to defending our digital exchanges and monetary transactions from the myriad of invisible threats that lurk online. It is the cornerstone that ensures trust and reliability in our increasingly interconnected world, where data breaches can have far-reaching and detrimental impacts. This blog provides a proper understanding of Information Security management and its importance, implementation, and benefits.
Table of Contents
1) What is Information Security Management?
2) How does Information Security work?
3) Objectives of Information Security Management
4) Benefits of Information Security Management
5) Information Security Management standards and compliance
6) Conclusion
What is Information Security Management?
Information Security Management (ISM) comprises strategies and practices to safeguard an organisation’s informational assets from various cyber threats. It aims to guarantee the privacy, security, and accessibility of data. ISM initiatives are often guided by internal corporate security guidelines. They are subject to regulatory requirements as well as other external factors, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS).
Why is Information Security Management important?
The importance of Information Security Management (ISM) cannot be underestimated in the current data-oriented business space. Companies handle sensitive information critical for service delivery, enhancing user experiences, and informed decision-making. Ensuring the safety of data is the key issue. Cyber incidents or privacy violations can have long–term unpleasant consequences.
The approval of laws such as the GDPR points to the deficiency in Information Security measures because the authorities will have the power to penalise non-compliance by imposing huge fines. Implementing a well-thought-out ISM system can be insurance against most data breach risks, which demonstrates to regulators the organisation's sincere attempts at data security. This forward-looking approach does not only cushion the regulatory scrutiny but might also result in either reduced sanctions or total relief in the event of a breach.
Be aware of virtual private networks to encrypt the connections and gain an understanding of Information Security with our Information Systems Security Management Training.
How does Information Security Management work?
Information Security Management operates through a systematic Risk Management approach, aiming to minimise unauthorised data access. Organisations tailor their security measures based on their unique data handling practices. The process involves:
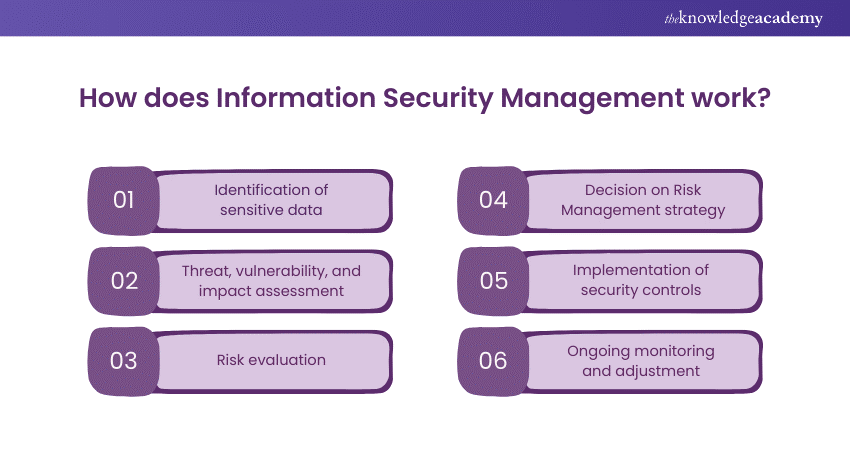
1) Identification of sensitive business data that requires protection like customer identities, health data, payment details, intellectual property, and internal communications.
2) Assessment of probable threats, vulnerabilities and consequences of each asset. Threats represent the types of risks (e.g., malware, phishing), vulnerabilities are the weaknesses that could be exploited, and impacts are the consequences of a threat materialising.
3) Evaluating the risk level by considering the likelihood of a threat occurring and its potential impact.
4) Deciding on a Risk Management strategy, which may include:
a) Avoidance: Changing operations to remove vulnerabilities.
b) Acceptance: Acknowledging minor risks that pose little harm.
c) Control: Implementing measures to reduce threat likelihood or impact.
d) Transfer: Outsourcing certain functions to shift the security burden.
Implementing necessary security controls to keep risks at an acceptable level.
4) Ongoing monitoring and adjustment of security strategies to counter new threats and vulnerabilities. Information Security Management (ISM) is a critical aspect of any organisation’s strategy to safeguard its data and assets. Here’s an expanded view of the ISM process:
5) Identification of critical information: Organisations must first determine what information is vital to their operations and therefore needs protection. This could include:
a) Customer identities
b) Health data
c) Payment details
d) Intellectual property
e) Internal communications
6) Threat, vulnerability, and impact assessment: Each piece of critical information is then assessed for:
a) Threats: These are the types of risks that could compromise the information, such as malware attacks or phishing schemes.
b) Vulnerabilities: These are the weaknesses within the system that could be exploited by threats.
c) Impacts: These are the potential consequences of a threat exploiting a vulnerability.
