We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +31 208081674 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Are you someone new to the field of Quality Management? If yes, then you might have wondered about Quality Assurance vs Quality Control: which one is better in ensuring the quality of products and services? In Quality Management, understanding the distinction between these two processes is essential for organisations to deliver superior products or services. So, let’s learn about their distinction in detail through this blog. In this blog, you will see: Quality Assurance vs Quality Control in detail, their key differences, processes and integration. Read ahead to learn more!
Table of Contents
1) What is Quality Assurance?
2) Quality Assurance process
3) Quality Control process
4) What is Quality Control?
5) Difference between Quality Assurance and Quality Control
6) The integration of Quality Assurance and Quality Control
7) Conclusion
What is Quality Assurance?
Quality Assurance (QA) is a systematic approach that ensures that the processes used to create and deliver a product or service are well-defined, consistent, and capable of meeting the specified requirements. It is like setting up a recipe for baking a cake and ensuring that you follow that recipe strictly every time. The goal of QA is to prevent mistakes or defects from occurring in the first place. Quality Assurance involves various elements, such as the following:
a) Adhering to standardised processes and procedures
b) Training employees to be skilled and knowledgeable
c) Conducting regular audits and assessments
These are done to ensure that everything is going as per the plan of the organisation. It helps to produce high-quality products or services consistently. As a result, it leads to happier customers and a strong reputation for the organisation.
Quality Assurance process
Discussed below are some of the key elements of the Quality Assurance process:
a) Process standardisation: QA teams work to define, document, and standardise the procedures, workflows, and best practices involved in production or service delivery. Standardisation gives clarity and consistency, reducing the chances of errors and variations.
b) Documentation and training: QA involves the creation and maintenance of comprehensive documentation that gives an idea of processes, guidelines, and quality standards. Employees are trained to read and follow these documented procedures. It ensures that all are on the same page when it comes to quality expectations.
c) Auditing and assessment: Regular audits and assessments are conducted to evaluate the extent to which processes adhere to established standards. Auditors review the documentation, observe the execution of tasks, and collect data to assess process effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
d) Root cause analysis: When deviations from quality standards are identified, QA processes delve into root cause analysis. This means identifying the basic reasons for quality issues and taking necessary actions to address these issues at their source.
e) Customer feedback integration: Customer feedback plays a vital role in QA processes. Customer complaints and suggestions are analysed and integrated into the process.
f) Risk management: QA also involves identifying and managing risks that could impact the quality of the product or service. By proactively addressing potential risks, QA helps prevent quality issues.
What is Quality Control?
Quality Control, often abbreviated as QC, is a systematic and methodical process. It ensures that the products or services an organisation produces meet specific quality standards. It involves the following:
a) Examining
b) Testing
c) Inspecting
Its primary goal is to ensure that what the customer receives is of the highest possible quality, free from any flaws or defects.
Quality Control process
Quality Control process involves a series of systematic steps and methods to identify and rectify defects or deviations. These are discussed below:
1) Inspection: Inspection is a fundamental step in QC, where products or services are carefully examined to identify any visible defects from established standards. This step ensures that what is being delivered is in good condition and meets quality expectations.
2) Testing: Testing involves subjecting the product or service to various assessments to verify its functionality, performance, and adherence to specific requirements. Testing may include performing the following:
a) Functionality tests
b) Stress tests
c) Performance tests
3) Statistical Process Control (SPC): SPC is a method used to monitor and control processes by collecting and analysing data during production. This data helps identify variations and trends that could lead to quality issues, allowing for timely corrective action.
4) Sampling: Sampling is a technique where a sample of products or services is selected from a larger batch or production run for inspection or testing. This approach is often used to assess the quality of a large number of items efficiently.
5) Quality data collection: During the QC process, data related to the quality of products or services is collected and documented. This data can include defect rates, measurements, and any other relevant information that helps evaluate quality.
Corrective action: Once defects or quality issues are identified, appropriate corrective measures are taken to address them. This may involve repairing or reworking the product, modifying the service, or other necessary actions to ensure quality compliance.
Elevate your managerial capability with our Supplier Quality Management Training – empower your team, enhance efficiency, and drive excellence!
Difference between Quality Assurance and Quality Control
Quality Assurance vs Quality Control are two critical components of Quality Management, each with distinct roles and objectives. So, let’s look at the key differences between both in detail:
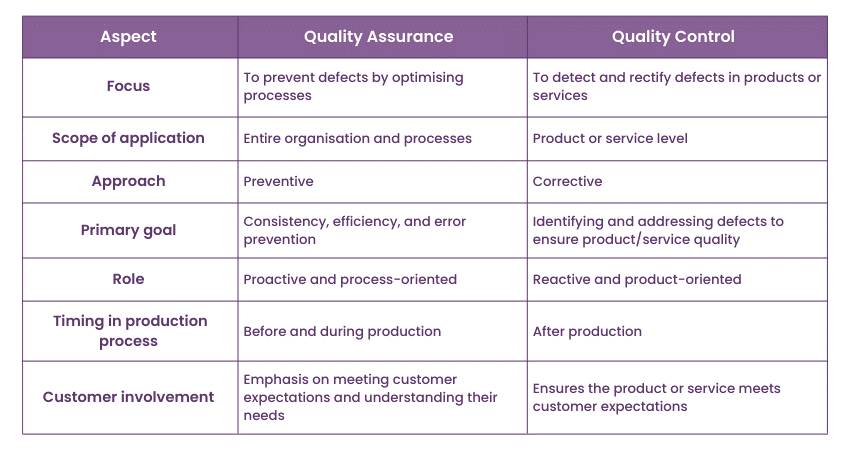
Quality Assurance is primarily concerned with optimising the processes and systems responsible for producing products or services. Its main objective is the prevention of defects and errors by ensuring that these processes are clearly defined, standardised, and consistently capable of delivering high-quality results.
