We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Are you faced with persistent problems or incidents in your organisation? Do you find yourself repeatedly failing to understand the underlying causes? If so, it’s time to know How to do Root Cause Analysis (RCA).
RCA is a powerful methodology that enables you to delve deep into the core reasons behind issues, allowing you to develop effective solutions and prevent future occurrences. However, unawareness about How to do Root Cause Analysis can hamper an organisation’s efficiency and reputation.
If you want to achieve a competitive edge in the market, it’s time to learn how to effectively implement this methodology effectively. Read this blog to learn about How to do Root Cause Analysis. Explore the step-by-step description and learn how RCA can benefit your organisation.
Table of Contents
1) How to Perform Root Cause Analysis?
2) The 3 Rs of Performing Root Cause Analysis
3) Popular Root Cause Analysis Methods
4) Tips for Performing Effective Root Cause Analysis
5) Conclusion
How to Perform Root Cause Analysis?
RCA follows a systematic approach that identifies the underlying causes of problems or incidents. By understanding this approach, organisations can implement effective solutions and prevent issues from recurring. So, let’s understand How to do Root Cause Analysis through the following step-by-step guide:
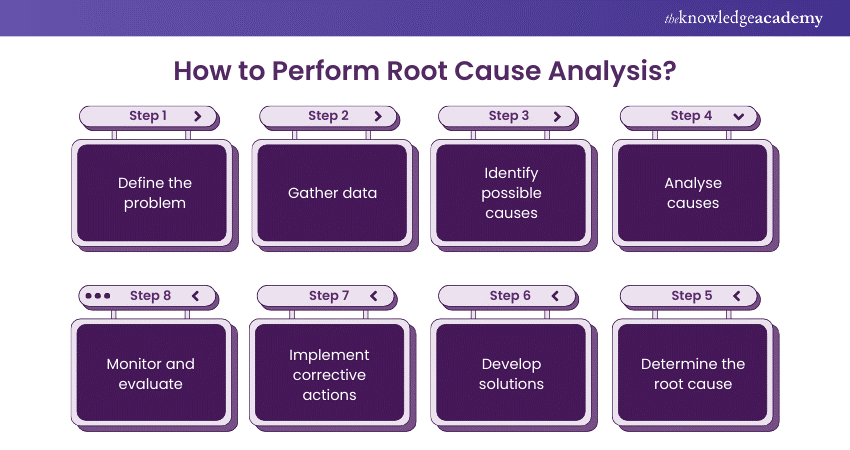
Step 1: Define the Problem
The first step in performing RCA involves clearly defining the problem or incident that requires analysis. Organisations should take time to understand the nature and scope of the problem. A well-defined problem statement helps ensure that the analysis remains focused and targeted.
Step 2: Gather Data
The next step in Root Cause Analysis is collecting relevant data and information related to the problem. This may involve the following:
a) Reviewing incident reports
b) Examining documentation
c) Conducting interviews
d) Gathering other sources of information
The data collected should be comprehensive and accurate to provide a solid foundation for the analysis.
Step 3: Identify Possible Causes
Step 3 involves extensive brainstorming sessions. Here, the team engages in the following activities:
a) Identifying potential causes that may contribute to the problem
b) Engaging a diverse group of individuals with different perspectives
c) Utilising techniques such as the "5 Whys" method or "Cause and Effect" analysis to dig deeper into the underlying factors and connections.
Step 4: Analyse Causes
Once you have identified the potential causes, it’s time to analyse each one in detail. This step involves evaluating the probability, impact, and relevance of each cause of the problem. The team also engages in prioritises the causes based on their significance and likelihood of contributing to the issue.
Perfect your IT Service Management techniques with our ITIL® Certification Training - secure your spot for our next session!
Step 5: Determine the Root Cause
After analysing the causes, pinpoint the root cause — the fundamental reason behind the problem. The root cause is the factor that, when addressed, will prevent the problem from recurring. It involves utilising Root Cause Analysis Tools like the "Ishikawa diagram" or "Pareto analysis" to aid in the identification of the root cause.
Step 6: Develop Solutions
Once the root cause is identified, the next step in Root Cause Analysis is to develop appropriate solutions to address it effectively. Here, the team brainstorm potential solutions that directly target the root cause. They also consider feasibility, cost-effectiveness, and potential impact in selecting the most suitable solution(s) for implementation.
Step 7: Implement Corrective Actions
Implement the selected solutions and monitor their progress. It involves allocating necessary resources, communicating responsibilities and ensuring effective collaboration. Further, regularly assessing the progress and adjusting the solutions can prevent their recurrences.