7) Risk Evaluation: The risk associated with each threat is evaluated based on:
a) The likelihood of the threat occurring
b) The potential impact if the threat were to occur
8) Risk Management Strategy Decision: Based on the risk evaluation, a strategy is chosen, which may include:
a) Avoidance: Modifying operations to eliminate vulnerabilities.
b) Acceptance: Recognising and accepting minor risks that are not deemed harmful.
c) Control: Putting in place measures to decrease the likelihood or impact of threats.
d) Transfer: Shifting the responsibility of certain risks by outsourcing.
9) Implementation of security controls: Appropriate security measures are implemented to maintain risks at an acceptable level. This could involve:
a) Firewalls
b) Encryption
c) Access controls
d) Security training for employees
10) Ongoing monitoring and adjustment: The security landscape is ever-changing, so ISM requires:
a) Continuous monitoring of security measures
b) Regular updates to strategies in response to new threats and vulnerabilities
This systematic approach ensures that an organisation’s information remains secure against unauthorised access and that security measures evolve alongside new threats. It’s a dynamic process that requires constant adaptation and vigilance.
Objectives of Information Security Management
At the core of organisational Information Security lies the CIA triad: confidentiality, integrity, and availability. This triad forms the foundation upon which InfoSec controls are established to protect sensitive data.
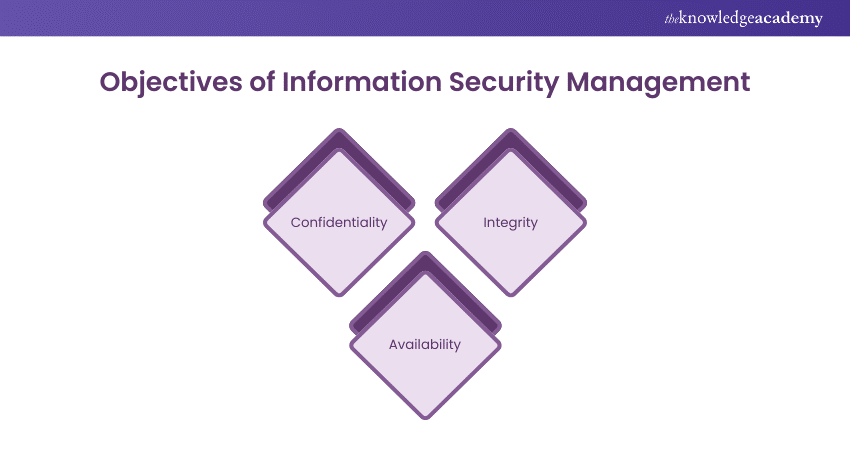
Confidentiality
This principle is about protecting sensitive information from unauthorised access and disclosure. It’s akin to ensuring that secrets remain secret. In practice, confidentiality measures might include:
a) Data encryption
b) Rigorous authentication processes
c) Role-based access controls
d) Regular audits to track data access
By categorising data based on sensitivity and applying appropriate levels of protection, organisations can create a secure environment that respects user privacy and regulatory requirements.
Integrity
This principle focuses on maintaining the trustworthiness and accuracy of data throughout its lifecycle. It ensures that information is reliable and unaltered from its original state. Measures to uphold integrity include:
a) Implementation of digital signatures
b) Use of hashing algorithms
c) Employment of error detection and correction protocols
d) Regular backups to prevent data loss
With these controls, organisations can detect and prevent unauthorised information tampering, ensuring that data remains intact and trustworthy.
Availability
This principle ensures that data and systems are available to authorised users when needed. It’s about making sure that the information is there for you, just like a reliable friend who’s always there when you call. To ensure availability, organisations implement:
a) Redundant systems and data storage
b) Network and system performance monitoring
c) Disaster recovery plans
d) Business continuity strategies
These measures help to minimise downtime and maintain business operations, even in the face of technical failures or cyber-attacks.
These three principles form the cornerstone of any Information Security program, providing a balanced approach to protecting data against various cyber threats. They help organisations not only defend against attacks but also build trust with stakeholders and customers through a commitment to security.
Acquire skills to explore Information Security control frameworks with our Chief Information Security Officer Training - join now!