QA achieves this by establishing guidelines, best practices, and standards to enhance the overall efficiency and effectiveness of operations. It is a proactive approach, actively addressing potential issues before they manifest during production, thereby reducing the likelihood of defects.
By focusing on continuous improvement and process refinement, it minimises the need for extensive corrective measures after production. This makes QA an integral part of ensuring consistent quality throughout the production process.
In contrast, Quality Control is centred on the final products or services. It is a reactive approach focused on detecting and addressing defects in the end results. QC involves the inspection, testing, and measurement of individual products to ensure they meet established quality standards. Unlike QA, QC's emphasis is on identifying and correcting defects rather than preventing them.
QC occurs after the production process and is the last line of defence to ensure that the product or service meets the required quality level. While it is essential for identifying and rectifying issues, it can be more resource-intensive and costly compared to QA. It is costly as it involves dealing with problems that have already occurred.
Thus, the key distinction lies in their roles. QA prevents defects by improving processes, while QC detects defects in the final product or service.
Master Quality Assurance with our comprehensive Quality Assurance Masterclass - join today!
The integration of Quality Assurance and Quality Control
The integration of Quality Assurance and Quality Control is an approach that organisations must use to build a robust Quality Management framework. It involves combining the strengths of both QA and QC to ensure that products or services not only meet predefined quality standards but also consistently exceed customer expectations. Here's how the integration of QA and QC works:
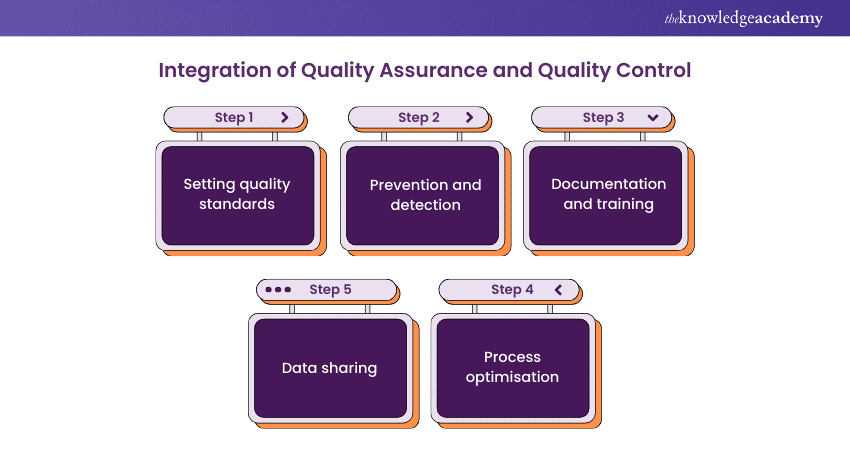
a) Setting quality standards: The integration begins by establishing clear quality standards that define what constitutes a high-quality product or service. These standards serve as a common reference point for both QA and QC.
b) Prevention and detection: QA focuses on preventing defects before they occur by optimising processes, while QC is primarily concerned with detecting defects in the final product or service. Integrating these approaches means actively working to prevent issues while also having robust systems in place to address any issues.
c) Documentation and training: The integration ensures that the documentation developed and training given to the employees in QA are effectively utilised in QC. QC teams follow the documented procedures, ensuring that everyone understands and follows the quality expectations.
d) Process optimisation: QA identifies areas where processes can be improved, standardised, and made more efficient. These enhancements reduce the likelihood of defects, lowering the need for extensive corrective actions in QC.
e) Data sharing: QA and QC processes generate valuable data that can be shared and analysed together. This data sharing allows organisations to identify trends, predict potential issues, and take proactive measures.
Conclusion
We hope this blog helped answer the question: Quality Assurance vs Quality Control – which one is better? Their differences highlight that they are two different processes essential for ensuring the quality of a product or service. Quality Assurance prevents quality issues through defined processes and continuous improvement, while Quality Control detects and rectifies defects in final output. Integration of both these processes helps in creating customer satisfaction.
Elevate your Management skills with our Management Training - sign up today to take your career forward!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Quality Assurance Training
Quality Assurance Training
Fri 10th Jan 2025
Fri 14th Mar 2025
Fri 9th May 2025
Fri 11th Jul 2025
Fri 12th Sep 2025
Fri 14th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