Step 8: Monitor and Evaluate
Monitoring effectiveness and evaluating the outcomes becomes the last step in implementing RCA. Here, the teams measure Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and gather stakeholder feedback. If the results are satisfactory, consider the problem resolved. If not, refine the solutions and iterate the process as required.
By following this step-by-step guide, organisations can effectively perform RCA, enabling them to understand the underlying causes of problems and implement solutions that prevent their recurrence.
Looking to advance your ITIL skills? Take the next step with our comprehensive ITIL® Certification Training.
The 3 Rs of Performing Root Cause Analysis
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) can be distilled into three key steps. Let's take a look at them:
a) Recognise: Begin by pinpointing the issue with a clear problem statement to guide a thorough investigation into its underlying cause.
b) Rectify: After identifying the root cause, implement solutions to prevent recurrence. A repeated issue may indicate only superficial symptoms were addressed.
c) Replicate: Testing the resolution involves replicating the problem or the conditions for a successful outcome to confirm the root cause has been effectively addressed.
Join our ITIL® 4 Specialist: Drive Stakeholder Value Course and learn to co-create unparalleled value with stakeholders – sign up now!
Popular Root Cause Analysis Methods
There are many methods for conducting RCA, but some of the most popular ones are:
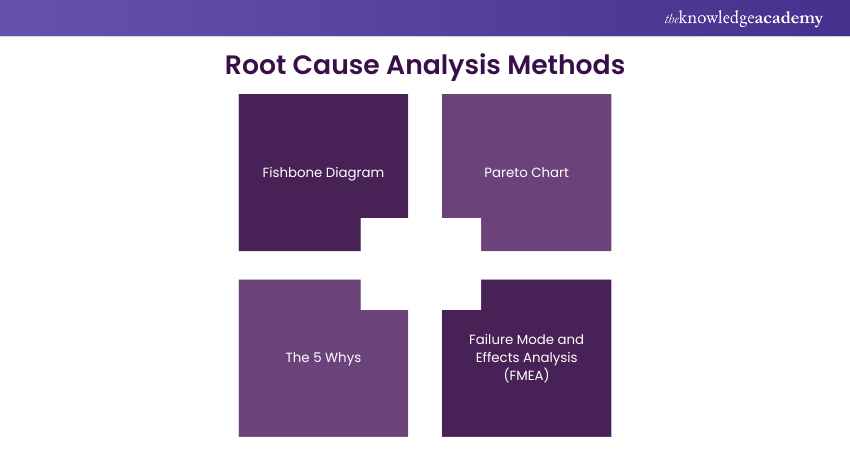
Fishbone Diagram
This Root Cause Analysis Fishbone method uses a visual diagram that resembles a fishbone to identify and categorise the possible causes of a problem. The head of the fish represents the problem, and the bones represent the main categories of causes, such as people, processes, equipment, environment, etc. Each category can be further divided into subcategories and specific causes. This method helps to organise and analyse the information and find the root cause.
Pareto Chart
This method uses bar and line graphs to show the frequency and impact of different problem causes. The bars represent the number or percentage of occurrences of each cause, and the line represents the cumulative percentage of the total occurrences.
The causes are arranged in descending order of frequency, from left to right. This method helps to identify the most significant causes of a problem and prioritise them according to the Pareto principle, which states that 80% of the effects come from 20% of the causes.
Advance your ITIL skills with our ITIL® 4 Foundation Certification Course – join us now and unlock new opportunities!
The 5 Whys
This method uses a series of questions to drill down to the root cause of a problem. The process starts with asking “Why?” to the problem statement and then asking “Why?” again to the answer until the root cause is reached. Usually, five questions are enough to find the root cause, but more or less may be needed depending on the situation. This method helps to explore the causal relationships and avoid jumping to conclusions.
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
This proactive approach identifies and evaluates potential failures and their effects on a product, process, or system. The process involves listing the possible failure modes, their causes, and their impact and rating them according to their severity, occurrence, and detection.
The ratings are multiplied to obtain a Risk Priority Number (RPN) for each failure mode. The failure modes with the highest RPNs are then targeted for improvement actions. This method helps to prevent or reduce the risk of failures and improve quality and reliability.
Tips for Performing Effective Root Cause Analysis
Some tips for performing practical Root Cause Analysis are:
a) Involve a team of people with different perspectives and expertise to identify and analyse the possible causes of a problem.
b) Use a structured and systematic approach, such as the Fishbone Diagram, the Pareto chart, the five whys, or the FMEA, to organise and visualise the information and find the root cause.
c) Focus on the facts and evidence, not on opinions or blame. Ask how and why something happened, not who was responsible.
d) Prioritise the most significant and frequent causes of a problem and address them with specific and actionable solutions. Use the Pareto principle to guide your decision-making.
Monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of your solutions and make adjustments as needed. Seek feedback and data to measure the impact of your actions. Explore the advantages and disadvantages of root cause analysis for deeper insights into problem-solving strategies.
Conclusion
Learning How to do Root Cause Analysis empowers organisations to tackle problems, enhance decision-making effectively, and drive continuous improvement. By following a systematic approach to identifying the underlying causes of issues, RCA provides a solid foundation for problem resolution and prevention.
Steer your IT projects in the right direction with our ITIL® 4 Strategist: Direct, Plan And Improve Training – register today!<
Frequently Asked Questions

Performing RCA benefits an organisation by preventing recurring problems, enhancing decision-making, optimising processes and efficiency, ensuring continuous improvement, maintaining customer satisfaction, and mitigating risks and identifying patterns.

Anyone can perform Root Cause Analysis if they follow a structured and systematic approach, such as the Fishbone Diagram, the Pareto chart, the five whys, or the FMEA. However, specialised training can help improve the skills and knowledge of the RCA practitioners and ensure better results.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various ITIL® Certification Training, including Root Cause Analysis, ITIL® 4 Specialist: Create Deliver and Support CDS Course, and ITIL® 4 Strategist: Direct, Plan and Improve DPI Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Root Cause Analysis Interview Questions and Answers.
Our IT Service Management Blogs cover a range of topics related to Root Cause Analysis, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your RCA skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming IT Service Management Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 ITIL® 4 Foundation Certification Course
ITIL® 4 Foundation Certification Course
Wed 18th Dec 2024
Mon 6th Jan 2025
Wed 8th Jan 2025
Mon 13th Jan 2025
Wed 15th Jan 2025
Mon 20th Jan 2025
Wed 22nd Jan 2025
Mon 27th Jan 2025
Wed 29th Jan 2025
Mon 3rd Feb 2025
Wed 5th Feb 2025
Mon 10th Feb 2025
Wed 12th Feb 2025
Mon 17th Feb 2025
Wed 19th Feb 2025
Mon 24th Feb 2025
Wed 26th Feb 2025
Mon 3rd Mar 2025
Wed 5th Mar 2025
Mon 10th Mar 2025
Wed 12th Mar 2025
Mon 17th Mar 2025
Wed 19th Mar 2025
Mon 24th Mar 2025
Wed 26th Mar 2025
Mon 31st Mar 2025
Wed 2nd Apr 2025
Mon 7th Apr 2025
Wed 9th Apr 2025
Mon 14th Apr 2025
Wed 16th Apr 2025
Tue 22nd Apr 2025
Mon 28th Apr 2025
Wed 30th Apr 2025
Tue 6th May 2025
Mon 12th May 2025
Wed 14th May 2025
Mon 19th May 2025
Wed 21st May 2025
Tue 27th May 2025
Mon 2nd Jun 2025
Wed 4th Jun 2025
Mon 9th Jun 2025
Wed 11th Jun 2025
Mon 16th Jun 2025
Wed 18th Jun 2025
Mon 23rd Jun 2025
Wed 25th Jun 2025
Mon 30th Jun 2025
Wed 2nd Jul 2025
Mon 7th Jul 2025
Wed 9th Jul 2025
Mon 14th Jul 2025
Wed 16th Jul 2025
Mon 21st Jul 2025
Wed 23rd Jul 2025
Mon 28th Jul 2025
Wed 30th Jul 2025
Mon 4th Aug 2025
Wed 6th Aug 2025
Mon 11th Aug 2025
Wed 13th Aug 2025
Mon 18th Aug 2025
Wed 20th Aug 2025
Mon 25th Aug 2025
Mon 1st Sep 2025
Wed 3rd Sep 2025
Mon 8th Sep 2025
Wed 10th Sep 2025
Mon 15th Sep 2025
Wed 17th Sep 2025
Mon 22nd Sep 2025
Wed 24th Sep 2025
Mon 29th Sep 2025
Wed 1st Oct 2025
Mon 6th Oct 2025
Wed 8th Oct 2025
Mon 13th Oct 2025
Wed 15th Oct 2025
Mon 20th Oct 2025
Wed 22nd Oct 2025
Mon 27th Oct 2025
Wed 29th Oct 2025
Mon 3rd Nov 2025
Wed 5th Nov 2025
Mon 10th Nov 2025
Wed 12th Nov 2025
Mon 17th Nov 2025
Wed 19th Nov 2025
Mon 24th Nov 2025
Wed 26th Nov 2025
Mon 1st Dec 2025
Wed 3rd Dec 2025
Mon 8th Dec 2025
Wed 10th Dec 2025
Mon 15th Dec 2025
Wed 17th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