Benefits of Information Security Management
The advantages associated with efficient Information Security Management (ISM) are significant. Here’s a detailed look at how such a program can enhance an organisation’s data security and culture:
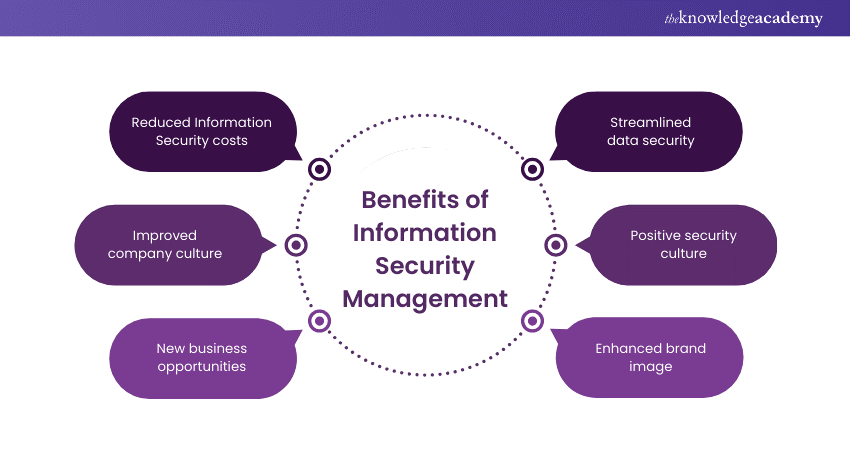
1) Reduced Information Security costs: An ISMS helps organisations to:
a) Avoid overspending on any security measures that may not be efficient.
b) Focusing on targeted, risk-based security investments is more likely to yield results.
2) Improved company culture: A successful ISMS implementation:
a) Encourages a culture of security awareness across all departments.
b) Ensures that employees perceive their role in security commitment, thus enhancing the sense of common responsibility.
3) New business opportunities: With an ISMS, organisations can:
a) Showcase a dedication to security, which is becoming an essential aspect of many partnerships.
b) Access new markets and sectors that have strict security requirements.
4) Streamlined data security: By adopting an ISMS, organisations benefit from:
a) A structured approach to data security, making it more manageable and effective.
b) The ability to streamline their security architecture, reducing redundancies and inefficiencies.
5) Positive security culture: Promoting an ISMS throughout the organisation:
a) Helps spread the ownership of Information Security beyond the IT department.
b) Builds a security-positive mindset among employees, leading to better adherence to security policies.
6) Enhanced brand image: A strong ISMS can:
a) Protect the organisation from the reputational damage associated with data breaches.
b) Increase customer and partner trust by demonstrating a dedication to keeping sensitive data secure.
These benefits collectively enhance an organisation’s resilience against cyber threats while supporting business growth and sustainability. The development of ISMS is not only about escaping negative implications; it is also about taking steps to implement a safe, reliable, and trustworthy environment.
Information Security management standards and compliance
Information Security management isn’t just a suggested protocol; it is a legal compliance requirement within industries. As an illustration, in order to get their ISO 27001 certification, the cream of the crop Information Security management System (ISMS) standards, the organisation will have to put in place a robust ISMS.
In payment processing, the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) also mandates an ISMS. The company should have in mind the protection of payment processing safety; this is a must for any company involved in credit card operations.
Healthcare organisations in the United States are similarly bound by the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPPA), which includes stringent requirements for protecting patient information, again underscoring the need for an effective ISMS.
It may not be a rule of the General Data Protection Regulation of the EU. However, it is undeniable that it helps organisations meet the EU’s GDPR requirements of “the adoption of appropriate organisational and technical measures” for safeguarding the processing of personal data.
The GDPR avoids the definition of the appropriate measures by referring to established methods such as ISO 27001. This approach allows companies to tailor their data protection strategies to their specific needs while still adhering to a recognised framework of security standards.
Join our CISSAP-ISSAP Training and gain in-depth knowledge of all the eight domains covered under the CISSP exam.
Conclusion
Information Security Management transcends mere protocol; it’s a strategic shield in the digital battleground. It’s the art of creating a fortress where business can flourish unimpeded and innovation can soar without the shackles of cyber threats. It’s a commitment to resilience, ensuring that the lifeblood of commerce—data—remains untainted and secure, propelling businesses towards a horizon of boundless potential and robust digital trust.
Frequently Asked Questions

The initial step in implementing ISM is conducting a risk assessment to identify potential vulnerabilities and threats to your information assets.

ISM practices should be reviewed regularly, at least once a year, or whenever significant changes occur within the organisation or its technology infrastructure.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

Discover CISM Courses with The Knowledge Academy, offering Information Systems Auditing, Control, and Security courses. Designed for diverse skill levels, these courses provide a comprehensive understanding of How to Become a CISSP.
Whether you are starting your journey or aiming to elevate your Information Security expertise, immerse yourself in our IT Security & Data Protection Blogs to discover more insights!
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 CISM Certified Information Security Manager
CISM Certified Information Security Manager
Mon 3rd Feb 2025
Mon 3rd Mar 2025
Mon 14th Apr 2025
Tue 6th May 2025
Mon 2nd Jun 2025
Mon 7th Jul 2025
Mon 4th Aug 2025
Mon 1st Sep 2025
Mon 6th Oct 2025
Mon 3rd Nov 2025
Mon 1st Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


